J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Feb;24(1):146-151. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.146.
Protective Effects of Gabapentin on Allodynia and alpha2delta1-Subunit of Voltage-dependent Calcium Channel in Spinal Nerve-Ligated Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hyunjooahn@skku.edu
- 2Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Sungkyunkwan University, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 1794421
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.146
Abstract
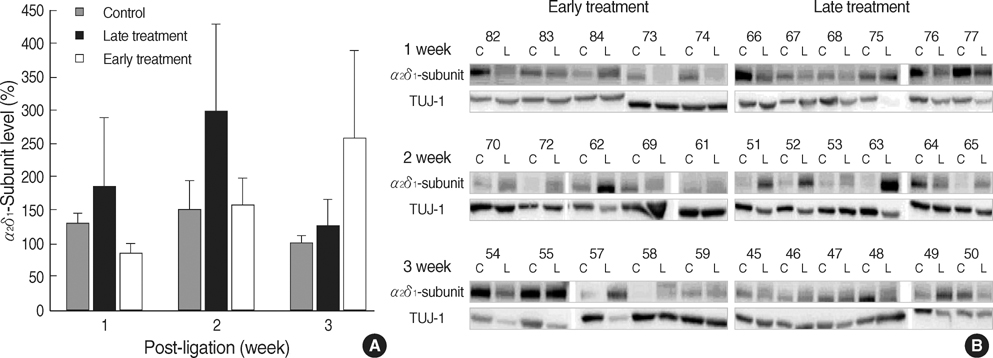
- This study was designed to determine whether early gabapentin treatment has a protective analgesic effect on neuropathic pain and compared its effect to the late treatment in a rat neuropathic model, and as the potential mechanism of protective action, the alpha2delta1-subunit of the voltage-dependent calcium channel (alpha2delta1-subunit) was evaluated in both sides of the L5 dorsal root ganglia (DRG). Neuropathic pain was induced in male Sprague-Dawley rats by a surgical ligation of left L5 nerve. For the early treatment group, rats were injected with gabapentin (100 mg/kg) intraperitoneally 15 min prior to surgery and then every 24 hr during postoperative day (POD) 1-4. For the late treatment group, the same dose of gabapentin was injected every 24 hr during POD 8-12. For the control group, L5 nerve was ligated but no gabapentin was administered. In the early treatment group, the development of allodynia was delayed up to POD 10, whereas allodynia was developed on POD 2 in the control and the late treatment group (p<0.05). The alpha2delta1-subunit was up-regulated in all groups, however, there was no difference in the level of the alpha2delta1-subunit among the three groups. These results suggest that early treatment with gabapentin offers some protection against neuropathic pain but it is unlikely that this action is mediated through modulation of the alpha2delta1-subunit in DRG.
MeSH Terms
-
Amines/administration & dosage/*therapeutic use
Analgesics/administration & dosage/*therapeutic use
Animals
Calcium Channels/genetics/*metabolism
Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acids/administration & dosage/*therapeutic use
Disease Models, Animal
Injections, Intraperitoneal
Ligation
Male
Neuralgia/*drug therapy/metabolism
Pain Measurement
Protein Subunits/genetics/metabolism
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Spinal Nerves/surgery
Up-Regulation
gamma-Aminobutyric Acid/administration & dosage/*therapeutic use
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dahl JB, Moiniche S. Pre-emptive analgesia. Br Med Bull. 2004. 71:13–27.
Article2. Bromley L. Pre-emptive analgesia and protective premedication. What is the difference? Biomed Pharmacother. 2006. 60:336–340.3. Gee NS, Brown JP, Dissanayake VU, Offord J, Thurlow R, Woodruff GN. The novel anticonvulsant drug, gabapentin (Neurontin), binds to the alpha2delta subunit of a calcium channel. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:5768–5776.4. Marais E, Klugbauer N, Hofmann F. Calcium channel alpha(2)delta subunits-structure and Gabapentin binding. Mol Pharmacol. 2001. 59:1243–1248.5. Cheng JK, Chen CC, Yang JR, Chiou LC. The antiallodynic action target of intrathecal gabapentin: Ca2+ channels, KATP channels or N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptors? Anesth Analg. 2006. 102:182–187.
Article6. Luo ZD, Chaplan SR, Higuera ES, Sorkin LS, Stauderman KA, Williams ME, Yaksh TL. Upregulation of dorsal root ganglion (alpha)2(delta) calcium channel subunit and its correlation with allodynia in spinal nerve-injured rats. J Neurosci. 2001. 21:1868–1875.7. Luo ZD, Calcutt NA, Higuera ES, Valder CR, Song YH, Svensson CI, Myers RR. Injury type-specific calcium channel alpha 2 delta-1 subunit up-regulation in rat neuropathic pain models correlates with antiallodynic effects of gabapentin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002. 303:1199–1205.8. Li CY, Song YH, Higuera ES, Luo ZD. Spinal dorsal horn calcium channel alpha2delta-1 subunit upregulation contributes to peripheral nerve injury-induced tactile allodynia. J Neurosci. 2004. 24:8494–8499.9. Xiao W, Boroujerdi A, Bennett GJ, Luo ZD. Chemotherapy-evoked painful peripheral neuropathy: analgesic effects of gabapentin and effects on expression of the alpha-2-delta type-1 calcium channel subunit. Neuroscience. 2007. 144:714–720.
Article10. Zimmermann M. Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain. 1983. 16:109–110.
Article11. Kim SH, Chung JM. An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain. 1992. 50:355–363.12. LaBuda CJ, Little PJ. Pharmacological evaluation of the selective spinal nerve ligation model of neuropathic pain in the rat. J Neurosci Methods. 2005. 144:175–181.
Article13. Hunter JC, Gogas KR, Hedley LR, Jacobson LO, Kassotakis L, Thompson J, Fontana DJ. The effect of novel anti-epileptic drugs in rat experimental models of acute and chronic pain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1997. 324:153–160.
Article14. Field MJ, Hughes J, Singh L. Further evidence for the role of the alpha(2)delta subunit of voltage dependent calcium channels in models of neuropathic pain. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. 131:282–286.15. Back SK, Won SY, Hong SK, Na HS. Gabapentin relieves mechanical, warm and cold allodynia in a rat model of peripheral neuropathy. Neurosci Lett. 2004. 368:341–344.
Article16. Dixon WJ. Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980. 20:441–462.
Article17. Chaplan SR, Pogrel JW, Yaksh TL. Role of voltage-dependent calcium channel subtypes in experimental tactile allodynia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994. 269:1117–1123.18. Rorarius MG, Mennander S, Suominen P, Rintala S, Puura A, Pirhonen R, Salmelin R, Haanpaa M, Kujansuu E, Yli-Hankala A. Gabapentin for the prevention of postoperative pain after vaginal hysterectomy. Pain. 2004. 110:175–181.
Article19. Kaneko M, Mestre C, Sanchez EH, Hammond DL. Intrathecally administered gabapentin inhibits formalin-evoked nociception and the expression of Fos-like immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000. 292:743–751.20. Coderre TJ, Kumar N, Lefebvre CD, Yu JS. Evidence that gabapentin reduces neuropathic pain by inhibiting the spinal release of glutamate. J Neurochem. 2005. 94:1131–1139.
Article21. Wallin J, Cui JG, Yakhnitsa V, Schechtmann G, Meyerson BA, Linderoth B. Gabapentin and pregabalin suppress tactile allodynia and potentiate spinal cord stimulation in a model of neuropathy. Eur J Pain. 2002. 6:261–272.
Article22. Maneuf YP, Hughes J, McKnight AT. Gabapentin inhibits the substance P-facilitated K(+)-evoked release of [(3)H]glutamate from rat caudial trigeminal nucleus slices. Pain. 2001. 93:191–196.23. Hara K, Sata T. Inhibitory effect of gabapentin on N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2007. 51:122–128.
Article24. Ng GY, Bertrand S, Sullivan R, Ethier N, Wang J, Yergey J, Belley M, Trimble L, Bateman K, Alder L, Smith A, McKernan R, Metters K, O'Neill GP, Lacaille JC, Hebert TE. Gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptors with specific heterodimer composition and postsynaptic actions in hippocampal neurons are targets of anticonvulsant gabapentin action. Mol Pharmacol. 2001. 59:144–152.25. Nemeroff CB. The role of GABA in the pathophysiology and treatment of anxiety disorders. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2003. 37:133–146.26. Dooley DJ, Donovan CM, Pugsley TA. Stimulus-dependent modulation of [(3)H]norepinephrine release from rat neocortical slices by gabapentin and pregabalin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000. 295:1086–1093.27. Freiman TM, Kukolja J, Heinemeyer J, Eckhardt K, Aranda H, Rominger A, Dooley DJ, Zentner J, Feuerstein TJ. Modulation of K+-evoked [3H]-noradrenaline release from rat and human brain slices by gabapentin: involvement of KATP channels. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001. 363:537–542.28. Mixcoatl-Zecuatl T, Medina-Santillan R, Reyes-Garcia G, Vidal-Cantu GC, Granados-Soto V. Effect of K+ channel modulators on the antiallodynic effect of gabapentin. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. 484:201–208.
Article29. Wilson JA, Garry EM, Anderson HA, Rosie R, Colvin LA, Mitchell R, Fleetwood-Walker SM. NMDA receptor antagonist treatment at the time of nerve injury prevents injury-induced changes in spinal NR1 and NR2B subunit expression and increases the sensitivity of residual pain behaviours to subsequently administered NMDA receptor antagonists. Pain. 2005. 117:421–432.
Article30. Visser E, Schug SA. The role of ketamine in pain management. Biomed Pharmacother. 2006. 60:341–348.31. Isom LL, De Jongh KS, Catterall WA. Auxiliary subunits of voltage-gated ion channels. Neuron. 1994. 12:1183–1194.
Article32. Gurnett CA, De Waard M, Campbell KP. Dual function of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel alpha 2 delta subunit in current stimulation and subunit interaction. Neuron. 1996. 16:431–440.33. Bolay H, Moskowitz MA. Mechanisms of pain modulation in chronic syndromes. Neurology. 2002. 59:5 Suppl 2. S2–S7.
Article34. Xie W, Strong JA, Meij JT, Zhang JM, Yu L. Neuropathic pain: early spontaneous afferent activity is the trigger. Pain. 2005. 116:243–256.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- NMDA Receptor Activation Mediates Neuropathic Pain States Induced by Calcium Channel alpha2delta1 Subunit
- The Expression of the Ca++ Channel alpha2delta Subunit and TRPM8 in the Dorsal Root Ganglion of Sympathetically Maintained Pain and Sympathetic Independent Pain Rat Models
- Glia Dose not Participate in Antinociceptive Effects of Gabapentin in Rats with Trigeminal Neuropathic Pain
- The Interaction of Gabapentin and N(6)-(2-phenylisopropyl)-adenosine R-(-)isomer (R-PIA) on Mechanical Allodynia in Rats with a Spinal Nerve Ligation
- Chromosomal Mapping and Brain Distribution of alpha1 Subunit of N-type Voltage Dependent Calcium Channel