Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2014 Nov;2(5):337-343. 10.4168/aard.2014.2.5.337.
Identification of IgE binding components of two major weed pollens, ragweed and mugwort
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy & Clinical Immunology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Biomedical Science, Ajou University Graduate School, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1803540
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2014.2.5.337
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Ragweed and mugwort pollens are the major weed allergens that cause pollinosis in Korea. The IgE-binding components to these 2 pollens and their cross-reactivity have not been reported in Korea, while several reports had been made in Western countries. We investigated IgE-binding components to ragweed and mugwort pollens and their allergenic relationship in patients sensitive to the 2 pollens.
METHODS
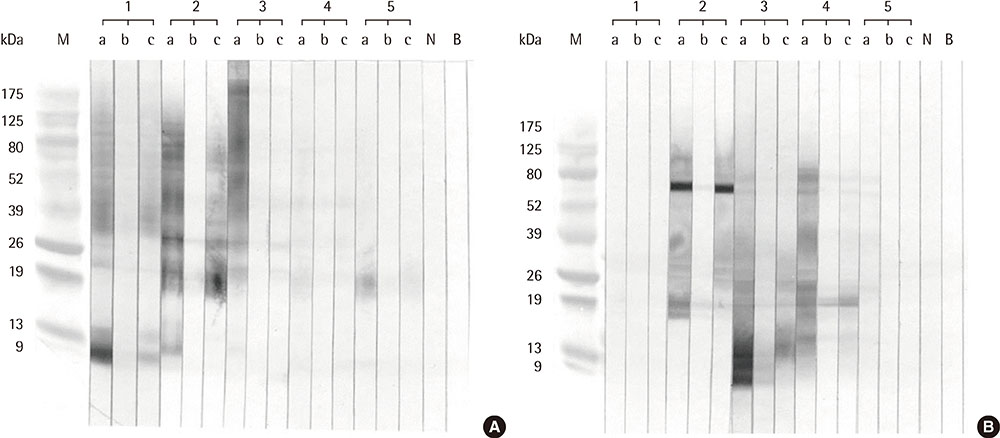
We enrolled 33 allergic rhinitis patients with typical seasonal pollinosis symptoms in autumn and elevated serum specific IgE levels to ragweed and/or mugwort pollens (>10 kU/L by ImmunoCAP). The protein bands of the 2 pollen extracts were determined using sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and IgE immunoblot analysis was performed to determine the IgE-binding components of each pollen extract. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) inhibition and immunoblot inhibition tests were performed to evaluate the cross-reactivity between ragweed and mugwort pollen extracts.
RESULTS
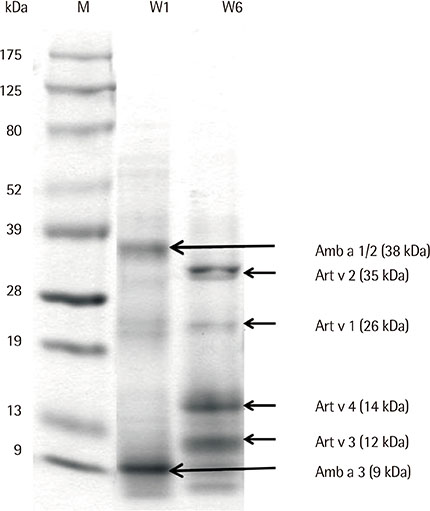
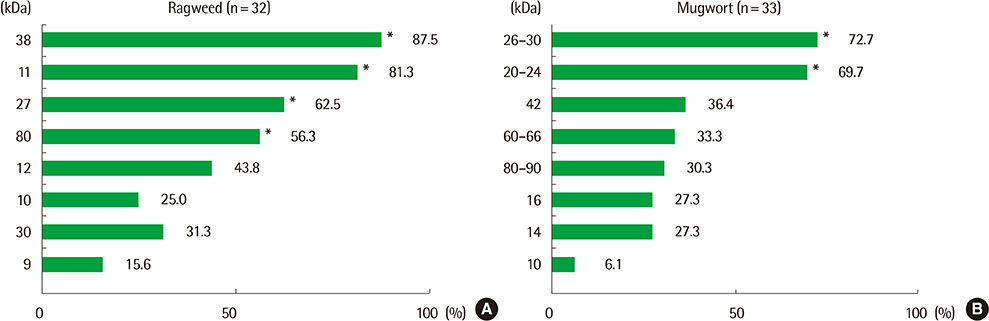
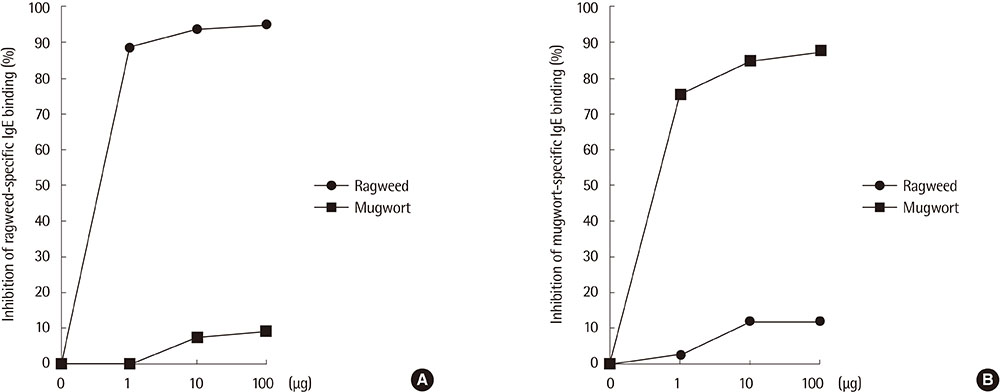
Eight IgE-binding components (9, 10, 11, 12, 27, 30, 38, and 80 kDa) were found in ragweed pollen extracts, of which 4 (38, 11, 27, and 80 kDa) were major IgE-binding components. Eight IgE-binding components (10, 14, 16, 20-24, 26-30, 42, 60-66, and 80-90 kDa) were found in mugwort pollen extracts, of which 2 components (26-30 and 20-24 kDa) were major IgE-binding components. No significant inhibitions were noted between ragweed and mugwort pollen extracts by the ELISA inhibition test. No significant changes were noted in IgE immunoblot inhibition analysis.
CONCLUSION
We identified 4 major IgE-binding components (38, 11, 35, 27, and 80 kDa) in ragweed pollens and 2 major IgE-binding components (26-30 and 20-24 kDa) in mugwort pollens. No cross-reactivity was found between ragweed and mugwort pollens.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cross-allergenicity between dandelion and major weed pollens
Ji Hye Kim, Moon-Kyung Yoon, Mi-Ae Kim, Yoo-Seob Shin, Young Min Ye, Hae-Sim Park
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(5):358-364. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.5.358.
Reference
-
1. Lee JW, Choi GS, Kim JE, Jin HJ, Kim JH, Ye YM, et al. Changes in sensitization rates to pollen allergens in allergic patients in the southern part of Gyeonggi province over the last 10 years. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:33–40.2. Oh JW, Lee HB, Kang IJ, Kim SW, Park KS, Kook MH, et al. The revised edition of Korean calendar for allergenic pollens. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:5–11.
Article3. Oh JW. Development of pollen concentration prediction models. J Korean Med Assoc. 2009; 52:579–591.
Article4. Oh JW, Kang IJ, Kim SW, Kook MH, Kim BS, Cheong JT, et al. The association between the concentration of pollen and outbreak of pollinosis in childhood. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2009; 19:4–11.5. Park SH, Lim DH, Son BK, Kim JH, Song YE, Oh IB, et al. Sensitization rates of airborne pollen and mold in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2012; 55:322–329.
Article6. Lee JE, Ahn JC, Han DH, Kim DY, Kim JW, Cho SH, et al. Variability of offending allergens of allergic rhinitis according to age: optimization of skin prick test allergens. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:47–54.
Article7. Wopfner N, Gadermaier G, Egger M, Asero R, Ebner C, Jahn-Schmid B, et al. The spectrum of allergens in ragweed and mugwort pollen. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005; 138:337–346.
Article8. Kim JH, Oh JW, Lee HB, Kim SW, Kang IJ, Kook MH, et al. Changes in sensitization rate to weed allergens in children with increased weeds pollen counts in Seoul metropolitan area. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:350–355.
Article9. Oh JW. Characteristics of allergic pollen and the pollen amount was recently changed in Korea. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 27:1–7.10. Oberhuber C, Ma Y, Wopfner N, Gadermaier G, Dedic A, Niggemann B, et al. Prevalence of IgE-binding to Art v 1, Art v 4 and Amb a 1 in mugwort-allergic patients. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2008; 145:94–101.
Article11. Moverare R, Larsson H, Carlsson R, Holmquist I. Mugwort-sensitized individuals from North Europe, South Europe and North America show different IgE reactivity patterns. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011; 154:164–172.
Article12. Han D, Lai X, Gjesing B, Zhong N, Zhang L, Spangfort MD. The specific IgE reactivity pattern of weed pollen-induced allergic rhinitis patients. Acta Otolaryngol. 2011; 131:533–538.
Article13. Katial RK, Lin FL, Stafford WW, Ledoux RA, Westley CR, Weber RW. Mugwort and sage (Artemisia) pollen cross-reactivity: ELISA inhibition and immunoblot evaluation. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997; 79:340–346.
Article14. Hirschwehr R, Heppner C, Spitzauer S, Sperr WR, Valent P, Berger U, et al. Identification of common allergenic structures in mugwort and ragweed pollen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998; 101(2 Pt 1):196–206.
Article15. Weber RW. Patterns of pollen cross-allergenicity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112:229–239.
Article16. Park HS, Kim MJ, Moon HB. Antigenic relationship between mugwort and ragweed pollens by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Korean Med Sci. 1994; 9:213–217.
Article17. Asero R, Wopfner N, Gruber P, Gadermaier G, Ferreira F. Artemisia and Ambrosia hypersensitivity: co-sensitization or co-recognition? Clin Exp Allergy. 2006; 36:658–665.
Article18. Yoon MG, Kim MA, Jin HJ, Shin YS, Park HS. Identification of immunoglobulin E binding components of two major tree pollens, birch and alder. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:216–220.
Article19. Hao GD, Zheng YW, Gjesing B, Kong XA, Wang JY, Song ZJ, et al. Prevalence of sensitization to weed pollens of Humulus scandens, Artemisia vulgaris, and Ambrosia artemisiifolia in northern China. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2013; 14:240–246.
Article20. Jahn-Schmid B, Hauser M, Wopfner N, Briza P, Berger UE, Asero R, et al. Humoral and cellular cross-reactivity between Amb a 1, the major ragweed pollen allergen, and its mugwort homolog Art v 6. J Immunol. 2012; 188:1559–1567.
Article21. Jahn-Schmid B, Kelemen P, Himly M, Bohle B, Fischer G, Ferreira F, et al. The T cell response to Art v 1, the major mugwort pollen allergen, is dominated by one epitope. J Immunol. 2002; 169:6005–6011.
Article22. Jimeno L, Duffort O, Serrano C, Barber D, Polo F. Monoclonal antibody-based ELISA to quantify the major allergen of Artemisia vulgaris pollen, Art v 1. Allergy. 2004; 59:995–1001.
Article23. Himly M, Jahn-Schmid B, Dedic A, Kelemen P, Wopfner N, Altmann F, et al. Art v 1, the major allergen of mugwort pollen, is a modular glycoprotein with a defensin-like and a hydroxyproline-rich domain. FASEB J. 2003; 17:106–108.
Article24. Canis M, Becker S, Groger M, Kramer MF. IgE reactivity patterns in patients with allergic rhinoconjunctivitis to ragweed and mugwort pollens. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2012; 26:31–35.
Article25. Gadermaier G, Wopfner N, Wallner M, Egger M, Didierlaurent A, Regl G, et al. Array-based profiling of ragweed and mugwort pollen allergens. Allergy. 2008; 63:1543–1549.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cross - reactivity between pollens in patients sensitlzed to multiple pollens
- Antigenic relationship between mugwort and ragweed pollens by crossed immunoelectrophoresis
- Cross-allergenicity between dandelion and major weed pollens
- Paradoxical Increase of IgE Binding Components during Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy in Pollinosis Patients
- Identification of immunoglobulin E binding components of two major tree pollens, birch and alder