Korean J Radiol.
2014 Dec;15(6):862-870. 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.862.
A Computed Tomography-Based Spatial Normalization for the Analysis of [18F] Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography of the Brain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 135-720, Korea. lyoochel@yuhs.ac
- 2Molecular Imaging Research Center, Korea Institute Radiological and Medical Science, Seoul 139-706, Korea.
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 135-720, Korea.
- KMID: 1794661
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.862
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
We developed a new computed tomography (CT)-based spatial normalization method and CT template to demonstrate its usefulness in spatial normalization of positron emission tomography (PET) images with [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET studies in healthy controls.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
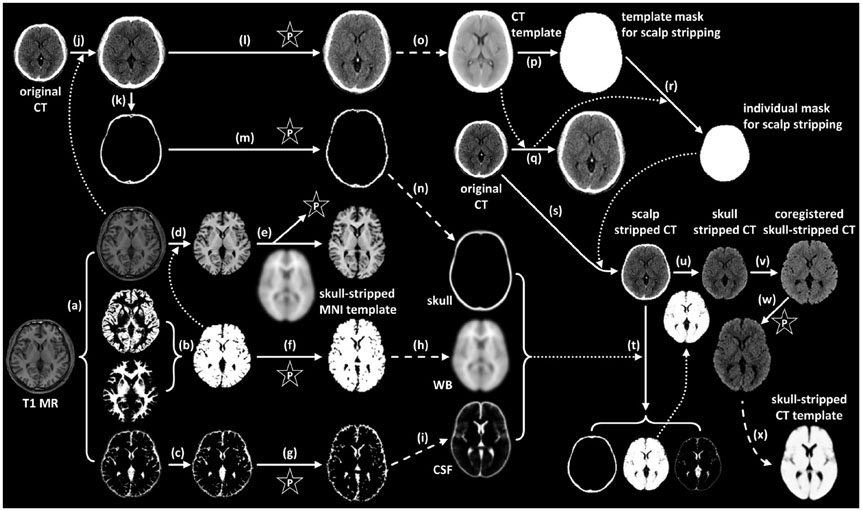
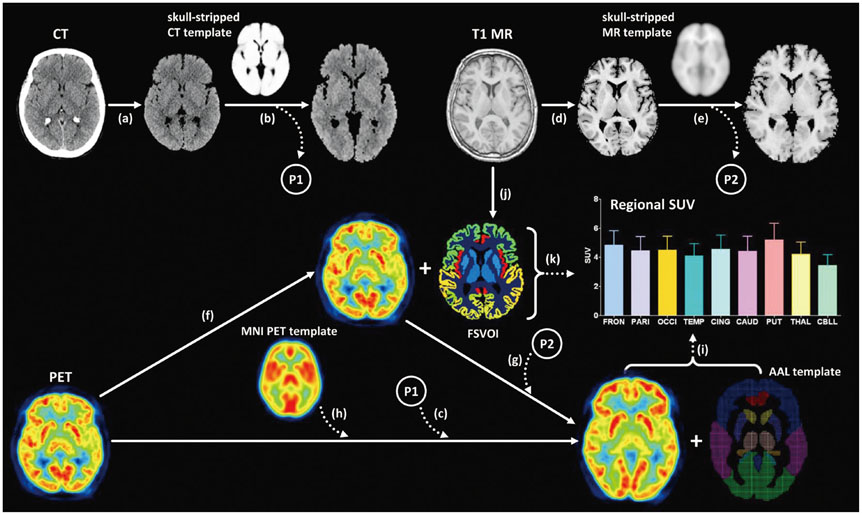
Seventy healthy controls underwent brain CT scan (120 KeV, 180 mAs, and 3 mm of thickness) and [18F] FDG PET scans using a PET/CT scanner. T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) images were acquired for all subjects. By averaging skull-stripped and spatially-normalized MR and CT images, we created skull-stripped MR and CT templates for spatial normalization. The skull-stripped MR and CT images were spatially normalized to each structural template. PET images were spatially normalized by applying spatial transformation parameters to normalize skull-stripped MR and CT images. A conventional perfusion PET template was used for PET-based spatial normalization. Regional standardized uptake values (SUV) measured by overlaying the template volume of interest (VOI) were compared to those measured with FreeSurfer-generated VOI (FSVOI).
RESULTS
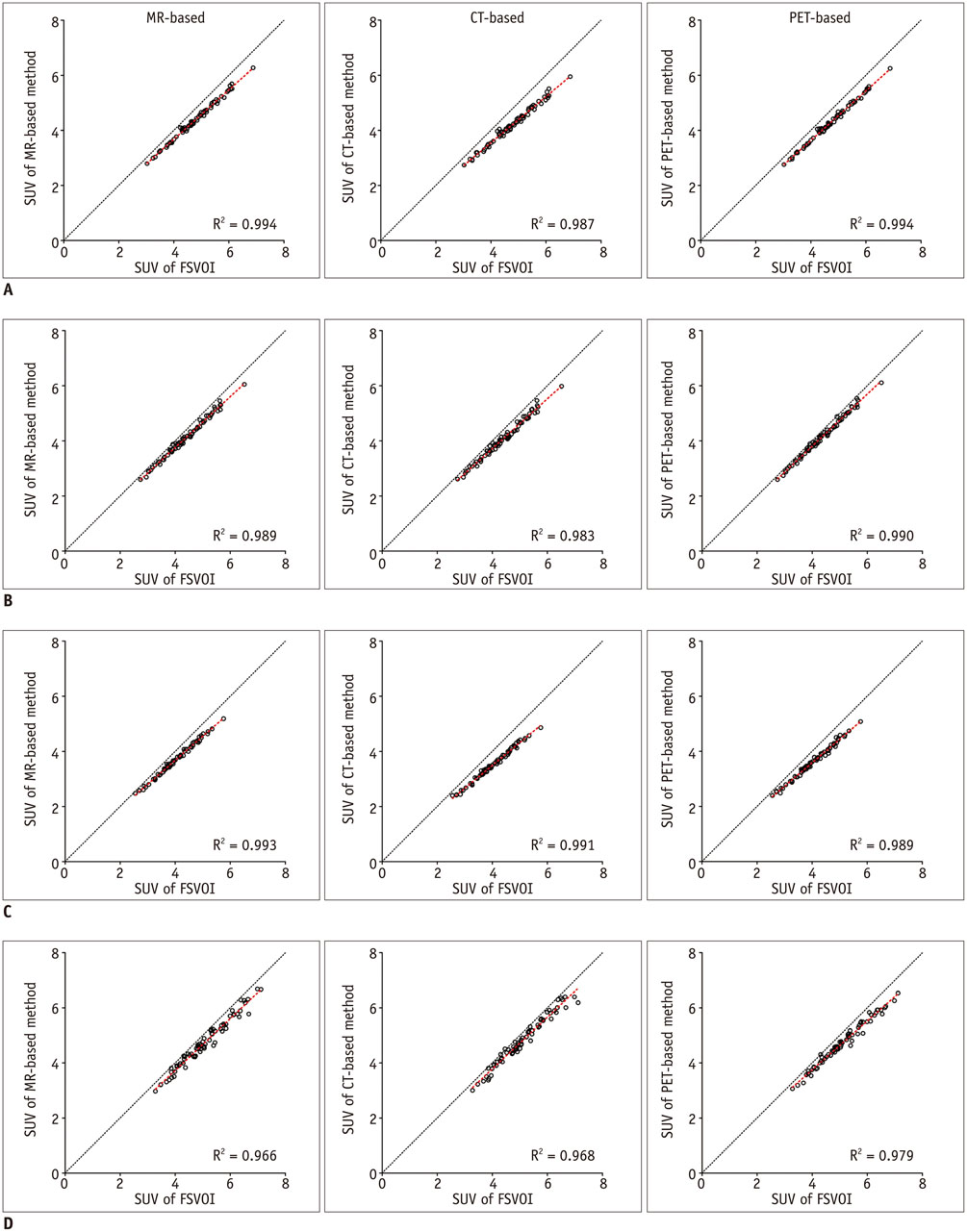
All three spatial normalization methods underestimated regional SUV values by 0.3-20% compared to those measured with FSVOI. The CT-based method showed slightly greater underestimation bias. Regional SUV values derived from all three spatial normalization methods were correlated significantly (p < 0.0001) with those measured with FSVOI.
CONCLUSION
CT-based spatial normalization may be an alternative method for structure-based spatial normalization of [18F] FDG PET when MR imaging is unavailable. Therefore, it is useful for PET/CT studies with various radiotracers whose uptake is expected to be limited to specific brain regions or highly variable within study population.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kuhn FP, Warnock GI, Burger C, Ledermann K, Martin-Soelch C, Buck A. Comparison of PET template-based and MRI-based image processing in the quantitative analysis of C11-raclopride PET. EJNMMI Res. 2014; 4:7.2. Yasuno F, Hasnine AH, Suhara T, Ichimiya T, Sudo Y, Inoue M, et al. Template-based method for multiple volumes of interest of human brain PET images. Neuroimage. 2002; 16(3 Pt 1):577–586.3. Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Nonlinear spatial normalization using basis functions. Hum Brain Mapp. 1999; 7:254–266.4. Gispert JD, Pascau J, Reig S, Martínez-Lázaro R, Molina V, García-Barreno P, et al. Influence of the normalization template on the outcome of statistical parametric mapping of PET scans. Neuroimage. 2003; 19:601–612.5. Rorden C, Bonilha L, Fridriksson J, Bender B, Karnath HO. Age-specific CT and MRI templates for spatial normalization. Neuroimage. 2012; 61:957–965.6. Solomon J, Raymont V, Braun A, Butman JA, Grafman J. User-friendly software for the analysis of brain lesions (ABLe). Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2007; 86:245–254.7. Acosta-Cabronero J, Williams GB, Pereira JM, Pengas G, Nestor PJ. The impact of skull-stripping and radio-frequency bias correction on grey-matter segmentation for voxel-based morphometry. Neuroimage. 2008; 39:1654–1665.8. Fein G, Landman B, Tran H, Barakos J, Moon K, Di Sclafani V, et al. Statistical parametric mapping of brain morphology: sensitivity is dramatically increased by using brain-extracted images as inputs. Neuroimage. 2006; 30:1187–1195.9. Fischmeister FP, Höllinger I, Klinger N, Geissler A, Wurnig MC, Matt E, et al. The benefits of skull stripping in the normalization of clinical fMRI data. Neuroimage Clin. 2013; 3:369–380.10. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975; 12:189–119.11. Desikan RS, Ségonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D, et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage. 2006; 31:968–980.12. Fischl B, van der Kouwe A, Destrieux C, Halgren E, Ségonne F, Salat DH, et al. Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2004; 14:11–22.13. Fischl B, Salat DH, Busa E, Albert M, Dieterich M, Haselgrove C, et al. Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron. 2002; 33:341–355.14. Kreisl WC, Lyoo CH, McGwier M, Snow J, Jenko KJ, Kimura N, et al. In vivo radioligand binding to translocator protein correlates with severity of Alzheimer's disease. Brain. 2013; 136(Pt 7):2228–2238.15. Thomas BA, Erlandsson K, Modat M, Thurfjell L, Vandenberghe R, Ourselin S, et al. The importance of appropriate partial volume correction for PET quantification in Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011; 38:1104–1119.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 18F-2-Deoxy-2-Fluoro-D-Glucose Positron Emission Tomography: Computed Tomography for Preoperative Staging in Gastric Cancer Patients
- Verification of the Dystonic Muscles Using 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography in a Patient with Cervical Dystonia: A case report
- Non-Malignant 18F-FDG Uptake in the Thorax by Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography Fusion Imaging
- Adult granulosa cell tumor presenting with massive ascites, elevated CA-125 level, and low 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake on positron emission tomography/computed tomography
- Oncocytic Schneiderian Papilloma Presenting as an Intensely Hypermetabolic Lesion of the Maxillary Sinus on 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/CT: A Case Report and Literature Review