J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Feb;24(1):132-137. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.132.
Proteomic Analysis of Rat Brains Following Exposure to Electroconvulsive Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, College of Medicine and Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. bjkim@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine and Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 3MRC for Neural Dysfunction, College of Medicine and Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 1794419
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.132
Abstract
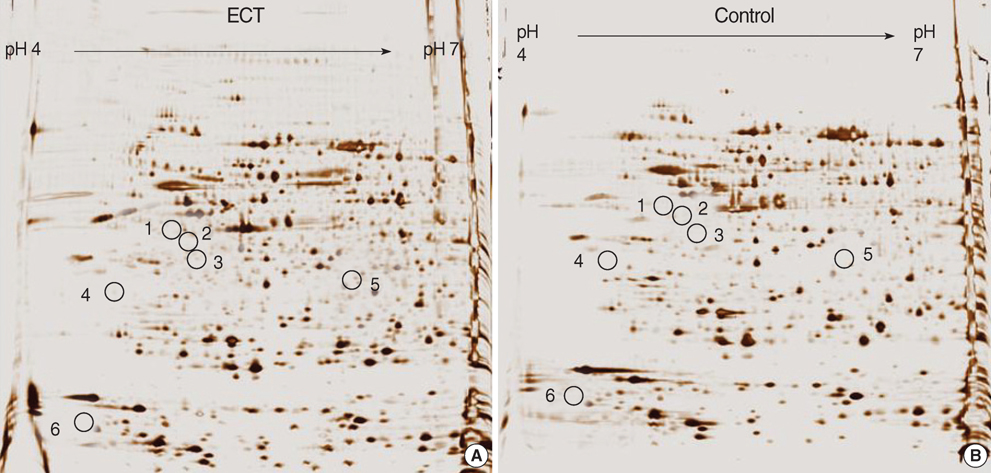
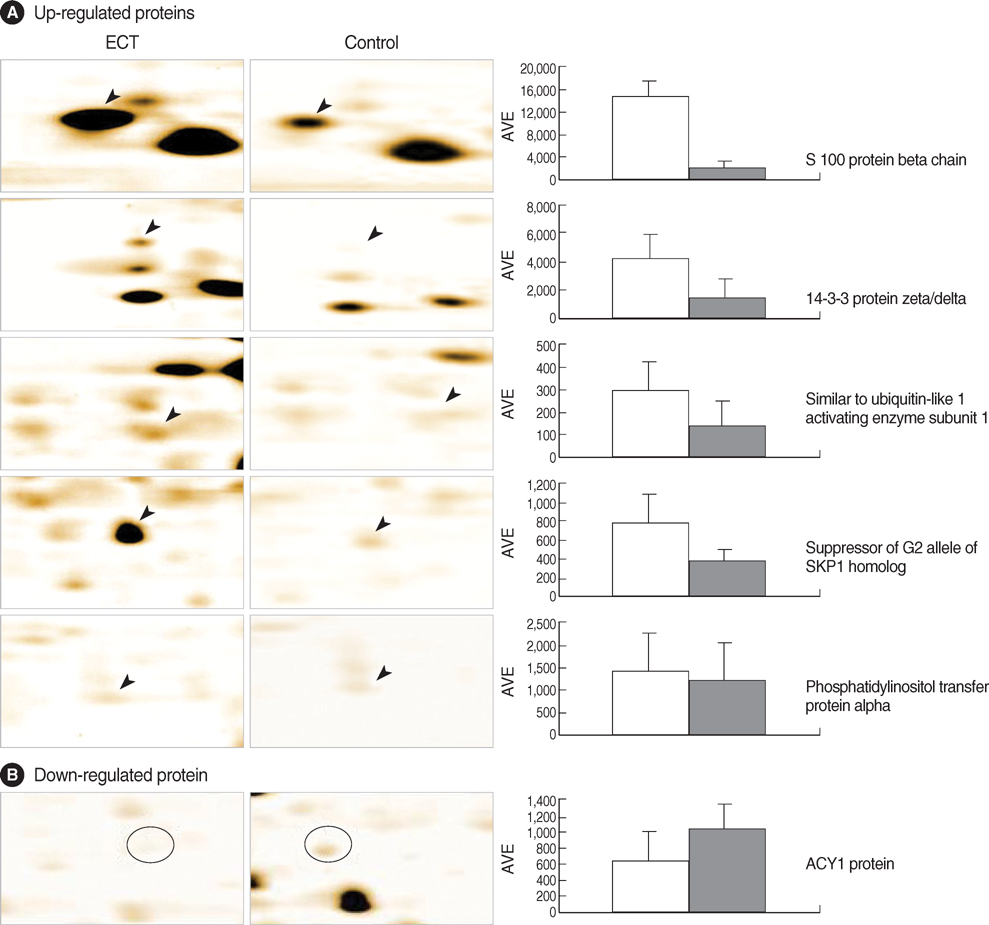
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is one of the most effective treatments used in psychiatry to date. The mechanisms of ECT action, however, are the least understood and still unclear. As a tool to elucidate the mechanisms of action of ECT, we employed proteomic analysis based on the identification of differentially expressed proteins after exposure to repeated ECT in rat brains. The expression of proteins was visualized by silver stain after two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Of 24 differentially expressed protein spots (p<0.05 by Student t-test), six different proteins from 7 spots were identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of flight (MALDI-TOF)/mass spectrometry. Among the identified proteins, there were five dominantly expressed proteins in the ECT-treated rat brain tissues (p<0.05); S100 protein beta chain, 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta, similar to ubiquitin-like 1 (sentrin) activating enzyme subunit 1, suppressor of G2 allele of SKP1 homolog, and phosphatidylinositol transfer protein alpha. The expression of only one protein, ACY1 protein, was repressed (p<0.05). These findings likely serve for a better understanding of mechanisms involved in the therapeutic effects of ECT.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shergill SS, Katona CL. Helmchen H, Henn F, Lauter H, Sartorius N, editors. Pharmacotherapy of affective disorders. Contemporary Psychiatry. 2001. 4th ed. Heidelberg: Springer;317–336.
Article2. Rohlff C. Proteomics in molecular medicine: applications in central nervous systems disorders. Electrophoresis. 2000. 21:1227–1234.
Article3. Morrison RS, Kinoshita Y, Johnson MD, Conrads TP. Proteomics in the postgenomic age. Adv Protein Chem. 2003. 65:1–23.
Article4. Moseley FL, Bicknell KA, Marber MS, Brooks G. The use of proteomics to identify novel therapeutic targets for the treatment of disease. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2007. 59:609–628.
Article5. Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976. 72:248–254.
Article6. Görg A, Weiss W, Dunn MJ. Current two-dimensional electrophoresis technology for proteomics. Proteomics. 2004. 4:3665–3685.
Article7. Hwa JS, Kim HJ, Goo BM, Park HJ, Kim CW, Chung KH, Park HC, Chang SH, Kim YW, Kim DR, Cho GJ, Choi WS, Kang KR. The expression of ketohexokinase is diminished in human clear cell type of renal cell carcinoma. Proteomics. 2006. 6:1077–1084.
Article8. Donato R. S100: a multigenic family of calcium-modulated proteins of the EF-hand type with intracellular and extracellular functional roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2001. 33:637–668.
Article9. Rothermundt M, Falkai P, Ponath G, Abel S, Burkle H, Diedrich M, Hetzel G, Peters M, Siegmund A, Pedersen A, Maier W, Schramm J, Suslow T, Ohrmann P, Arolt V. Glial cell dysfunction in schizophrenia indicated by increased S100B in the CSF. Mol Psychiatry. 2004. 9:897–899.
Article10. Busnello JV, Leke R, Oses JP, Feier G, Bruch R, Quevedo J, Kapczinski F, Souza DO, Cruz Portela LV. Acute and chronic electroconvulsive shock in rats: effects on peripheral markers of neuronal injury and glial activity. Life Sci. 2006. 78:3013–3017.
Article11. Yaffe MB, Rittinger K, Volinia S, Caron PR, Aitken A, Leffers H, Gamblin SJ, Smerdon SJ, Cantley LC. The structural basis for 14-3-3: phosphopeptide binding specificity. Cell. 1997. 91:961–971.12. Urschel S, Bassermann F, Bai RY, Munch S, Peschel C, Duyster J. Phosphorylation of Grb10 regulates its interaction with 14-3-3. J Biol Chem. 2005. 280:16987–16993.
Article13. Bell R, Munro J, Russ C, Powell JF, Bruinvels A, Kerwin RW, Collier DA. Systematic screening of the 14-3-3 eta (n) chain gene for polymorphic variants and case-control analysis in schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet. 2000. 96:736–743.14. Vawter MP, Barrett T, Cheadle C, Sokolov BP, Wood WH 3rd, Donovan DM, Webster M, Freed WJ, Becker KG. Application of cDNA microarrays to examine gene expression differences in schizophrenia. Brain Res Bull. 2001. 55:641–650.
Article15. Wong AH, Macciardi F, Klempan T, Kawczynski W, Barr CL, Lakatoo S, Wong M, Buckle C, Trakalo J, Boffa E, Oak J, Azevedo MH, Dourado A, Coelho I, Macedo A, Vicente A, Valente J, Ferreira CP, Pato MT, Pato CN, Kennedy JL, Van Tol HH. Identification of candidate genes for psychosis in rat models, and possible association between schizophrenia and the 14-3-3eta gene. Mol Psychiatry. 2003. 8:156–166.16. Middleton FA, Peng L, Lewis DA, Levitt P, Mirnics K. Altered expression of 14-3-3 genes in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005. 30:974–983.
Article17. Thomas GM, Cunningham E, Fensome A, Ball A, Totty NF, Truong O, Hsuan JJ, Cockcroft S. An essential role for phosphatidylinositol transfer protein in phospholipase C-mediated inositol lipid signaling. Cell. 1993. 74:919–928.
Article18. Kauffmann-Zeh A, Thomas GM, Ball A, Prosser S, Cunningham E, Cockcroft S, Hsuan JJ. Requirement for phosphatidylinositol transfer protein in epidermal growth factor signaling. Science. 1995. 268:1188–1190.
Article19. Baraban JM. Toward a crystal-clear view of lithium's site of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA. 1994. 91:5738–5739.
Article20. Pollack SJ, Atack JR, Knowles MR, McAllister G, Ragan CI, Baker R, Fletcher SR, Iversen LL, Broughton HB. Mechanism of inositol monophosphatase, the putative target of lithium therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA. 1994. 91:5766–5770.
Article21. Manji HK, Chen G, Hsiao JK, Risby ED, Masana MI, Potter WZ. Regulation of signal transduction pathways by mood-stabilizing agents: implications for the delayed onset of therapeutic efficacy. J Clin Psychiatry. 1996. 57:Suppl 13. 34–46.22. Giardina T, Biagini A, Massey-Harroche D, Puigserver A. Distribution and subcellular localization of acylpeptide hydrolase and acylase I along the hog gastro-intestinal tract. Biochimie. 1999. 81:1049–1055.
Article23. Lindner H, Hopfner S, Tafler-Naumann M, Miko M, Konrad L, Rohm KH. The distribution of aminoacylase I among mammalian species and localization of the enzyme in porcine kidney. Biochimie. 2000. 82:129–137.
Article24. Cook RM, Franklin WA, Moore MD, Johnson BE, Miller YE. Mutational inactivation of aminoacylase-I in a small cell lung cancer cell line. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1998. 21:320–325.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Differential changes in the expression of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoforms in rat brains by chronic treatment with electroconvulsive shock
- Anesthetic care for electroconvulsive therapy during pregnancy: A case report
- Anesthetic Management during Electroconvulsive Therapy
- A New Gene Regulated by Electroconvulsive Shock in Rat Brains
- Combined Clozapine and Electroconvulsive Therapy in a Japanese Schizophrenia Patient: A Case Report