Ann Lab Med.
2014 Jul;34(4):293-299. 10.3343/alm.2014.34.4.293.
Epidemiological Characterizations of Class 1 Integrons from Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter Isolates in Daejeon, Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Far East University, Eumseong, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. shkoo@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1791937
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2014.34.4.293
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Multidrug-resistant (MDR) Acinetobacter spp. acquire antimicrobial agent-resistance genes via class 1 integrons. In this study, integrons were characterized to investigate the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of MDR Acinetobacter isolates. In addition, the relationship between the integron type and integron-harboring bacterial species was analyzed by using epidemiological typing methods.
METHODS
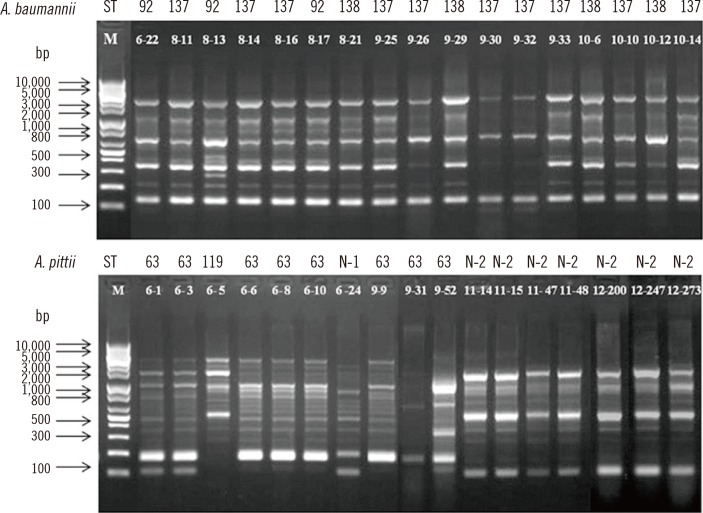
Fifty-six MDR Acinetobacter spp.-A. baumannii (N=30), A. bereziniae (N=4), A. nosocomialis (N=5), and A. pittii (N=17)-were isolated. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined on the basis of the results of the Epsilometer test (Etest). PCR and DNA sequencing was performed to characterize the gene cassette arrays of class 1 integrons. Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) and repetitive extragenic palindromic sequence (REP)-PCR were performed for epidemiological typing.
RESULTS
Class 1 integrons were detected in 50 (89.3%) of the 56 isolates, but no class 2 or 3 integron was found within the cohorts. The class 1 integrons were classified into 4 types: 2.3-kb type A (aacA4-catB8-aadA1), 3.0-kb type B (aacA4-blaI(MP-1)-bla(OXA-2)), 3.0-kb type C (bla(VIM-2)-aacA7-aadA1), and 1.8-kb type D (aac3-1-bla(OXA-2)-orfD). Type A was most prevalent and was detected only in A. baumannii isolates, except for one A. bereziniae isolate; however, type B was amplified in all Acinetobacter isolates except for A. baumannii isolates, regardless of clone and separation time of the bacteria.
CONCLUSIONS
Although class 1 integron can be transferred horizontally between unrelated isolates belonging to different species, certain types of class 1 integrons tend to transfer horizontally and vertically among A. baumannii or non-baumannii Acinetobacter isolates.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acinetobacter/drug effects/isolation & purification/*metabolism
Acinetobacter Infections/epidemiology/microbiology
Acinetobacter baumannii/drug effects/isolation & purification/metabolism
Anti-Bacterial Agents/pharmacology
DNA, Bacterial/chemistry/metabolism
Drug Resistance, Multiple, Bacterial
Humans
Integrons/*genetics
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
Multilocus Sequence Typing
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Republic of Korea
Anti-Bacterial Agents
DNA, Bacterial
Figure
Reference
-
1. Maragakis LL, Perl TM. Acinetobacter baumannii: epidemiology, antimicrobial resistance, and treatment options. Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 46:1254–1263. PMID: 18444865.2. Navon-Venezia S, Ben-Ami R, Carmeli Y. Update on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii infections in the healthcare setting. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2005; 18:306–313. PMID: 15985826.3. Cisneros JM, Reyes MJ, Pachón J, Becerril B, Caballero FJ, García-Garmendía JL, et al. Bacteremia due to Acinetobacter baumannii: epidemiology, clinical findings, and prognostic features. Clin Infect Dis. 1996; 22:1026–1032. PMID: 8783704.4. Sung JY, Kwon KC, Cho HH, Koo SH. Antimicrobial resistance determinants in imipenem-nonsusceptible Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-baumannii complex isolated in Daejeon, Korea. Korean J Lab Med. 2011; 31:265–270. PMID: 22016680.5. Esterly JS, Griffith M, Qi C, Malczynski M, Postelnick MJ, Scheetz MH. Impact of carbapenem resistance and receipt of active antimicrobial therapy on clinical outcomes of Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011; 55:4844–4849. PMID: 21825287.6. Ko WC, Lee NY, Su SC, Dijkshoorn L, Vaneechoutte M, Wang LR, et al. Oligonucleotide array-based identification of species in the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-A. baumannii complex in isolates from blood cultures and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of the isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2008; 46:2052–2059. PMID: 18385442.7. van den Broek PJ, van der Reijden TJ, van Strijen E, Helmig-Schurter AV, Bernards AT, Dijkshoorn L. Endemic and epidemic acinetobacter species in a university hospital: an 8-year survey. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:3593–3599. PMID: 19794057.8. Gootz TD, Marra A. Acinetobacter baumannii: an emerging multidrug-resistant threat. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008; 6:309–325. PMID: 18588496.9. Machado E, Coque TM, Cantón R, Sousa JC, Peixe L. Antibiotic resistance integrons and extended-spectrum β-lactamases among Enterobacteriaceae isolates recovered from chickens and swine in Portugal. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008; 62:296–302. PMID: 18456652.
Article10. Cambray G, Guerout AM, Mazel D. Integrons. Annu Rev Genet. 2010; 44:141–166. PMID: 20707672.11. Da Silva GJ, Correia M, Vital C, Ribeiro G, Sousa JC, Leitão R, et al. Molecular characterization of blaIMP-5, a new integron-borne metallo-β-lactamase gene from an Acinetobacter baumannii nosocomial isolate in Portugal. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002; 215:33–39. PMID: 12393197.12. Gombac F, Riccio ML, Rossolini GM, Lagatolla C, Tonin E, Monti-Bragadin C, et al. Molecular characterization of integrons in epidemiologically unrelated clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii from Italian hospitals reveals a limited diversity of gene cassette arrays. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002; 46:3665–3668. PMID: 12384388.13. Nemec A, Dolzani L, Brisse S, van den Broek P, Dijkshoorn L. Diversity of aminoglycoside-resistance genes and their association with class 1 integrons among strains of pan-European Acinetobacter baumannii clones. J Med Microbiol. 2004; 53:1233–1240. PMID: 15585503.14. Mazel D. Integrons: agents of bacterial evolution. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2006; 4:608–620. PMID: 16845431.
Article15. Cho YJ, Moon DC, Jin JS, Choi CH, Lee YC, Lee JC. Genetic basis of resistance to aminoglycosides in Acinetobacter spp. and spread of armA in Acinetobacter baumannii sequence group 1 in Korean hospitals. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009; 64:185–190. PMID: 19361944.16. Srinivasan VB, Rajamohan G, Pancholi P, Stevenson K, Tadesse D, Patchanee P, et al. Genetic relatedness and molecular characterization of multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolated in central Ohio, USA. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2009; 8:21. PMID: 19531268.
Article17. Gundi VA, Dijkshoorn L, Burignat S, Raoult D, La Scola B. Validation of partial rpoB gene sequence analysis for the identification of clinically important and emerging Acinetobacter species. Microbiology. 2009; 155:2333–2341. PMID: 19389786.18. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Twentieth Informational supplement, M100-S20. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2010.19. Dillon B, Thomas L, Mohmand G, Zelynski A, Iredell J. Multiplex PCR for screening of integrons in bacterial lysates. J Microbiol Methods. 2005; 62:221–232. PMID: 16009279.
Article20. White PA, McIver CJ, Rawlinson WD. Integrons and gene cassettes in the enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001; 45:2658–2661. PMID: 11502548.21. Diancourt L, Passet V, Nemec A, Dijkshoorn L, Brisse S. The population structure of Acinetobacter baumannii: expanding multiresistant clones from an ancestral susceptible genetic pool. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e10034. PMID: 20383326.22. Bartual SG, Seifert H, Hippler C, Luzon MA, Wisplinghoff H, Rodríguez-Valera F. Development of a multilocus sequence typing scheme for characterization of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:4382–4390. PMID: 16145081.23. Bou G, Cerveró G, Domínguez MA, Quereda C, Martínez-Beltrán J. PCR-based DNA fingerprinting (REP-PCR, AP-PCR) and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis characterization of a nosocomial outbreak caused by imipenem- and meropenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2000; 6:635–643. PMID: 11284921.24. Wu K, Wang F, Sun J, Wang Q, Chen Q, Yu S, et al. Class 1 integron gene cassettes in multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in southern China. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012; 40:264–267. PMID: 22817917.
Article25. Golanbar GD, Lam CK, Chu YM, Cueva C, Tan SW, Silva I, et al. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of Acinetobacter clinical isolates obtained from inmates of California correctional facilities. J Clin Microbiol. 2011; 49:2121–2131. PMID: 21450955.26. Turton JF, Kaufmann ME, Glover J, Coelho JM, Warner M, Pike R, et al. Detection and typing of integrons in epidemic strains of Acinetobacter baumannii found in the United Kingdom. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:3074–3082. PMID: 16000417.27. Lin YC, Sheng WH, Chen YC, Chang SC, Hsia KC, Li SY. Differences in carbapenem resistance genes among Acinetobacter baumannii, Acinetobacter genospecies 3 and Acinetobacter genospecies 13TU in Taiwan. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2010; 35:439–443. PMID: 20106635.28. Park YK, Jung SI, Park KH, Kim SH, Ko KS. Characteristics of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter spp. other than Acinetobacter baumannii in South Korea. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012; 39:81–85. PMID: 21996405.29. Higgins PG, Janssen K, Fresen MM, Wisplinghoff H, Seifert H. Molecular epidemiology of Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream isolates obtained in the United States from 1995 to 2004 using rep-PCR and multilocus sequence typing. J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 50:3493–3500. PMID: 22895032.30. Park S, Kim HS, Lee KM, Yoo JS, Yoo JI, Lee YS, et al. Molecular and epidemiological characterization of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in non-tertiary Korean hospitals. Yonsei Med J. 2013; 54:177–182. PMID: 23225816.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Integron Carriage in Multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains
- High Prevalence of Class 1 to 3 Integrons Among Multidrug-Resistant Diarrheagenic
Escherichia coli in Southwest of Iran - Antimicrobial Resistance and Integrons Found in Commensal Escherichia coli Isolates from Healthy Humans
- Genetic Basis of Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates from Three University Hospitals in Chungcheong Province, Korea
- Detection of Integrons and Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec Types in Clinical Methicillin-resistant Coagulase Negative Staphylococci Strains