Cancer Res Treat.
2011 Mar;43(1):19-23.
Phase II Clinical Trial of Genexol(R) (Paclitaxel) and Carboplatin for Patients with Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- 2Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea. dshong@schbc.ac.kr
- 4Division of Allergy and Respiratory Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This phase II clinical trial was conducted to evaluate the activity and safety of a combination treatment of paclitaxel (Genexol(R)) plus carboplatin in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemotherapy-naive patients having histologically confirmed advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer were enrolled. Genexol(R) was administered at 225 mg/m2 intravenous (IV) infusion over 3 hours, followed by carboplatin (area under the concentration-time curve=6) IV on day 1 every 3 weeks.
RESULTS
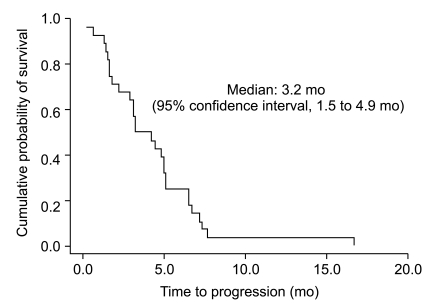
Twenty-eight patients were enrolled between January 2003 and January 2005. A total of 110 cycles of chemotherapy were given. The median number of chemotherapy cycles was 4. A total of 25 study patients were evaluable. On an intent-to-treat basis, there were ten partial responses (response rate 35.7%). The median time-to-progression was 3.2 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.5 to 4.9) and the median overall survival was 8.2 months (95% CI, 4.1 to 12.3). The main hematologic grade 3/4 toxicity was neutropenia, which was observed in 14 (50.0%) patients. The main non-hematologic toxicity was peripheral neuropathy, which was observed in 12 patients (42.9%). Grade 3/4 neuropathy occurred in 8 patients (28.6%) and three patients discontinued treatment because of neuropathy.
CONCLUSION
In this trial, the combination of Genexol(R) and carboplatin showed significant activity as first line treatment for patients with advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. However, a modest dose reduction of Genexol(R) is needed due to sensory neuropathy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Headquarters of Central Cancer Registry. 2007 Annual report of the Korea Cancer Registration. 2009. Seoul: Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs.2. Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:92–98. PMID: 11784875.
Article3. Kelly K, Crowley J, Bunn PA Jr, Presant CA, Grevstad PK, Moinpour CM, et al. Randomized phase III trial of paclitaxel plus carboplatin versus vinorelbine plus cisplatin in the treatment of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group trial. J Clin Oncol. 2001; 19:3210–3218. PMID: 11432888.
Article4. Lee SH, Park K, Suh C, Kim HK, Kim JS, Im YH, et al. A multi-center, phase II clinical trial of Genexol® (paclitaxel) and cisplatin for patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2003; 35:30–34.5. Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J, Davis TE, McFadden ET, et al. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol. 1982; 5:649–655. PMID: 7165009.
Article6. Smit EF, van Meerbeeck JP, Lianes P, Debruyne C, Legrand C, Schramel F, et al. Three-arm randomized study of two cisplatin-based regimens and paclitaxel plus gemcitabine in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. A phase III trial of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Lung Cancer Group: EORTC 08975. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:3909–3917. PMID: 14581415.7. Scagliotti GV, Parikh P, von Pawel J, Biesma B, Vansteenkiste J, Manegold C, et al. Phase III study comparing cisplatin plus gemcitabine with cisplatin plus pemetrexed in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:3543–3551. PMID: 18506025.
Article8. Kosmidis P, Mylonakis N, Skarlos D, Samantas E, Dimopoulos M, Papadimitriou C, et al. Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) plus carboplatin (6 AUC) versus paclitaxel (225 mg/m2) plus carboplatin (6 AUC) in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a multicenter randomized trial. Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group (HeCOG). Ann Oncol. 2000; 11:799–805. PMID: 10997806.9. Morère JF, Piperno-Neumann S, Coulon MA, Vaylet F, L'Her P, Brunet A, et al. Dose-finding study of paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 2000; 11:541–548. PMID: 11036956.
Article10. Huizing MT, Giaccone G, van Warmerdam LJ, Rosing H, Bakker PJ, Vermorken JB, et al. Pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel and carboplatin in a dose-escalating and dosesequencing study in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: the European Cancer Centre. J Clin Oncol. 1997; 15:317–329. PMID: 8996159.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Safety and Tolerability of Weekly Genexol-PM, a Cremophor-Free Polymeric Micelle Formulation of Paclitaxel, with Carboplatin in Gynecologic Cancer: A Phase I Study
- An open-label, multicenter, phase I trial of a cremophor-free, polymeric micelle formulation of paclitaxel combined with carboplatin as a first-line treatment for advanced ovarian cancer: a Korean Gynecologic Oncology Group study (KGOG-3016)
- A Multi-Center, Phase II Clinical Trial of Genexol(R) (Paclitaxel) and Cisplatin for Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- An Open-Label, Randomized, Parallel, Phase II Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of a Cremophor-Free Polymeric Micelle Formulation of Paclitaxel as First-Line Treatment for Ovarian Cancer: A Korean Gynecologic Oncology Group Study (KGOG-3021)
- A case of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with taxol / carboplatin in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer