J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Aug;23(4):667-673. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.4.667.
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p27(Kip1) Controls Growth and Cell Cycle Progression in Human Uterine Leiomyoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Keimyung University, School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. c0035@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Keimyung University, School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Oncology, Lombardi Cancer Center, Georgetown University, USA.
- KMID: 1785827
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.4.667
Abstract
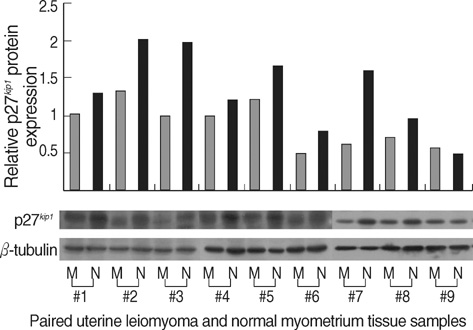
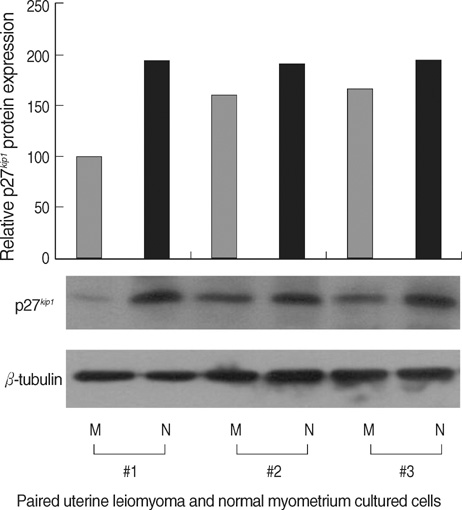
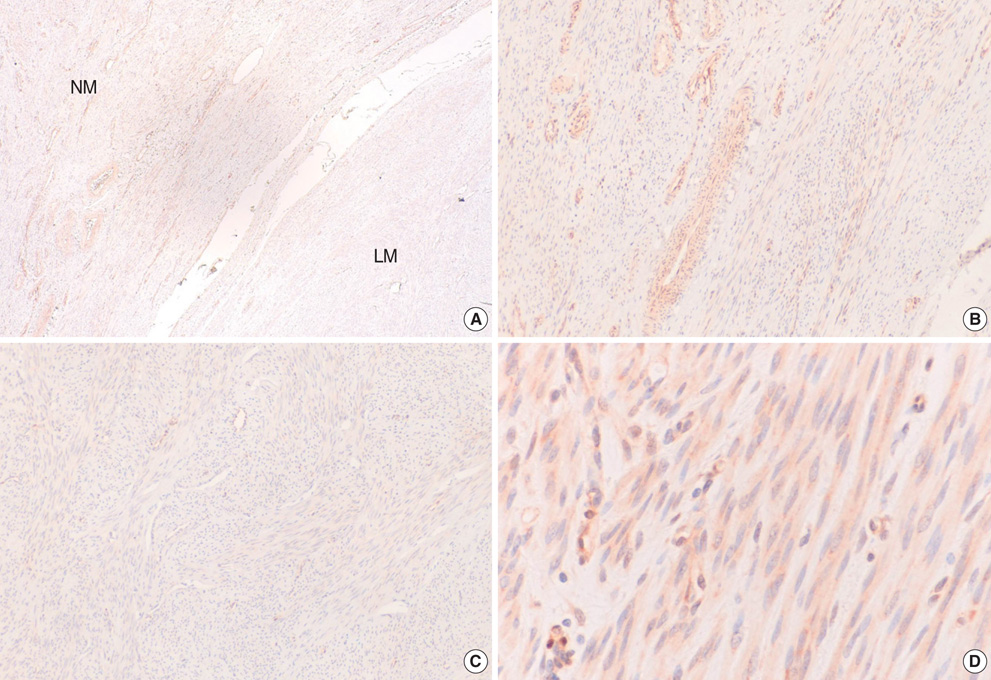
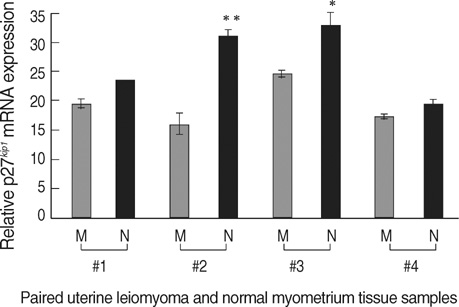
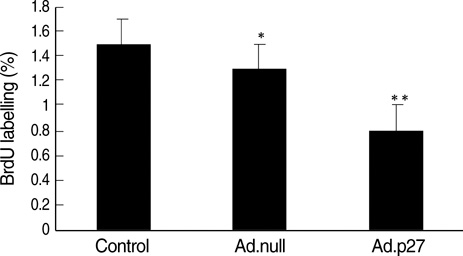
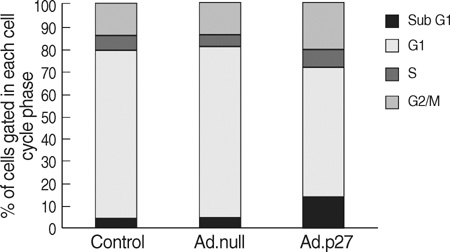
- The molecular mechanism of the cell-cycle machinery in uterine leiomyoma has not yet been fully elucidated. Among the various types of cell-cycle regulators, p27(Kip1)(p27) is considered to be a potent tumor suppressor. To provide further molecular basis for understanding the progression of uterine leiomyoma, our objective was to evaluate the expression level of p27 in normal myometrium and uterine leiomyoma tissue and its effect on cytogenic growth. Western blot analysis, real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and immunohistochemical staining revealed that p27 protein and messenger RNA were down-regulated in uterine leiomyoma tissue and cultured cells compared to normal myometerium. Full-length human p27 cDNA was transferred using a replication-deficient recombinant adenoviral vector (Ad.p27) into uterine leiomyoma cells and evaluated the effect on cell proliferation. Transfection of Ad.p27 into uterine leiomyoma cells resulted in the induction of apoptosis, reduction in viability and proliferation of uterine leiomyoma cells. Our results suggest a new paradigm that down-regulated p27 protein expression is the possible underlying mechanism for the growth of uterine leiomyoma and over-expression of p27 induces cell death. This study provides better understanding of the control exerted by p27 in regulating growth and disease progression of uterine leiomyoma.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Buttram VC, Reiter RC. Uterine leiomyomata: etiology, symptomatology, and management. Fertil Steril. 1981. 36:433–445.2. Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999. 13:1501–1512.
Article3. Tchernev G, Orfanos CE. Downregulation of cell cycle modulators p21, p27, p53, Rb and proapoptotic Bcl-2-related proteins Bax and Bak in cutaneous melanoma is associated with worse patient prognosis: preliminary findings. J Cutan Pathol. 2007. 34:247–256.
Article4. Matsuda Y, Ichida T. p16 and p27 are functionally correlated during the progress of hepatocarcinogenesis. Med Mol Morphol. 2006. 39:169–175.
Article5. Shariat SF, Ashfaq R, Sagalowsky AI, Lotan Y. Predictive value of cell cycle biomarkers in nonmuscle invasive bladder transitional cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2007. 177:481–487.
Article6. Saltman B, Singh B, Hedvat CV, Wreesmann VB, Ghossein R. Patterns of expression of cell cycle/apoptosis genes along the spectrum of thyroid carcinoma progression. Surgery. 2006. 140:899–905.
Article7. Tan P, Cady B, Wanner M, Worland P, Cukor B, Magi-Galluzzi C, Lavin P, Draetta G, Pagano M, Loda M. The cell cycle inhibitor p27 is an independent prognostic marker in small (T1a,b) invasive breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1997. 57:1259–1263.8. Tsihlias J, Kapusta LR, DeBoer G, Morava-Protzner I, Zbieranowski I, Bhattacharya N, Catzavelos GC, Klotz LH, Slingerland JM. Loss of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 is a novel prognostic factor in localized human prostate adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1998. 58:542–548.9. Lahav-Baratz S, Ben-Izhak O, Sabo E, Ben-Eliezer S, Lavie O, Ishai D, Ciechanover A, Dirnfeld M. Decreased level of the cell cycle regulator p27 and increased level of its ubiquitin ligase Skp2 in endometrial carcinoma but not in normal secretory or in hyperstimulated endometrium. Mol Hum Reprod. 2004. 10:567–572.
Article10. Tong W, Pollard JW. Progesterone inhibits estrogen-induced cyclin D1 and cdk4 nuclear translocation, cyclin E- and cyclin A-cdk2 kinase activation, and cell proliferation in uterine epithelial cells in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. 19:2251–2264.
Article11. Shiozawa T, Horiuchi A, Kato K, Obinata M, Konishi I, Fujii S, Nikaido T. Up-regulation of p27Kip1 by progestins is involved in the growth suppression of the normal and malignant human endometrial glandular cells. Endocrinology. 2001. 142:4182–4188.
Article12. Slingerland J, Pagano M. Regulation of the cdk inhibitor p27 and its deregulation in cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2000. 183:10–17.
Article13. Dobashi Y, Noguchi T, Nasuno S, Katayama K, Kameya T. CDK-inhibitors-associated kinase activity: a possible determinant of malignant potential in smooth muscle tumors of the external soft tissue. Int J Cancer. 2001. 94:353–362.
Article14. Leiser AL, Anderson SE, Nonaka D, Chuai S, Olshen AB, Chi DS, Soslow RA. Apoptotic and cell cycle regulatory markers in uterine leiomyosarcoma. Gynecol Oncol. 2006. 101:86–91.
Article15. Luo X, Ding L, Xu J, Chegini N. Gene expression profiling of leiomyoma and myometrial smooth muscle cells in response to transforming growth factor-beta. Endocrinology. 2005. 146:1097–1118.16. Liu S, Bishop WR, Liu M. Differential effects of cell cycle regulatory protein p21 (WAF1/Cip1) on apoptosis and sensitivity to cancer chemotherapy. Drug Resist Updat. 2003. 6:183–195.17. Park KH, Seol JY, Yoo CG, Kim YW, Han SK, Lee EH, Kim CM, Shim YS, Lee CT. Adenovirus expressing p27Kip1 induces growth arrest of lung cancer cell lines and suppresses the growth of established lung cancer xenografts. Lung Cancer. 2001. 31:149–155.18. Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 1995. 9:1149–1163.19. Fredersdorf S, Burns J, Milne AM, Packham G, Fallis L, Gillett CE, Royds JA, Peston D, Hall PA, Hanby AM, Barnes DM, Shousha S, O'Hare MJ, Lu X. High level expression of p27Kip1 and cyclin D1 in some human breast cancer cells: inverse correlation between the expression of p27Kip1 and degree of malignancy in human breast and colorectal cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997. 94:6380–6385.
Article20. Ciaparrone M, Yamamoto H, Yao Y, Sgambato A, Cattoretti G, Tomita N, Monden T, Rotterdam H, Weinstein IB. Localization and expression of p27Kip1 in multistage colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1998. 58:114–122.21. Singh SP, Lipman J, Goldman H, Ellis FH Jr, Aizenman L, Cangi MG, Signoretti S, Chiaur DS, Pagano M, Loda M. Loss or altered subcellular localization of p27 in Barrett's associated adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1998. 58:1730–1735.22. Chen TP, Chen CM, Chang HW, Wang JS, Chang WC, Hsu SI, Cho CL. Increased expression of SKP2 and phospho-MAPK/ERK1/2 and decreased expression of p27 during tumor progression of cervical neoplasms. Gynecol Oncol. 2007. 104:516–523.
Article23. Pateras IS, Apostolopoulou K, Koutsami M, Evangelou K, Tsantoulis P, Liloglou T, Nikolaidis G, Sigala F, Kittas C, Field JK, Kotsinas A, Gorgoulis VG. Downregulation of the KIP family members p27 (KIP1) and p57 (KIP2) by SKP2 and the role of methylation in p57 (KIP2) inactivation in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2006. 119:2546–2556.24. Dvorackova J, Uvirova M. A molecularly genetic determination of prognostic factors of the prostate cancer and their relationships to expression of protein p27kip1. Neoplasma. 2007. 54:149–154.25. Akiyama T, Ohuchi T, Sumida S, Matsumoto K, Toyoshima K. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein by cdk2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992. 89:7900–7904.
Article26. Weinberg RA. Tumor suppressor genes. Science. 1991. 254:1138–1146.
Article27. Hong FD, Chen J, Donovan S, Schneider N, Nisen PD. Taxol, vincristine or nocodazole induces lethality in G1-checkpoint-defective human astrocytoma U373MG cells by triggering hyperploid progression. Carcinogenesis. 1999. 20:1161–1168.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- MicroRNA-186 targets SKP2 to induce p27(Kip1)-mediated pituitary tumor cell cycle deregulation and modulate cell proliferation
- The Relevance of Women's Diseases, Jun Activation-domain Binding Protein 1 (JAB1) and p27(kip1)
- The function of p27(KIP1) during tumor development
- Prognostic Implications of Cyclin B1, p34cdc2, p27(Kip1) and p53 Expression in Gastric Cancer
- p27(Kip1) and Ki-67 Expression in Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma