J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Jul;29(7):1025-1029. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.7.1025.
Paradoxical Increase of IgE Binding Components during Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy in Pollinosis Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Biomedical Sciences, Ajou University Graduate School, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1789967
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.7.1025
Abstract
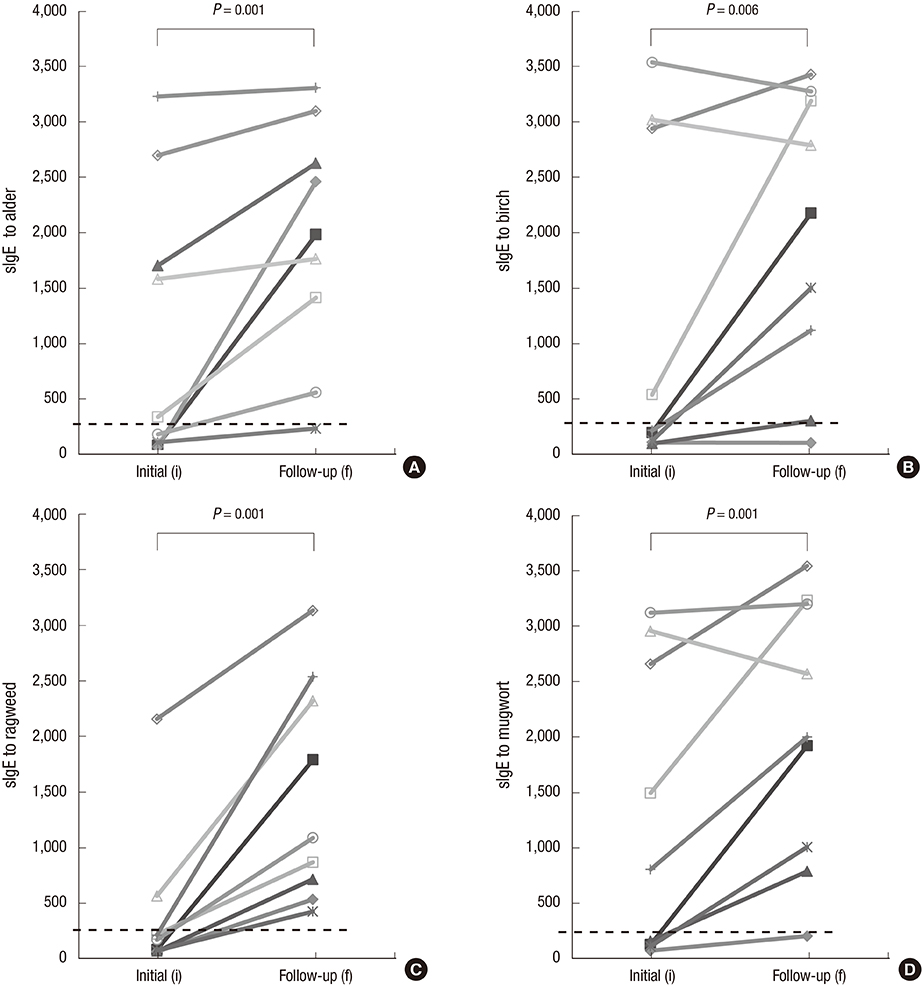
- Allergen-specific immunotherapy (SIT) reduces allergen specific IgE (sIgE) levels and achieves clinical and immunological tolerance by modulating innate and adaptive immunological responses. Increased temperature and CO2 concentrations caused by climate changes contribute to an increase of pollen count and allergenicity that influences clinical SIT outcomes. In this study, we investigated the changes of IgE binding components to tree and weed pollens in pollinosis patients who showed a paradoxical increase of serum sIgE level during pollen-SIT. We enrolled nine patients who showed an increasing pattern of serum sIgE level to alder, birch, ragweed and mugwort pollens by enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay. IgE immunoblot analysis confirmed the intensification or new generation of major IgE binding components that could be induced by climate change. The findings suggest that the regular monitoring of sIgE levels and symptom changes is required to improve the clinical outcomes of SIT in patients undergoing SIT for tree and weed pollens.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Oh JW, Lee HB, Kang IJ, Kim SW, Park KS, Kook MH, Kim BS, Baek HS, Kim JH, Kim JK, et al. The revised edition of Korean calendar for allergenic pollens. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:5–11.2. Min YG. The pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2010; 2:65–76.3. Jung JW, Choi JC, Shin JW, Kim JY, Park IW, Choi BW. Clinical characteristics according to sensitized allergens in adult Korean patients with bronchial asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2010; 2:102–107.4. Zhang Y, Zhang L. Prevalence of allergic rhinitis in China. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:105–113.5. Lee JM. Practice patterns of allergen immunotherapy in Korea: where are we? Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013; 5:249–250.6. Lee JE, Ahn JC, Han DH, Kim DY, Kim JW, Cho SH, Park HW, Rhee CS. Variability of offending allergens of allergic rhinitis according to age: optimization of skin prick test allergens. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:47–54.7. Dretzke J, Meadows A, Novielli N, Huissoon A, Fry-Smith A, Meads C. Subcutaneous and sublingual immunotherapy for seasonal allergic rhinitis: a systematic review and indirect comparison. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:1361–1366.8. Hur GY, Kim TB, Han MY, Nahm DH, Park JW. Allergen and Immunotherapy Work Group of the Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology (KAAACI). A survey of the prescription patterns of allergen immunotherapy in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013; 5:277–282.9. Matsuoka T, Shamji MH, Durham SR. Allergen immunotherapy and tolerance. Allergol Int. 2013; 62:403–413.10. Ziska LH, Beggs PJ. Anthropogenic climate change and allergen exposure: the role of plant biology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129:27–32.11. D'Amato G, Rottem M, Dahl R, Blaiss M, Ridolo E, Cecchi L, Rosario N, Motala C, Ansotegui I, Annesi-Maesano I. Climate change, migration, and allergic respiratory diseases: an update for the allergist. World Allergy Organ J. 2011; 4:120–125.12. Jin HJ, Choi GS, Shin YS, Kim JH, Kim JE, Ye YM, Park HS. The allergenic potency of Japanese hop pollen is increasing with environmental changes in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013; 5:309–314.13. Dapul-Hidalgo G, Bielory L. Climate change and allergic diseases. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012; 109:166–172.14. Weber RW. Impact of climate change on aeroallergens. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012; 108:294–299.15. Lin GC, Zacharek MA. Climate change and its impact on allergic rhinitis and other allergic respiratory diseases. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012; 20:188–193.16. Kim JH, Oh JW, Lee HB, Kim SW, Kang IJ, Kook MH, Kim BS, Park KS, Baek HS, Kim KR, et al. Changes in sensitization rate to weed allergens in children with increased weeds pollen counts in Seoul Metropolitan area. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:350–355.17. Yoon MG, Kim MA, Jin HJ, Shin YS, Park HS. Identification of immunoglobulin E binding components of two major tree pollens, birch and alder. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:216–220.18. Sastre J. Molecular diagnosis in allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010; 40:1442–1460.19. Shamji MH, Ljørring C, Würtzen PA. Predictive biomarkers of clinical efficacy of allergen-specific immunotherapy: how to proceed. Immunotherapy. 2013; 5:203–206.20. Kim J, Lee SW, Woo SY, Han YS, Lee JH, Lee IY, Lim IS, Choi ES, Choi BW, Cheong HK, et al. The indoor level of house dust mite allergen is associated with severity of atopic dermatitis in children. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28:74–79.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Features of Patients with Apple Allergy and Identification of IgE-Binding Components of Apple
- Allergen Specific Immunotherapy in Allergic Rhinitis
- Identification of immunoglobulin E binding components of two major tree pollens, birch and alder
- Influence of conventional house-dust-mite immunotherapy on histamine releasability from the basophil
- Update in the Mechanisms of Allergen-Specific Immunotheraphy