Intest Res.
2015 Jan;13(1):11-18. 10.5217/ir.2015.13.1.11.
Intestinal Permeability Regulation by Tight Junction: Implication on Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Pharmaceutical Research and Development, Wonkwang University College of Pharmacy, Iksan, Korea. gsseo@wku.ac.kr
- 2BK21plus program & Department of Smart Life-Care Convergence, Wonkwang University Graduate School, Iksan, Korea.
- KMID: 1807372
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2015.13.1.11
Abstract
- Epithelial tight junctions (TJs) are the key structures regulating paracellular trafficking of macromolecules. The TJ is multi-protein complex that forms a selective permeable seal between adjacent epithelial cells and demarcates the boundary between apical and basolateral membrane domains. Disruption of the intestinal TJ barrier, followed by permeation of luminal noxious molecules, induces a perturbation of the mucosal immune system and inflammation, which can act as a trigger for the development of intestinal and systemic diseases. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients demonstrate increased intestinal paracellular permeability. Although it remains unclear whether barrier dysfunction precedes disease or results from active inflammation, increased intestinal TJ disruption is observed in IBD patients suggest that dysregulation of TJ barrier integrity may predispose or enhance IBD progression. Therefore, therapeutic target to restore the TJ barrier integrity may provide effective therapeutic and preventive approaches against IBD. This review discusses the molecular structure and regulation of intestinal TJs and the involvement of intestinal TJs in IBD pathogenesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
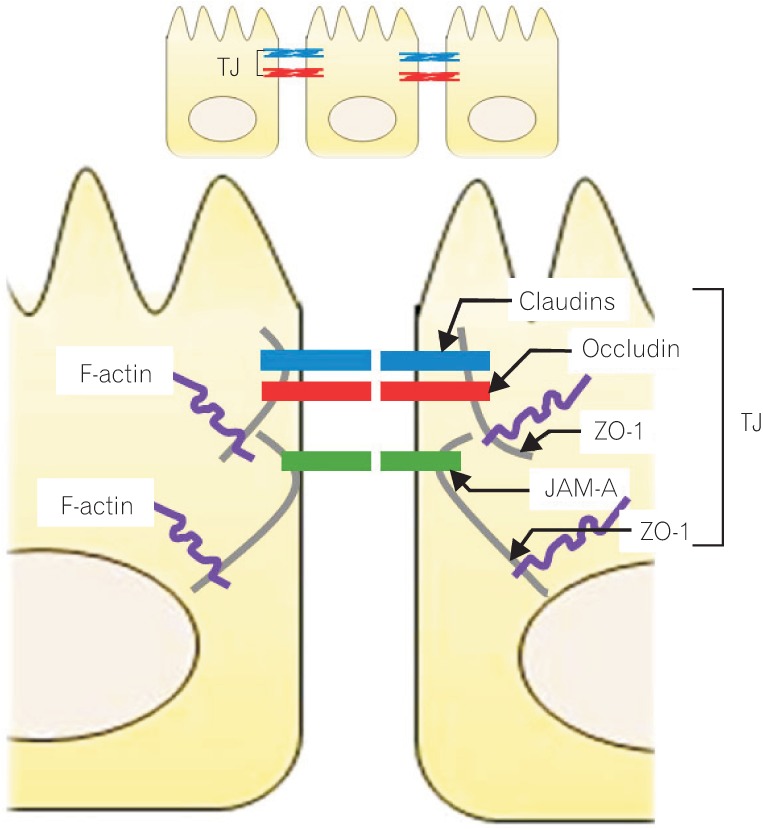
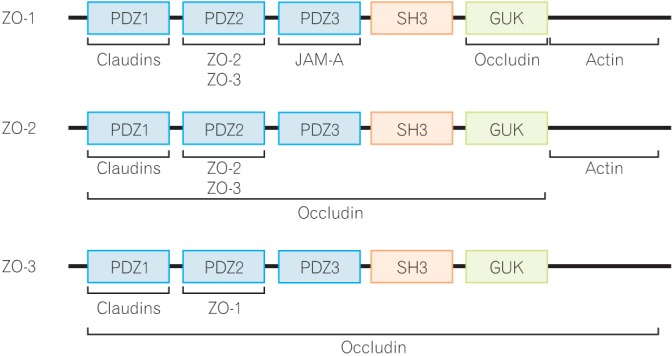
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of Lycium barbarum on polarized human intestinal epithelial cells
So-Rok Lee, Hye-Jeong Hwang, Ju-Gyeong Yoon, Eun-Young Bae, Kyo-Suk Goo, Sang-Joon Cho, Jin Ah Cho
Nutr Res Pract. 2019;13(2):95-104. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2019.13.2.95.Polymorphisms in
PRKCDBP , a Transcriptional Target of TNF-α, Are Associated With Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Korean
Jung-Wook Kim, Chang Kyun Lee, Hyo Jong Kim, Jae-Jun Shim, Jae Young Jang, Seok Ho Dong, Byung-Ho Kim, Young Woon Chang, Sung-Gil Chi
Intest Res. 2015;13(3):242-249. doi: 10.5217/ir.2015.13.3.242.Zonula occludens proteins and their impact on the cancer microenvironment
Min-Hye Kim, Hee-Jae Cha
Kosin Med J. 2024;39(4):246-253. doi: 10.7180/kmj.24.136.
Reference
-
1. Turner JR. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009; 9:799–809. PMID: 19855405.
Article2. van Elburg RM, Uil JJ, Mulder CJ, Heymans HS. Intestinal permeability in patients with coeliac disease and relatives of patients with coeliac disease. Gut. 1993; 34:354–357. PMID: 8472983.
Article3. Dunlop SP, Hebden J, Campbell E, et al. Abnormal intestinal permeability in subgroups of diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:1288–1294. PMID: 16771951.
Article4. Bosi E, Molteni L, Radaelli MG, et al. Increased intestinal permeability precedes clinical onset of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2006; 49:2824–2827. PMID: 17028899.
Article5. Sharpstone D, Neild P, Crane R, et al. Small intestinal transit, absorption, and permeability in patients with AIDS with and without diarrhoea. Gut. 1999; 45:70–76. PMID: 10369707.
Article6. Yacyshyn B, Meddings J, Sadowski D, Bowen-Yacyshyn MB. Multiple sclerosis patients have peripheral blood CD45RO+ B cells and increased intestinal permeability. Dig Dis Sci. 1996; 41:2493–2498. PMID: 9011463.
Article7. Martínez-González O, Cantero-Hinojosa J, Paule-Sastre P, Gómez-Magán JC, Salvatierra-Ríos D. Intestinal permeability in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and their healthy relatives. Br J Rheumatol. 1994; 33:644–647. PMID: 8019793.
Article8. Turner JR. Molecular basis of epithelial barrier regulation: from basic mechanisms to clinical application. Am J Pathol. 2006; 169:1901–1909. PMID: 17148655.9. Nusrat A, Turner JR, Madara JL. Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions. IV. Regulation of tight junctions by extracellular stimuli: nutrients, cytokines, and immune cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000; 279:G851–G857. PMID: 11052980.10. Farhadi A, Banan A, Fields J, Keshavarzian A. Intestinal barrier: an interface between health and disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003; 18:479–497. PMID: 12702039.
Article11. Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001; 2:285–293. PMID: 11283726.
Article12. Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM. Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006; 68:403–429. PMID: 16460278.
Article13. Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S. Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol. 1993; 123:1777–1788. PMID: 8276896.
Article14. Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiiragi T, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S. Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J Cell Biol. 1998; 141:1539–1550. PMID: 9647647.
Article15. Martín-Padura I, Lostaglio S, Schneemann M, et al. Junctional adhesion molecule, a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that distributes at intercellular junctions and modulates monocyte transmigration. J Cell Biol. 1998; 142:117–127. PMID: 9660867.
Article16. Ikenouchi J, Furuse M, Furuse K, Sasaki H, Tsukita S. Tricellulin constitutes a novel barrier at tricellular contacts of epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 2005; 171:939–945. PMID: 16365161.
Article17. González-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Nava P, Jaramillo BE. Tight junction proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2003; 81:1–44. PMID: 12475568.
Article18. Turner JR, Rill BK, Carlson SL, et al. Physiological regulation of epithelial tight junctions is associated with myosin light-chain phosphorylation. Am J Physiol. 1997; 273:C1378–C1385. PMID: 9357784.
Article19. Walsh SV, Hopkins AM, Chen J, Narumiya S, Parkos CA, Nusrat A. Rho kinase regulates tight junction function and is necessary for tight junction assembly in polarized intestinal epithelia. Gastroenterology. 2001; 121:566–579. PMID: 11522741.
Article20. Furuse M, Itoh M, Hirase T, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S. Direct association of occludin with ZO-1 and its possible involvement in the localization of occludin at tight junctions. J Cell Biol. 1994; 127:1617–1626. PMID: 7798316.
Article21. Al-Sadi R, Khatib K, Guo S, Ye D, Youssef M, Ma T. Occludin regulates macromolecule flux across the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011; 300:G1054–G1064. PMID: 21415414.
Article22. Sakakibara A, Furuse M, Saitou M, Ando-Akatsuka Y, Tsukita S. Possible involvement of phosphorylation of occludin in tight junction formation. J Cell Biol. 1997; 137:1393–1401. PMID: 9182670.
Article23. Rao R. Occludin phosphorylation in regulation of epithelial tight junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009; 1165:62–68. PMID: 19538289.
Article24. Jain S, Suzuki T, Seth A, Samak G, Rao R. Protein kinase Cζ phosphorylates occludin and promotes assembly of epithelial tight junctions. Biochem J. 2011; 437:289–299. PMID: 21545357.
Article25. McKenzie JA, Riento K, Ridley AJ. Casein kinase I epsilon associates with and phosphorylates the tight junction protein occludin. FEBS Lett. 2006; 580:2388–2394. PMID: 16616143.
Article26. Elias BC, Suzuki T, Seth A, et al. Phosphorylation of Tyr-398 and Tyr-402 in occludin prevents its interaction with ZO-1 and destabilizes its assembly at the tight junctions. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284:1559–1569. PMID: 19017651.
Article27. Atkinson KJ, Rao RK. Role of protein tyrosine phosphorylation in acetaldehyde-induced disruption of epithelial tight junctions. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001; 280:G1280–G1288. PMID: 11352822.
Article28. Tsukita S, Furuse M. Pores in the wall: claudins constitute tight junction strands containing aqueous pores. J Cell Biol. 2000; 149:13–16. PMID: 10747082.29. Tamura A, Hayashi H, Imasato M, et al. Loss of claudin-15, but not claudin-2, causes Na+ deficiency and glucose malabsorption in mouse small intestine. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140:913–923. PMID: 20727355.
Article30. Fujibe M, Chiba H, Kojima T, et al. Thr203 of claudin-1, a putative phosphorylation site for MAP kinase, is required to promote the barrier function of tight junctions. Exp Cell Res. 2004; 295:36–47. PMID: 15051488.
Article31. Cunningham SA, Arrate MP, Rodriguez JM, et al. A novel protein with homology to the junctional adhesion molecule. Characterization of leukocyte interactions. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:34750–34756. PMID: 10945976.32. Bazzoni G. The JAM family of junctional adhesion molecules. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003; 15:525–530. PMID: 14519386.
Article33. Liu Y, Nusrat A, Schnell FJ, et al. Human junction adhesion molecule regulates tight junction resealing in epithelia. J Cell Sci. 2000; 113:2363–2374. PMID: 10852816.
Article34. Laukoetter MG, Nava P, Lee WY, et al. JAM-A regulates permeability and inflammation in the intestine in vivo. J Exp Med. 2007; 204:3067–3076. PMID: 18039951.
Article35. Haskins J, Gu L, Wittchen ES, Hibbard J, Stevenson BR. ZO-3, a novel member of the MAGUK protein family found at the tight junction, interacts with ZO-1 and occludin. J Cell Biol. 1998; 141:199–208. PMID: 9531559.
Article36. Willott E, Balda MS, Fanning AS, Jameson B, Van Itallie C, Anderson JM. The tight junction protein ZO-1 is homologous to the Drosophila discs-large tumor suppressor protein of septate junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993; 90:7834–7838. PMID: 8395056.
Article37. Fanning AS, Ma TY, Anderson JM. Isolation and functional characterization of the actin binding region in the tight junction protein ZO-1. FASEB J. 2002; 16:1835–1837. PMID: 12354695.38. Umeda K, Matsui T, Nakayama M, et al. Establishment and characterization of cultured epithelial cells lacking expression of ZO-1. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:44785–44794. PMID: 15292177.
Article39. Stallmach A, Giese T, Schmidt C, Ludwig B, Mueller-Molaian I, Meuer SC. Cytokine/chemokine transcript profiles reflect mucosal inflammation in Crohn's disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2004; 19:308–315. PMID: 14605835.
Article40. Bruewer M, Utech M, Ivanov AI, Hopkins AM, Parkos CA, Nusrat A. Interferon-γ induces internalization of epithelial tight junction proteins via a macropinocytosis-like process. FASEB J. 2005; 19:923–933. PMID: 15923402.
Article41. Schulzke JD, Bojarski C, Zeissig S, Heller F, Gitter AH, Fromm M. Disrupted barrier function through epithelial cell apoptosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006; 1072:288–299. PMID: 17057208.
Article42. Ma TY, Boivin MA, Ye D, Pedram A, Said HM. Mechanism of TNF-α modulation of Caco-2 intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier: role of myosin light-chain kinase protein expression. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005; 288:G422–G430. PMID: 15701621.
Article43. Mankertz J, Amasheh M, Krug SM, et al. TNFα up-regulates claudin-2 expression in epithelial HT-29/B6 cells via phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling. Cell Tissue Res. 2009; 336:67–77. PMID: 19214581.
Article44. Dinarello CA. The interleukin-1 family: 10 years of discovery. FASEB J. 1994; 8:1314–1325. PMID: 8001745.45. Barksby HE, Lea SR, Preshaw PM, Taylor JJ. The expanding family of interleukin-1 cytokines and their role in destructive inflammatory disorders. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007; 149:217–225. PMID: 17590166.
Article46. Al-Sadi R, Ye D, Dokladny K, Ma TY. Mechanism of IL-1β-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability. J Immunol. 2008; 180:5653–5661. PMID: 18390750.
Article47. Al-Sadi R, Ye D, Said HM, Ma TY. IL-1β-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability is mediated by MEKK-1 activation of canonical NF-κB pathway. Am J Pathol. 2010; 177:2310–2322. PMID: 21048223.
Article48. Kusugami K, Fukatsu A, Tanimoto M, et al. Elevation of interleukin-6 in inflammatory bowel disease is macrophage- and epithelial cell-dependent. Dig Dis Sci. 1995; 40:949–959. PMID: 7729284.
Article49. Suzuki T, Yoshinaga N, Tanabe S. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) regulates claudin-2 expression and tight junction permeability in intestinal epithelium. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286:31263–31271. PMID: 21771795.
Article50. Kucharzik T, Lugering N, Pauels HG, Domschke W, Stoll R. IL-4, IL-10 and IL-13 down-regulate monocyte-chemoattracting protein-1 (MCP-1) production in activated intestinal epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998; 111:152–157. PMID: 9472675.
Article51. Madsen KL, Malfair D, Gray D, Doyle JS, Jewell LD, Fedorak RN. Interleukin-10 gene-deficient mice develop a primary intestinal permeability defect in response to enteric microflora. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 1999; 5:262–270. PMID: 10579119.
Article52. Kansagra K, Stoll B, Rognerud C, et al. Total parenteral nutrition adversely affects gut barrier function in neonatal piglets. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003; 285:G1162–G1170. PMID: 12969831.
Article53. Sun X, Yang H, Nose K, et al. Decline in intestinal mucosal IL-10 expression and decreased intestinal barrier function in a mouse model of total parenteral nutrition. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008; 294:G139–G147. PMID: 17991705.
Article54. Pappu R, Ramirez-Carrozzi V, Sambandam A. The interleukin-17 cytokine family: critical players in host defence and inflammatory diseases. Immunology. 2011; 134:8–16. PMID: 21726218.
Article55. Kinugasa T, Sakaguchi T, Gu X, Reinecker HC. Claudins regulate the intestinal barrier in response to immune mediators. Gastroenterology. 2000; 118:1001–1011. PMID: 10833473.
Article56. Basuroy S, Seth A, Elias B, Naren AP, Rao R. MAPK interacts with occludin and mediates EGF-induced prevention of tight junction disruption by hydrogen peroxide. Biochem J. 2006; 393:69–77. PMID: 16134968.
Article57. Samak G, Aggarwal S, Rao RK. ERK is involved in EGF-mediated protection of tight junctions, but not adherens junctions, in acetaldehyde-treated Caco-2 cell monolayers. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011; 301:G50–G59. PMID: 21474650.
Article58. Howe KL, Reardon C, Wang A, Nazli A, McKay DM. Transforming growth factor-β regulation of epithelial tight junction proteins enhances barrier function and blocks enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7-induced increased permeability. Am J Pathol. 2005; 167:1587–1597. PMID: 16314472.
Article59. Söderholm JD, Peterson KH, Olaison G, et al. Epithelial permeability to proteins in the noninflamed ileum of Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1999; 117:65–72. PMID: 10381911.
Article60. Zeissig S, Bürgel N, Günzel D, et al. Changes in expression and distribution of claudin 2, 5 and 8 lead to discontinuous tight junctions and barrier dysfunction in active Crohn's disease. Gut. 2007; 56:61–72. PMID: 16822808.
Article61. Vetrano S, Rescigno M, Cera MR, et al. Unique role of junctional adhesion molecule-a in maintaining mucosal homeostasis in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2008; 135:173–184. PMID: 18514073.62. Blair SA, Kane SV, Clayburgh DR, Turner JR. Epithelial myosin light chain kinase expression and activity are upregulated in inflammatory bowel disease. Lab Invest. 2006; 86:191–201. PMID: 16402035.
Article63. Murch SH, Braegger CP, Walker-Smith JA, MacDonald TT. Location of tumour necrosis factor alpha by immunohistochemistry in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1993; 34:1705–1709. PMID: 8031350.
Article64. Louis E, Belaiche J, van Kemseke C, et al. A high serum concentration of interleukin-6 is predictive of relapse in quiescent Crohn's disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1997; 9:939–944. PMID: 9391781.
Article65. Suenaert P, Bulteel V, Lemmens L, et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment restores the gut barrier in Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:2000–2004. PMID: 12190167.
Article66. Schmitz H, Fromm M, Bentzel CJ, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα) regulates the epithelial barrier in the human intestinal cell line HT-29/B6. J Cell Sci. 1999; 112(Pt 1):137–146. PMID: 9841910.67. Wang F, Graham WV, Wang Y, Witkowski ED, Schwarz BT, Turner JR. Interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor-α synergize to induce intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction by up-regulating myosin light chain kinase expression. Am J Pathol. 2005; 166:409–419. PMID: 15681825.
Article68. Graham WV, Wang F, Clayburgh DR, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-induced long myosin light chain kinase transcription is regulated by differentiation-dependent signaling events. Characterization of the human long myosin light chain kinase promoter. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:26205–26215. PMID: 16835238.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antibodies to Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Its Correlation with Intestinal Permeability
- Effects of 17β-Estradiol on Colonic Permeability and Inflammation in an Azoxymethane/Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis Mouse Model
- Probiotic Yeast from Miso Ameliorates Stress-Induced Visceral Hypersensitivity by Modulating the Gut Microbiota in a Rat Model of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Curcumin protects against the intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury: involvement of the tight junction protein ZO-1 and TNF-alpha related mechanism
- Role of Ultrastructural Alterations of Intercellular Junction and Tight-junction Proteins in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease