Yonsei Med J.
2014 Sep;55(5):1260-1266. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.5.1260.
Clinical Outcomes of Initial Dexamethasone Treatment Combined with a Single High Dose of Intravenous Immunoglobulin for Primary Treatment of Kawasaki Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hwaseong, Korea.
- 2Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Department of Pediatrics, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jwjung@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1799489
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.5.1260
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the clinical effects of a single high dose intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) combined with initial dexamethasone as a primary treatment on Kawasaki disease (KD).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between January 2008 and December 2010, we reviewed the medical records of 216 patients with complete KD patients that were admitted to a single medical center. 106 patients were treated with a single high dose of IVIG (2 g/kg) alone and 110 patients received IVIG and dexamethasone (0.3 mg/kg per day for three days).
RESULTS
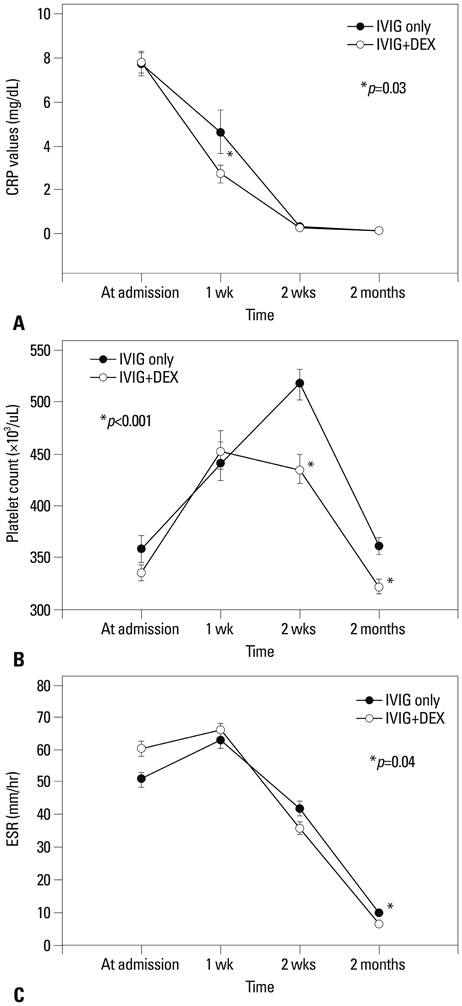
The combined IVIG plus dexamethasone patient group had a significantly shorter febrile period and duration of hospital stay (1.4+/-0.7 days vs. 2.0+/-1.2 days, p<0.001; 5.8+/-1.7 days vs. 6.9+/-2.5 days, p<0.001, respectively) than the IVIG alone group. The combined IVIG plus dexamethasone group required IVIG retreatment significantly less than the IVIG only group (12.7% vs. 32%, p=0.003). After completion of the initial IVIG, C-reactive protein levels in the combined IVIG plus dexamethasone group were significantly lower than those in the IVIG only group (2.7+/-4.0 mg/dL vs. 4.6+/-8.7 mg/dL, p=0.03). In the combined IVIG plus dexamethasone group, the incidence of coronary artery lesions tended to be lower without worse outcomes at admission after initial infusion of IVIG and in follow-up at two months; however, the differences were not significant (8.2% vs. 11.3%, p=0.22; 0.9% vs. 2.8%, p=0.29).
CONCLUSION
Initial combined therapy with dexamethasone and a single high-dose of IVIG resulted in an improved clinical course, in particular a shorter febrile period, less IVIG retreatment, and shorter hospital stay without worse coronary outcomes.
MeSH Terms
-
Child, Preschool
Dexamethasone/administration & dosage/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Female
Fever/drug therapy
Glucocorticoids/administration & dosage/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Humans
Immunoglobulins, Intravenous/administration & dosage/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Immunologic Factors/administration & dosage/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Infant
Length of Stay
Male
Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome/*drug therapy
Treatment Outcome
Dexamethasone
Glucocorticoids
Immunoglobulins, Intravenous
Immunologic Factors
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The impact of single dose intravenous dexamethasone as an adjunctive therapy for primary treatment on concentrations of inflammatory biomarkers in children with Kawasaki disease
Jung Eun Kwon
Pediatr Emerg Med J. 2022;9(1):23-28. doi: 10.22470/pemj.2022.00423.
Reference
-
1. Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics. 2004; 114:1708–1733.
Article2. Han RK, Silverman ED, Newman A, McCrindle BW. Management and outcome of persistent or recurrent fever after initial intravenous gamma globulin therapy in acute Kawasaki disease. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2000; 154:694–699.
Article3. Wright DA, Newburger JW, Baker A, Sundel RP. Treatment of immune globulin-resistant Kawasaki disease with pulsed doses of corticosteroids. J Pediatr. 1996; 128:146–149.
Article4. Blaisdell LL, Hayman JA, Moran AM. Infliximab treatment for pediatric refractory Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 2011; 32:1023–1027.
Article5. Hashino K, Ishii M, Iemura M, Akagi T, Kato H. Re-treatment for immune globulin-resistant Kawasaki disease: a comparative study of additional immune globulin and steroid pulse therapy. Pediatr Int. 2001; 43:211–217.
Article6. Kato H, Koike S, Yokoyama T. Kawasaki disease: effect of treatment on coronary artery involvement. Pediatrics. 1979; 63:175–179.
Article7. Kijima Y, Kamiya T, Suzuki A, Hirose O, Manabe H. A trial procedure to prevent aneurysm formation of the coronary arteries by steroid pulse therapy in Kawasaki disease. Jpn Circ J. 1982; 46:1239–1242.
Article8. Jibiki T, Terai M, Kurosaki T, Nakajima H, Suzuki K, Inomata H, et al. Efficacy of intravenous immune globulin therapy combined with dexamethasone for the initial treatment of acute Kawasaki disease. Eur J Pediatr. 2004; 163:229–233.
Article9. Sundel RP, Baker AL, Fulton DR, Newburger JW. Corticosteroids in the initial treatment of Kawasaki disease: report of a randomized trial. J Pediatr. 2003; 142:611–616.
Article10. Rosenberg GA. Brain Edema and Disorders of Cerebrospinal Fluid Circulation. In : Bradley WG, Daroff RB, Fenichel GM, Jankovic J, editors. Neurology in Clinical Practice. 2nd ed. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann Limited;2000. p. 1545–1549.11. Makata H, Ichiyama T, Uchi R, Takekawa T, Matsubara T, Furukawa S. Anti-inflammatory effect of intravenous immunoglobulin in comparison with dexamethasone in vitro: implication for treatment of Kawasaki disease. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2006; 373:325–332.
Article12. Furusho K, Kamiya T, Nakano H, Kiyosawa N, Shinomiya K, Hayashidera T, et al. High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin for Kawasaki disease. Lancet. 1984; 2:1055–1058.
Article13. Dajani AS, Taubert KA, Gerber MA, Shulman ST, Ferrieri P, Freed M, et al. Diagnosis and therapy of Kawasaki disease in children. Circulation. 1993; 87:1776–1780.
Article14. Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Beiser AS, Burns JC, Bastian J, Chung KJ, et al. A single intravenous infusion of gamma globulin as compared with four infusions in the treatment of acute Kawasaki syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991; 324:1633–1639.
Article15. Sato N, Sugimura T, Akagi T, Yamakawa R, Hashino K, Eto G, et al. Selective high dose gamma-globulin treatment in Kawasaki disease: assessment of clinical aspects and cost effectiveness. Pediatr Int. 1999; 41:1–7.
Article16. Weiss JE, Eberhard BA, Chowdhury D, Gottlieb BS. Infliximab as a novel therapy for refractory Kawasaki disease. J Rheumatol. 2004; 31:808–810.17. Furukawa T, Kishiro M, Akimoto K, Nagata S, Shimizu T, Yamashiro Y. Effects of steroid pulse therapy on immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease. Arch Dis Child. 2008; 93:142–146.
Article18. Burns JC. Revisiting steroids in the primary treatment of acute Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2006; 149:291–292.
Article19. Shulman ST. Is there a role for corticosteroids in Kawasaki disease? J Pediatr. 2003; 142:601–603.
Article20. Dahlem PG, von Rosenstiel IA, Lam J, Kuijpers TW. Pulse methylprednisolone therapy for impending cardiac tamponade in immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease. Intensive Care Med. 1999; 25:1137–1139.
Article21. Dale RC, Saleem MA, Daw S, Dillon MJ. Treatment of severe complicated Kawasaki disease with oral prednisolone and aspirin. J Pediatr. 2000; 137:723–726.
Article22. Shinohara M, Sone K, Tomomasa T, Morikawa A. Corticosteroids in the treatment of the acute phase of Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 1999; 135:465–469.
Article23. Okada Y, Shinohara M, Kobayashi T, Inoue Y, Tomomasa T, Kobayashi T, et al. Effect of corticosteroids in addition to intravenous gamma globulin therapy on serum cytokine levels in the acute phase of Kawasaki disease in children. J Pediatr. 2003; 143:363–367.
Article24. Kobayashi T, Inoue Y, Otani T, Morikawa A, Kobayashi T, Takeuchi K, et al. Risk stratification in the decision to include prednisolone with intravenous immunoglobulin in primary therapy of Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009; 28:498–502.
Article25. Wooditch AC, Aronoff SC. Effect of initial corticosteroid therapy on coronary artery aneurysm formation in Kawasaki disease: a meta-analysis of 862 children. Pediatrics. 2005; 116:989–995.
Article26. Inoue Y, Okada Y, Shinohara M, Kobayashi T, Kobayashi T, Tomomasa T, et al. A multicenter prospective randomized trial of corticosteroids in primary therapy for Kawasaki disease: clinical course and coronary artery outcome. J Pediatr. 2006; 149:336–341.
Article27. Sinha A, Bagga A. Pulse steroid therapy. Indian J Pediatr. 2008; 75:1057–1066.
Article28. Schimmer BP, Parker KL. Adrenocorticotropic hormones; adrenocortical steroids and their synthetic analog; inhibitors of the synthesis and actions of adrenocortical hormone. In : Brunton L, Lazo J, Parker K, editors. Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 11th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional;2006. p. 1587–1612.29. Kwak JH, Song J, Kang IS, Huh J, Lee HJ. Changes in coronary perfusion after occlusion of coronary arteries in Kawasaki disease. Yonsei Med J. 2014; 55:353–359.
Article30. Burns JC, Best BM, Mejias A, Mahony L, Fixler DE, Jafri HS, et al. Infliximab treatment of intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2008; 153:833–838.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Dexamethasone Therapy for Coronary Lesion after Immunoglobulin-retreated Kawasaki Disease
- The Efficacy and Safety of High-Dose Intravenous Immunoglobulin in the Treatment of Kawasaki Disease: How Can We Predict Resistance to Intravenous Immunoglobulin Treatment of Kawasaki Disease?
- The impact of single dose intravenous dexamethasone as an adjunctive therapy for primary treatment on concentrations of inflammatory biomarkers in children with Kawasaki disease
- A Comparison of Concentrations of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma between the Dose of Intravenous Immunoglobulin 1 gm/kg and 2 gm/kg in the Patients with Kawasaki Disease
- A Case of Intravenous Immunoglobulin-Resistant Kawasaki Disease Treated with Methotrexate