Infect Chemother.
2012 Dec;44(6):508-511. 10.3947/ic.2012.44.6.508.
Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head in HIV-infected Patients: Case Reports and Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. molder@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 1806944
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2012.44.6.508
Abstract
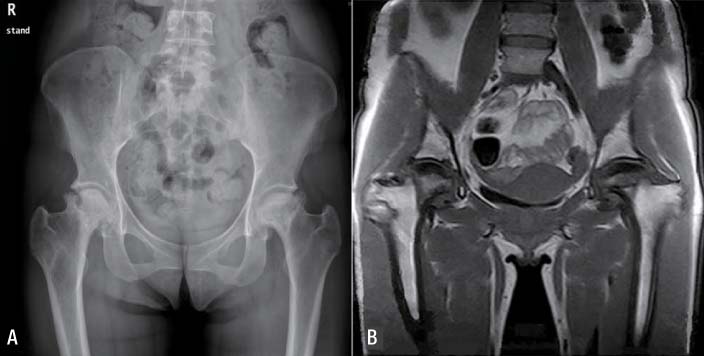
- After introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy, the incidence of opportunistic infections and malignancies in HIV patients decreased. On the other hand, several osteoarticular complications are increasingly reported. Avascular necrosis of femoral head is one of such complications. HIV-infected patients have an 100-fold increased risk of avascular necrosis of femoral head compared to the general population. Many risk factors for this debilitating complication have been suggested. This paper reports five cases of avascular necrosis of femoral head in HIV-infected patients with review of literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goorney BP, Lacey H, Thurairajasingam S, Brown JD. Avascular necrosis of the hip in a man with HIV infection. Genitourin Med. 1990. 66:451–452.
Article2. Keruly JC, Chaisson RE, Moore RD. Increasing incidence of avascular necrosis of the hip in HIV-infected patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2001. 28:101–102.
Article3. Hasse B, Ledergerber B, Egger M, Flepp M, Bachmann S, Bernasconi E, Egger M, Guyot S, Hirschel B, Weber R, Günthard HF. Swiss HIV Cohort Study. Antiretroviral treatment and osteonecrosis in patients of the Swiss HIV Cohort Study: a nested case-control study. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2004. 20:909–915.
Article4. Miller KD, Masur H, Jones EC, Joe GO, Rick ME, Kelly GG, Mican JM, Liu S, Gerber LH, Blackwelder WC, Falloon J, Davey RT, Polis MA, Walker RE, Lane HC, Kovacs JA. High prevalence of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in HIV-infected adults. Ann Intern Med. 2002. 137:17–25.
Article5. Park KS, Diwanji SR, Park SJ, Cho SG, Yim JH, Yoon TR. Avascular necrosis of femoral head treated by total hip replacement in AIDS patients: a case report. J Korean Hip Soc. 2007. 19:508–512.
Article6. Allison GT, Bostrom MP, Glesby MJ. Osteonecrosis in HIV disease: epidemiology, etiologies, and clinical management. AIDS. 2003. 17:1–9.7. Molia AC, Strady C, Rouger C, Beguinot IM, Berger JL, Trenque TC. Osteonecrosis in six HIV-infected patients receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. Ann Pharmacother. 2004. 38:2050–2054.
Article8. Koller E, Mann M, Malozowski S, Bacsanyi J, Gibert C. Aseptic necrosis in HIV seropositive patients: a possible etiologic role for megestrol acetate. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2000. 14:405–410.
Article9. Calza L, Manfredi R, Mastroianni A, Chiodo F. Osteonecrosis and highly active antiretroviral therapy during HIV infection: report of a series and literature review. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2001. 15:385–389.
Article10. Glesby MJ, Hoover DR, Vaamonde CM. Osteonecrosis in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus: a case-control study. J Infect Dis. 2001. 184:519–523.
Article11. Mary-Krause M, Billaud E, Poizot-Martin I, Simon A, Dhiver C, Dupont C, Salmon D, Roudiere L, Costagliola D. Clinical Epidemiology Group of the French Hospital Database. Risk factors for osteonecrosis in HIV-infected patients: impact of treatment with combination antiretroviral therapy. AIDS. 2006. 20:1627–1635.
Article12. Sighinolfi L, Carradori S, Ghinelli F. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head: a side effect of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) in HIV patients? Infection. 2000. 28:254–255.
Article13. Lee MJ, Corrigan J, Stack JP, Ennis JT. A comparison of modern imaging modalities in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Radiol. 1990. 42:427–432.
Article14. Van den Wyngaert T, Huizing MT, Vermorken JB. Osteonecrosis of the jaw related to the use of bisphosphonates. Curr Opin Oncol. 2007. 19:315–322.
Article15. Hernigou P, Poignard A, Nogier A, Manicom O. Fate of very small asymptomatic stage-I osteonecrotic lesions of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86:2589–2593.
Article16. Morse CG, Mican JM, Jones EC, Joe GO, Rick ME, Formentini E, Kovacs JA. The incidence and natural history of osteonecrosis in HIV-infected adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. 44:739–748.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Femoral Head and Neck Fractures developed in Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head
- Bilateral Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head in a Patient with Asymptomatic Adrenal Incidentaloma
- Non-traumatic Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head
- Increase of Femoral Anteversion after Experimental Induction of Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head
- Histological and Histochemical Study of the Acetabular Articular Cartilage in Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head