Ann Lab Med.
2014 Mar;34(2):177-179. 10.3343/alm.2014.34.2.177.
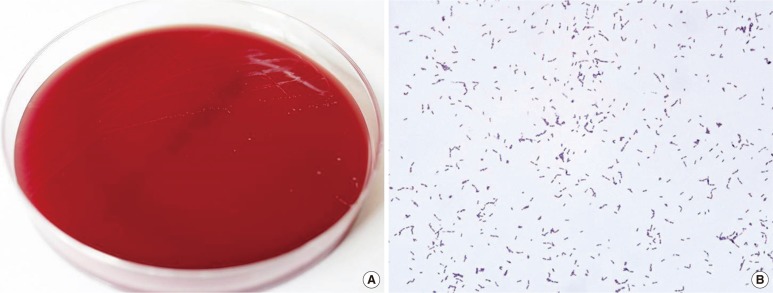
The First Case of Eggerthella lenta Bacteremia in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. trust99@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1791917
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2014.34.2.177
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Bacteremia Caused by Eggerthella lenta in an Elderly Patient with an Intra-abdominal Abscess
Ki-Won Eom, Sollip Kim, Tae Hyun Um, Chong Rae Cho
Lab Med Online. 2016;6(2):106-110. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2016.6.2.106.
Reference
-
1. Kageyama A, Benno Y, Nakase T. Phylogenetic evidence for the transfer of Eubacterium lentum to the genus Eggerthella as Eggerthella lenta gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1999; 49:1725–1732. PMID: 10555354.2. Eggerth AH. The gram-positive non-spore-bearing anaerobic bacilli of human feces. J Bacteriol. 1935; 30:277–299. PMID: 16559837.
Article3. Würdemann D, Tindall BJ, Pukall R, Lünsdorf H, Strömpl C, Namuth T. Gordonibacterpamelaeae gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the Coriobacteriaceae isolated from a patient with Crohn's disease, and reclassification of Eggerthella hongkongensis Lau et al. 2006 as Paraeggerthella hongkongensis gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2009; 59:1405–1415. PMID: 19502325.4. Bok CW, Ng YS. Eggerthella lenta as a cause of anaerobic spondylodiscitis. Singapore Med J. 2009; 50:e393–e396. PMID: 20087537.5. Lattuada E, Zorzi A, Lanzafame M, Antolini D, Fontana R, Vento S, et al. Cutaneous abscess due to Eubacterium lentum in injection drug user: a case report and review of the literature. J Infect. 2005; 51:E71–E72. PMID: 16038756.6. Rautio M, Saxén H, Siitonen A, Nikku R, Jousimies-Somer H. Bacteriology of histopathologically defined appendicitis in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000; 19:1078–1083. PMID: 11099090.
Article7. Brook I, Frazier EH. Significant recovery of nonsporulating anaerobic rods from clinical specimens. Clin Infect Dis. 1993; 16:476–480. PMID: 8513050.
Article8. Chan RC, Mercer J. First Australian description of Eggerthellalenta bacteraemia identified by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Pathology. 2008; 40:409–410. PMID: 18446634.9. Landais C, Doudier B, Imbert G, Fenollar F, Brouqui P. Application of rrs gene sequencing to elucidate the clinical significance of Eggerthelalenta infection. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:1063–1065. PMID: 17229865.10. Lau SK, Woo PC, Woo GK, Fung AM, Wong MK, Chan KM. Eggerthella hongkongensis sp. nov. and eggerthella sinensis sp. nov., two novel Eggerthella species, account for half of the cases of Eggerthella bacteremia. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2004; 49:255–263. PMID: 15313530.11. Liderot K, Larsson M, Boräng S, Ozenci V. Polymicrobial bloodstream infection with Eggerthella lenta and Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:3810–3812. PMID: 20720029.12. Lee MR, Huang YT, Liao CH, Chuang TY, Wang WJ, Lee SW, et al. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of bacteremia caused by Eggerthella, Paraeggerthella, and Eubacterium species at a university hospital in Taiwan from 2001 to 2010. J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 50:2053–2055. PMID: 22495556.13. Venugopal AA, Szpunar S, Johnson LB. Risk and prognostic factors among patients with bacteremia due to Eggerthella lenta. Anaerobe. 2012; 18:475–478. PMID: 22677263.14. Moore WE, Cato EP, Holdeman LV. Eubacteriumlentum (Eggerth) Prévot 1938: emendation of description and designation of the neotype strain. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1971; 21:299–303.15. Jang JH, Kim SJ. Anaerobic bacterial isolation in patients with chronic prostatitis syndrome. Korean J Urol. 1994; 35:640–645.16. Thota VR, Dacha S, Natarajan A, Nerad J. Eggerthella lenta bacteremia in a Crohn's disease patient after ileocecal resection. Future Microbiol. 2011; 6:595–597. PMID: 21585265.17. Justesen US, Holm A, Knudsen E, Andersen LB, Jensen TG, Kemp M, et al. Species identification of clinical isolates of anaerobic bacteria: a comparison of two matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry systems. J Clin Microbiol. 2011; 49:4314–4318. PMID: 21998433.
Article18. Coltella L, Mancinelli L, Onori M, Lucignano B, Menichella D, Sorge R, et al. Advancement in the routine identification of anaerobic bacteria by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013; 32:1183–1192. PMID: 23584672.
Article19. Barreau M, Pagnier I, La Scola B. Improving the identification of anaerobes in the clinical microbiology laboratory through MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Anaerobe. 2013; 22:123–125. PMID: 23639482.
Article20. Mosca A, Summanen P, Finegold SM, De Michele G, Miragliotta G. Cellular fatty acid composition, soluble-protein profile, and antimicrobial resistance pattern of Eubacterium lentum. J Clin Microbiol. 1998; 36:752–755. PMID: 9508307.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Eggerthella Lenta Bacteremia after Appendectomy in a Healthy Patient
- Bacteremia Caused by Eggerthella lenta in an Elderly Patient with an Intra-abdominal Abscess
- Eggerthella lenta Bacteremia after Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in an End-Stage Renal Disease Patient
- Rapidly Progressive Malignant Pelvic Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Neoplasm (PEComa) Associated with Eggerthella lenta Bloodstream Infection
- A Case of Shigella sonnei Bacteremia in an Adult