Imaging Sci Dent.
2012 Dec;42(4):237-242. 10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.237.
Diagnostic reference levels in intraoral dental radiography in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Dankook University College of Dentistry, Cheonan, Korea. ekkim@dankook.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, College of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea.
- 3Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1806790
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.237
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The objectives of this study were to survey the radiographic exposure parameters, to measure the patient doses for intraoral dental radiography nationwide, and thus to establish the diagnostic reference levels (DRLs) in intraoral dental X-ray examination in Korea.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
One hundred two intraoral dental radiographic machines from all regions of South Korea were selected for this study. Radiographic exposure parameters, size of hospital, type of image receptor system, installation duration of machine, and type of dental X-ray machine were documented. Patient entrance doses (PED) and dose-area products (DAP) were measured three times at the end of the exit cone of the X-ray unit with a DAP meter (DIAMENTOR M4-KDK, PTW, Freiburg, Germany) for adult mandibular molar intraoral dental radiography, and corrections were made for room temperature and pressure. Measured PED and DAP were averaged and compared according to the size of hospital, type of image receptor system, installation duration, and type of dental X-ray machine.
RESULTS
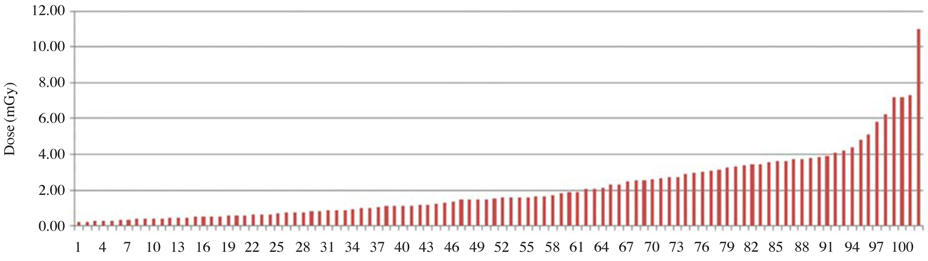
The mean exposure parameters were 62.6 kVp, 7.9 mA, and 0.5 second for adult mandibular molar intraoral dental radiography. The mean patient dose was 2.11 mGy (PED) and 59.4 mGycm2 (DAP) and the third quartile one 3.07 mGy (PED) and 87.4 mGycm2 (DAP). Doses at university dental hospitals were lower than those at dental clinics (p<0.05). Doses of digital radiography (DR) type were lower than those of film-based type (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
We recommend 3.1 mGy (PED), 87.4 mGycm2 (DAP) as the DRLs in adult mandibular molar intraoral dental radiography in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. White SC, Pharoah MJ. Oral Radiology: principles and interpretation. 2008. 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;32–43.2. Leitz W, Gron P, Servomaa A, Einarsson G, Olerud H. In : Paile W, editor. Nordic working group for medical x-ray diagnostics: diagnostic reference levels within x-ray diagnostics - experiences in the Nordic countries. Radiation protection in the 2000s - Theory and practice. 2003. Nordic society for radiation protection: Proceedings of the XIII ordinary meeting; August 25-29, 2002; Turku/Åbo, Finland. Helsinki: Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority;256–261.3. Council directive 97/43/Euratom of 30 June 1997 on health protection of individuals against the dangers of ionizing radiation in relation to medical exposures, and repealing Directive 84/466/Euratom [Internet]. 1997. cited 2012 April 30. Luxemburg: European Commission;Available from http://ec.europa.eu/energy/nuclear/radioprotection/doc/legislation/9743_en.pdf.4. Diagnostic reference levels in medical imaging: review and additional advice. Ann ICRP. 2001. 31:33–52.5. Poppe B, Looe HK, Pfaffenberger A, Eenboom F, Chofor N, Sering M, et al. Radiation exposure and dose evaluation in intraoral dental radiology. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2007. 123:262–267.
Article6. Napier ID. Reference doses for dental radiography. Br Dent J. 1999. 186:392–396.
Article7. Gulson AD, Knapp TA, Ramsden PG. HPA-RPD-022. Doses to patients arising from dental X-ray examinations in the UK, 2002-2004. A review of dental X-ray protection service data [Internet]. 2007. cited 2012 April 30. Chilton: HPARPD;Available from http://www.hpa.org.uk/web/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1194947326586.8. Wall BF. Radiation protection dosimetry for diagnostic radiology patients. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2004. 109:409–419.
Article9. Faulkner K, Broadhead DA, Harrison RM. Patient dosimetry measurement methods. Appl Radiat Isot. 1999. 50:113–123.
Article10. Helmrot E, Alm Carlsson G. Measurement of radiation dose in dental radiology. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2005. 114:168–171.
Article11. Tierris CE, Yakoumakis EN, Bramis GN, Georgiou E. Dose area product reference levels in dental panoramic radiology. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2004. 111:283–287.
Article12. Looe HK, Eenboom F, Chofor N, Pfaffenberger A, Sering M, Rühmann A, et al. Dose-area product measurements and determination of conversion coefficients for the estimation of effective dose in dental lateral cephalometric radiology. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2007. 124:181–186.
Article13. SEDENTEXCT. Radiation protection: cone beam CT for dental and maxillofacial radiology. Evidence based guidelines 2011 (v2.0) [Internet]. 2011. cited 2012 April 30. SEDENTEXCT project;Available from: http://www.sedentexct.eu/content/guidelines-cbct-dental-and-maxillofacial-radiology.14. Hart D, Hillier MC, Wall BF. HPA-RPD-029. Doses to patients from radiographic and fluoroscopi x-ray imaging procedures in the UK - 2005 review [Internet]. 2007. cited 2012 April 30. Chilton: HPARPD;Available from http://www.hpa.org.uk/webc/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1194947413167.15. IAEA. International basic safety standards for protection against ionizing radiation and for the safety of radiation source, jointly sponsored by FAO, IAEA, ILO, OECD/NEA, PAHO and WHO. Safety Series No. 115 [internet]. 1996. cited 2012 April 30. Vienna: IAEA;Available from http://www-pub.iaea.org/mtcd/publications/pdf/ss-115-web/pub996_web-1a.pdf.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Extraoral periapical radiography: an alternative approach to intraoral periapical radiography
- Radiography Work Performed by Dental Hygienists according to the Workplace Type
- Comparative study of digital and conventional radiography for the diagnostic ability of artificial proximal surface caries
- Diagnostic Performance of the Intraoral Radiographs on the Interproximal Dental Caries
- Determination and classification of intraoral phosphor storage plate artifacts and errors