J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Sep;25(9):1359-1363. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.9.1359.
Motor Unit Number Estimation in Evaluating Disease Progression in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kwoo@plaza.snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Neurology, Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1785917
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.9.1359
Abstract
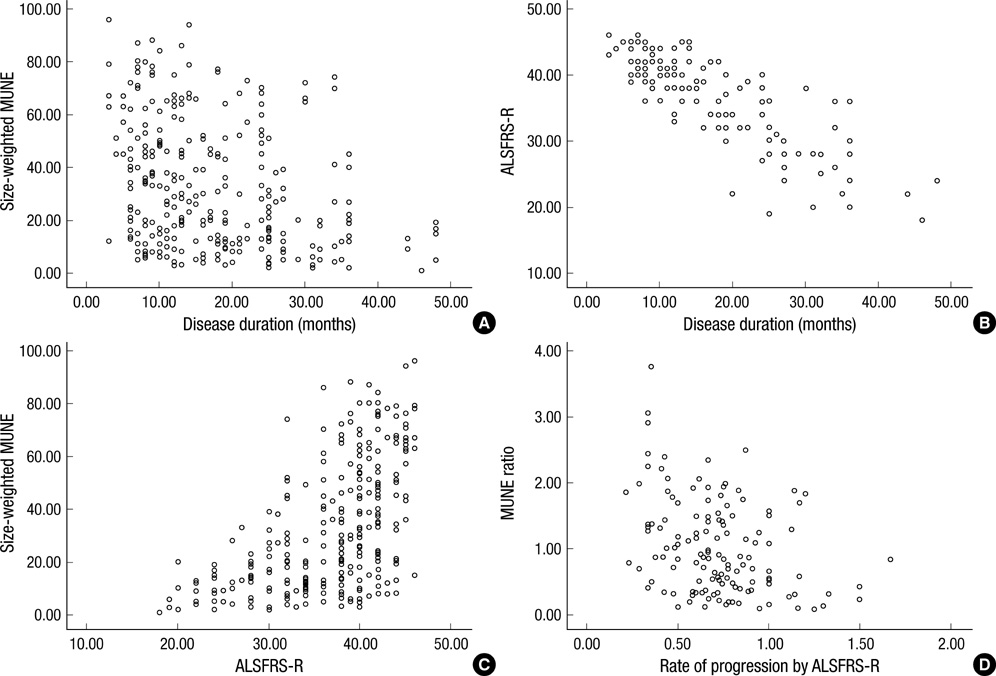
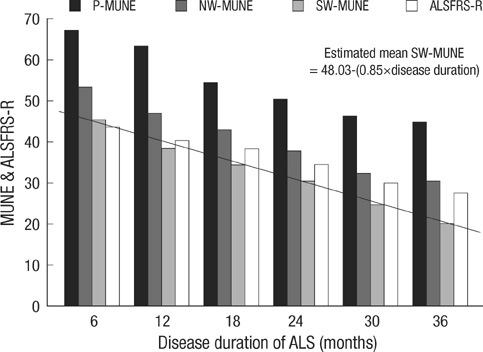
- We investigated the availability of motor unit number estimation (MUNE) as a quantitative method to assess the severity and clinical progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The 143 ALS patients were evaluated by statistical MUNE and the revised amyotrophic lateral sclerosis functional rating scale (ALSFRS-R). By using mean values of MUNE according to disease duration, regression equation between mean MUNE and disease duration was presented as a formula. The individual MUNE ratio was calculated by dividing individual MUNE value by mean MUNE value. All patients were classified into 2 groups (MUNE ratio <1 vs. MUNE ratio > or =1) according to the MUNE ratio. Comparison between the 2 groups revealed that the patients in MUNE ratio <1 group or MUNE ratio > or =1 group were respectively assigned to rapid progression or slow progression. We recommended informative mean values of MUNE and best regression equation in ALS patients according to disease duration. These values allow us to evaluate the severity and rapidity of progression in ALS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Diagnosis and management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Je-Young Shin, Kwang-Woo Lee
J Korean Med Assoc. 2015;58(2):131-138. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2015.58.2.131.
Reference
-
1. Del Aguila MA, Longstreth WT Jr, McGuire V, Koepsell TD, van Belle G. Prognosis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a population-based study. Neurology. 2003. 60:813–819.
Article2. Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL. World Federation of Neurology Research Group on Motor Neuron Diseases. El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2000. 1:293–299.
Article3. Armon C, Brandstater ME. Motor unit number estimate-based rates of progression of ALS predict patient survival. Muscle Nerve. 1999. 22:1571–1575.
Article4. Sartucci F, Maritato P, Moscato G, Orlandi G, Calabrese R, Domenici GL, Murri L. Motor unit number estimation (mune) as a quantitative measure of disease progression and motor unit reorganization in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Int J Neurosci. 2007. 117:1229–1236.
Article5. Bromberg MB. Updating motor unit number estimation (MUNE). Clin Neurophysiol. 2007. 118:1–8.
Article6. Daube J. Estimating the number of motor units in a muscle. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1995. 12:585–594.
Article7. Gooch CL, Shefner JM. ALS surrogate markers. MUNE. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2004. 5:Suppl 1. 104–107.8. Lomen-Hoerth C, Slawnych MP. Statistical motor unit number estimation: from theory to practice. Muscle Nerve. 2003. 28:263–272.
Article9. Shefner JM, Cudkowicz ME, Zhang H, Schoenfeld D, Jillapalli D. Northeast ALS Consortium. The use of statistical MUNE in a multicenter clinical trial. Muscle Nerve. 2004. 30:463–469.
Article10. Boe SG, Stashuk DW, Doherty TJ. Motor unit number estimates and quantitative motor unit analysis in healthy subjects and patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve. 2007. 36:62–70.
Article11. Kwon O, Lee KW. Reproducibility of statistical motor unit number estimates in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: comparisons between size- and number-weighted modifications. Muscle Nerve. 2004. 29:211–217.
Article12. Olney RK, Yuen EC, Engstrom JW. Statistical motor unit number estimation: reproducibility and sources of error in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve. 2000. 23:193–197.
Article13. Shefner JM. Motor unit number estimation in human neurological diseases and animal models. Clin Neurophysiol. 2001. 112:955–964.
Article14. Hong YH, Sung JJ, Park KS, Kwon O, Min JH, Lee KW. Statistical MUNE: a comparison of two methods of setting recording windows in healthy subjects and ALS patients. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007. 118:2605–2611.
Article15. Cedarbaum JM, Stambler N, Malta E, Fuller C, Hilt D, Thurmond B, Nakanishi A. BDNF ALS Study Group (Phase III). The ALSFRS-R: a revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. J Neurol Sci. 1999. 169:13–21.
Article16. Ellis CM, Simmons A, Andrews C, Dawson JM, Williams SC, Leigh PN. A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic study in ALS: correlation with clinical findings. Neurology. 1998. 51:1104–1109.17. Kim W, Kim JS, Lee KS, Gwoun YJ, Kim JM, Lee KH. Anticipation and phenotypic heterogeneity in Korean familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with superoxide dismutase 1 gene mutation. J Clin Neurol. 2007. 3:38–44.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Apraxia of Eyelid Closure and Motor Impersistence of Eyelid in a Patient with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Syndrome of Progressive Bulbar Palsy in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Case Report
- Update of Therapeutic Clinical Trials for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Diagnosis and management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Evolving Diagnostic Criteria in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Its Differential Diagnosis