J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2014 Jun;21(2):90-96. 10.4184/jkss.2014.21.2.90.
Spinal Epidural Abscess and Psoas Abscess Combined with Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis Following Vertebroplasty: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. ssurgeon@gsnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1800404
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2014.21.2.90
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Case report.
OBJECTIVES
To report a case of extensive spinal epidural abscess and bilateral psoas abscesses combined with pyogenic spondylodiscitis after a L3 vertebroplasty. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Infection after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty is a rare medical complication. Few reports on spinal epidural abscess and bilateral psoas abscesses, coupled with pyogenic spondylodiscitis after vertebroplasty, are available in the English medical literature.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The authors performed a clinical and radiographic case review.
RESULTS
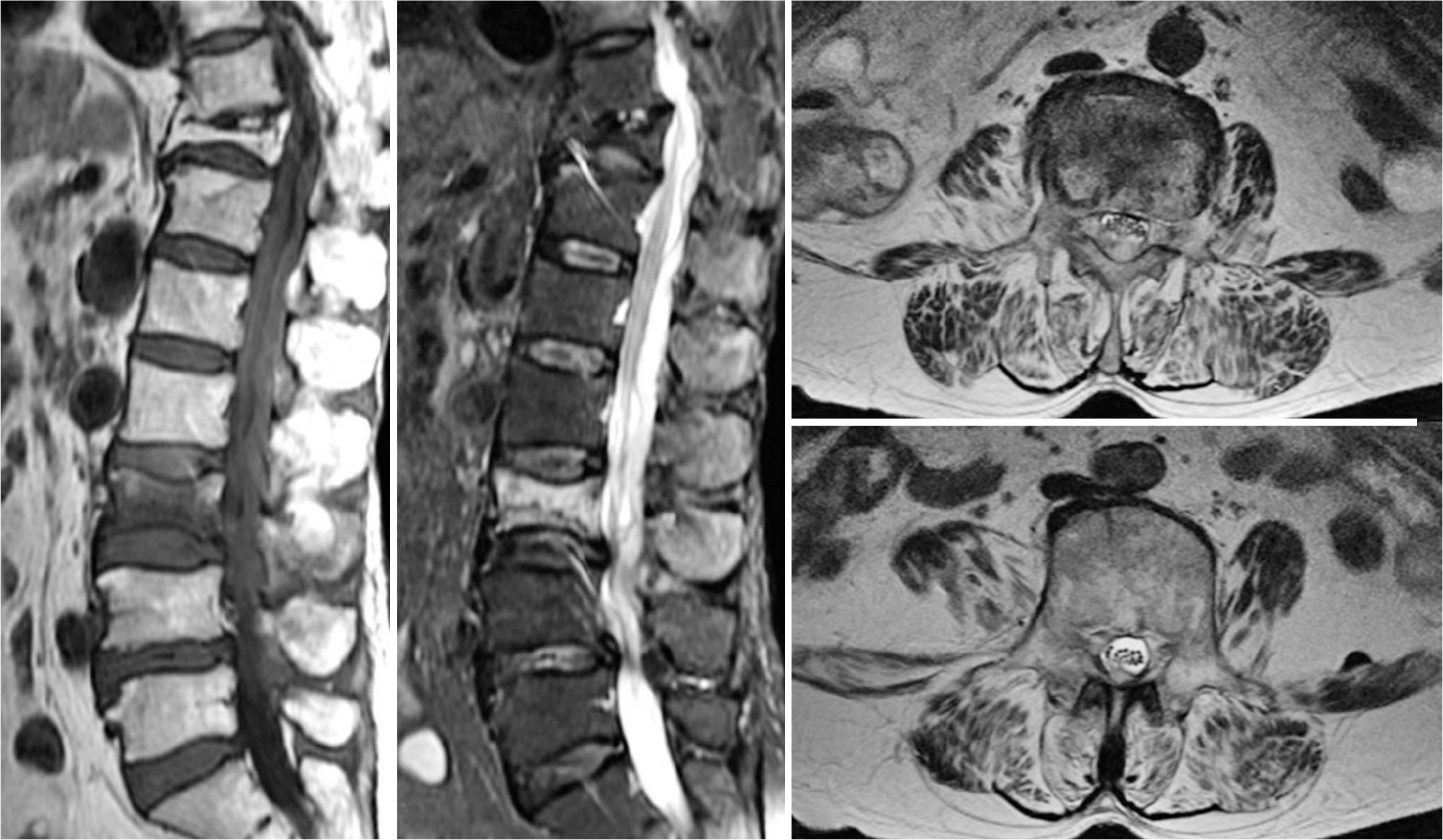
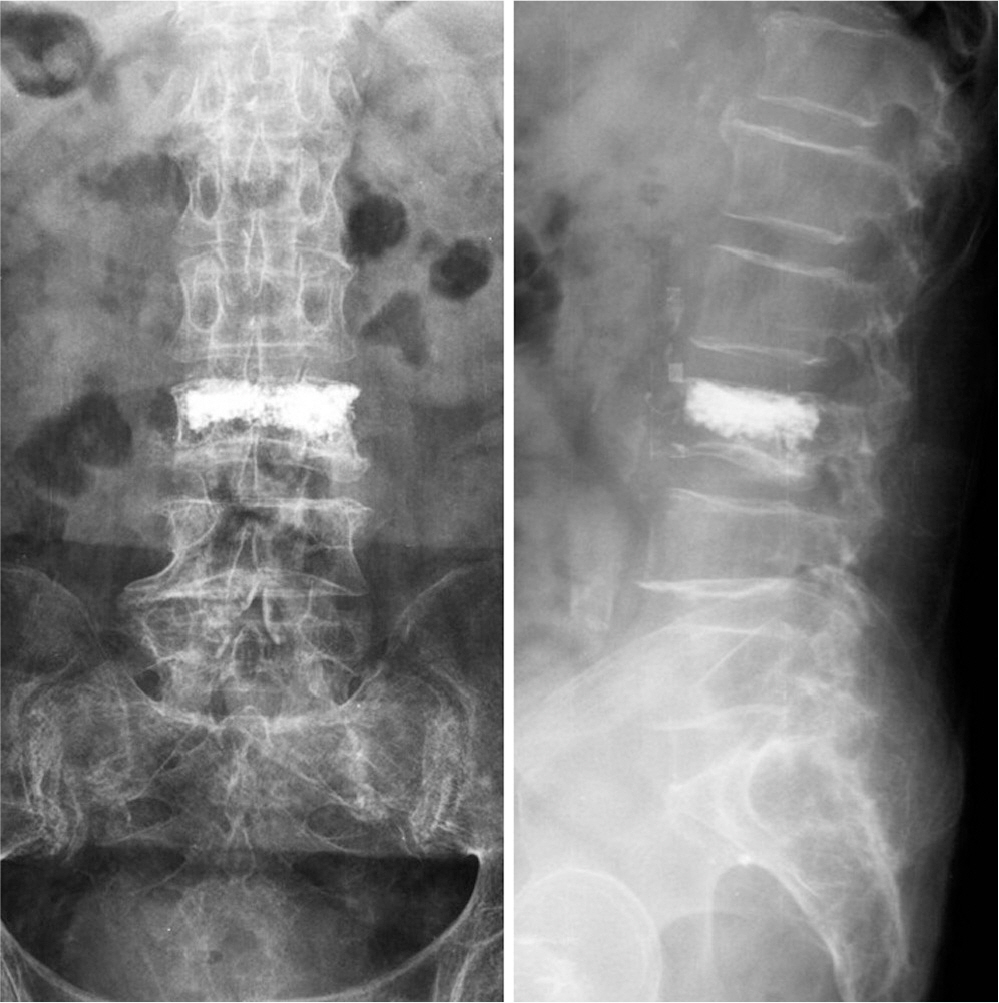
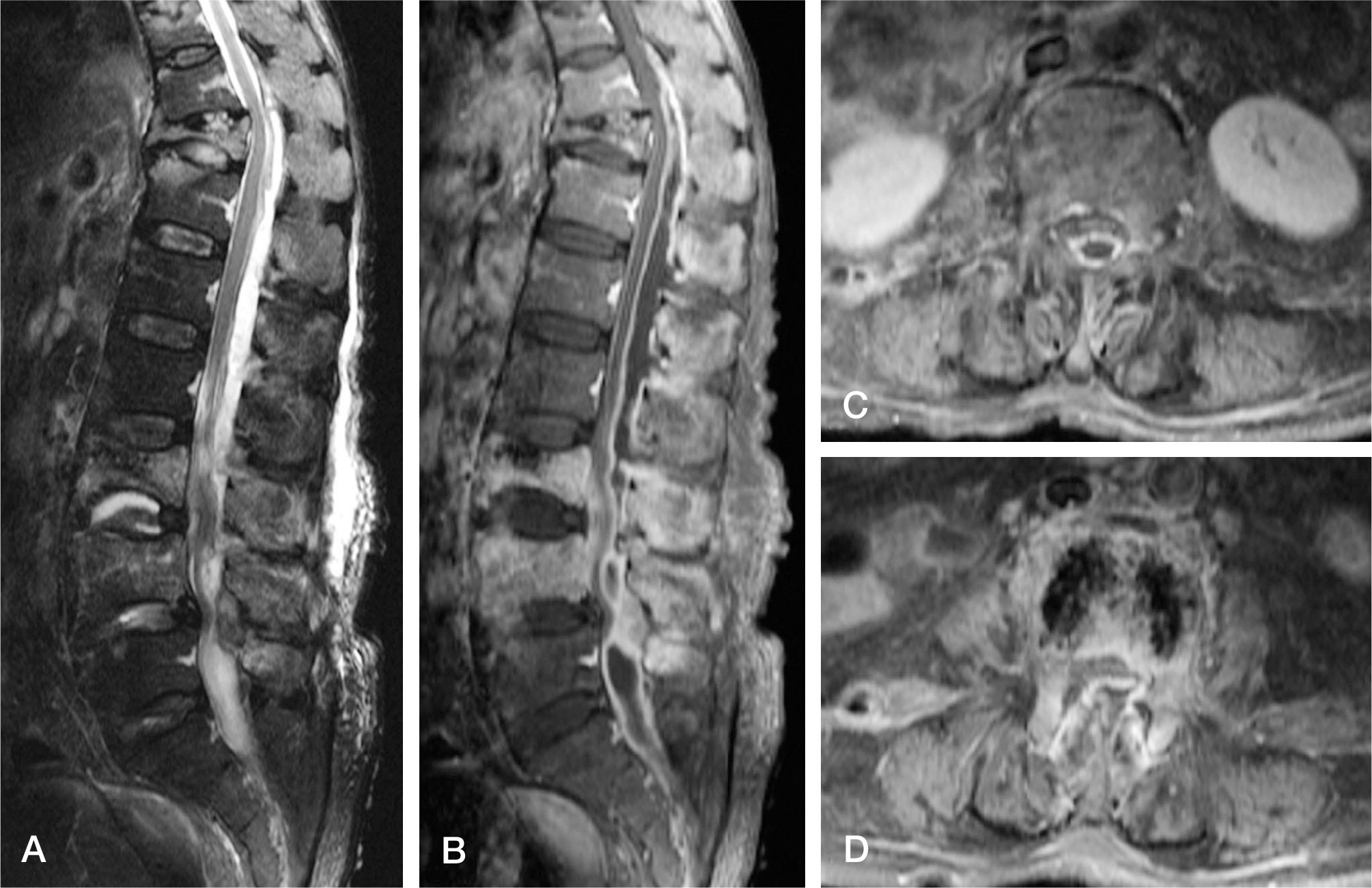
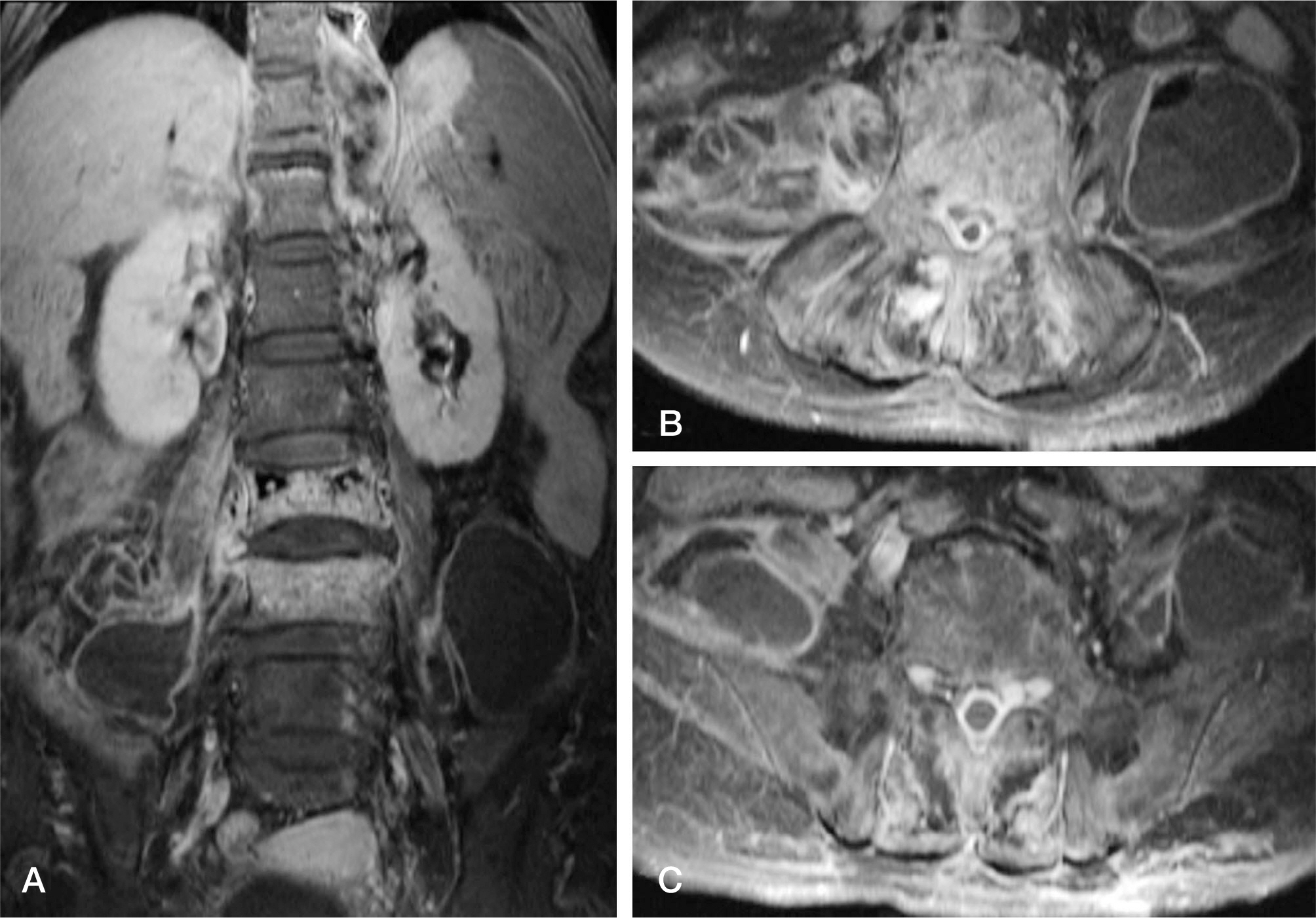
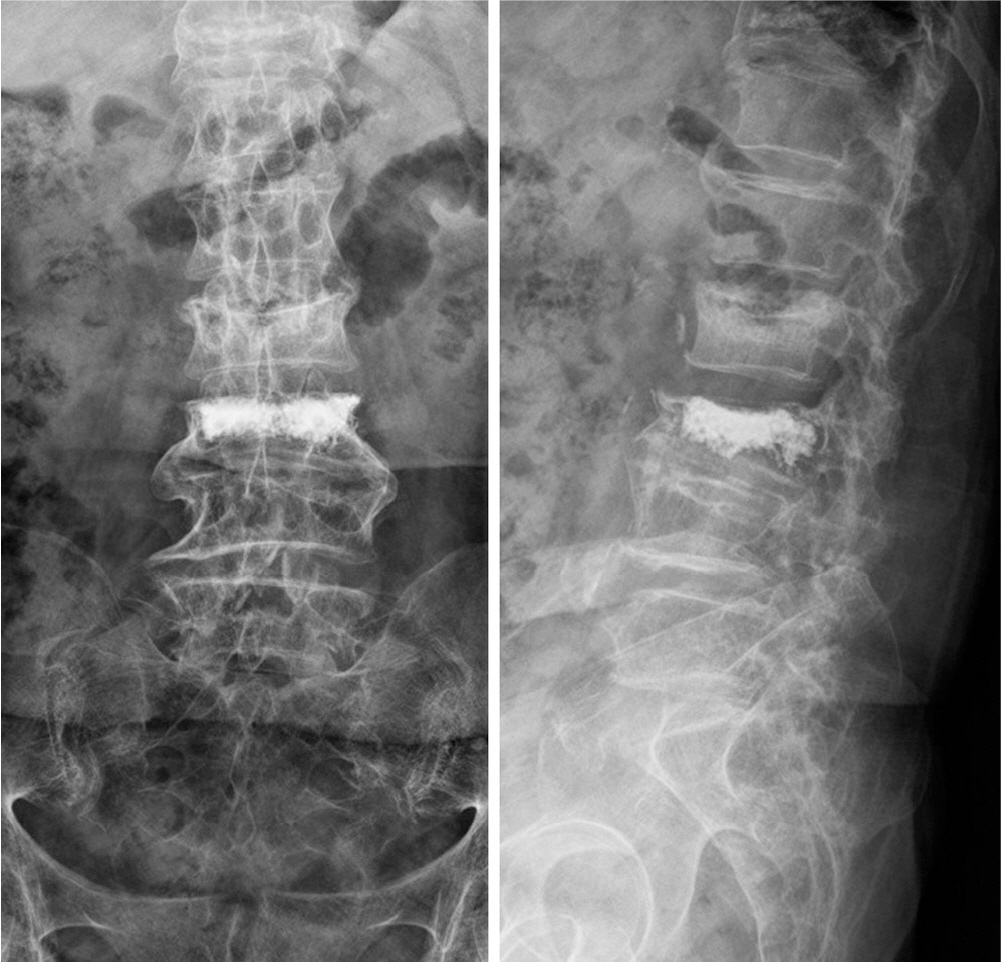
A 74-year-old woman, without any existing medical illness, presented with a history of three weeks of lower back pain, fever, and neurologic deficits of both legs after vertebroplasty performed in another hospital. Magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated an extensive spinal epidural abscess from T10 to S1 and huge bilateral psoas abscesses combined with spondylodiscitis at L3-4. Urgent limited laminectomies and abscess drainage were performed from L1 to S1. The day after the operation, ultrasound-guided percutaneous drainage was performed to manage bilateral psoas abscesses. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus was identified by intraoperative culture. Antibiotic therapy during hospitalization was maintained for six weeks with vancomycin and rifampicin. The infection was successfully treated without any neurologic deficit and spinal deformity.
CONCLUSIONS
Vertebroplasty is relative safe and simple procedure; however, the procedure also may cause severe spinal infection. Aseptic techniques under sterile environment was required during surgery. It is important that early diagnosis and prompt surgical decompression in spinal epidural abscess with neurologic deficit. Limited surgery and antibiotic therapy could be a good treatment option in spinal epidural abscess combined with pyogenic spondylodiscitis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Abscess
Aged
Congenital Abnormalities
Decompression, Surgical
Discitis*
Drainage
Early Diagnosis
Epidural Abscess*
Female
Fever
Hospitalization
Humans
Kyphoplasty
Laminectomy
Leg
Low Back Pain
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Neurologic Manifestations
Psoas Abscess*
Rifampin
Vancomycin
Vertebroplasty*
Rifampin
Vancomycin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yu SW, Chen WJ, Lin WC, Chen YJ, Tu YK. Serious pyogenic spondylitis following vertebroplasty-a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:E209–11.
Article2. Lee JS, Choi SM, Kim KW. Triparesis caused by gas-con-taining extensive epidural abscess secondary to Aeromonas hydrophila infection of a thoracic vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine J. 2013; 13:E9–E14.
Article3. Panagiotopoulos V, Konstantinou D, Solomou E, Panagiotopoulos E, Marangos M, Maraziotis T. Extended cervi-columbar spinal epidural abscess associated with paraparesis successfully decompressed using a minimally invasive technique. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:E300–3.
Article4. Payer M, Walser H. Evacuation of a 14-vertebral-level cervico-thoracic epidural abscess and review of surgical options for extensive spinal epidural abscesses. J Clin Neurosci. 2008; 15:483–6.
Article5. Rigamonti D, Liem L, Sampath P, et al. Spinal epidural abscess: contemporary trends in etiology, evaluation, and management. Surg Neurol. 1999; 52:189–96.
Article6. Yacoub WN, Sohn HJ, Chan S, et al. Psoas abscess rarely requires surgical intervention. Am J Surg. 2008; 196:223–7.
Article7. Shin JH, Ha KY, Kim KW, Lee JS, Joo MW, Surgical treatment for delayed pyogenic spondylitis after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Report of 4 cases. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008; 9:265–72.8. Kwon KH, Park JH, Chae IJ. Percutaneous drainage and irrigation in pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1998; 5:122–8.9. Lee CY, Huang TJ, Li YY, Cheng CC, Wu MH. Comparison of minimal access and traditional anterior spinal surgery in managing infectious spondylitis: a minimum 2-year followup. Spine J. 2014; 14:1099–105.
Article10. Kim YM, Won CH, Seo JB, Choi ES, Lee HS, Um SM. Pyogenic L4-5 spondylitis managed with percutaneous drainage followed by posterior lumbar interbody fusion- a case report. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2001; 8:513–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spondylodiscitis with Epidural Abscess Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Pyogenic Spinal Epidural Abscess: A Case Report
- Primary Pyogenic Psoas Abscess in Child
- The Epidural and Psoas Abscess Recognized after Lumbar Epidural Block: A case report
- Minimally Invasive Surgical Treatment of the Pan-Spinal Anterior Epidural Abscess Using a Nasogastric Tube and Guide Wire