PHEX Gene Mutations and Genotype-Phenotype Analysis of Korean Patients with Hypophosphatemic Rickets
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Rare Diseases Institute, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. jungsc@ewha.ac.kr
- 3Clinical Research Institute, Labgenomics Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Biomedical and Analytical Chemistry, College of Pharmacy, Duksung Women s University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1785757
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.6.981
Abstract
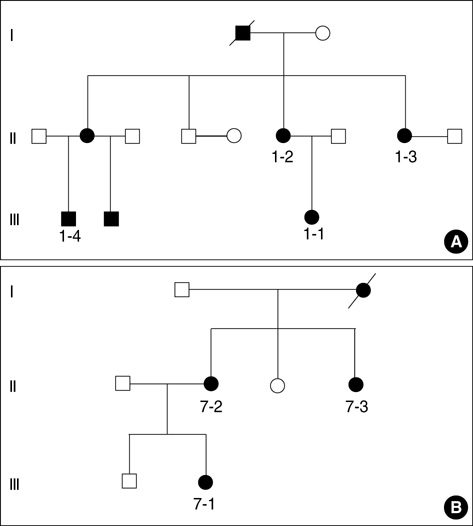
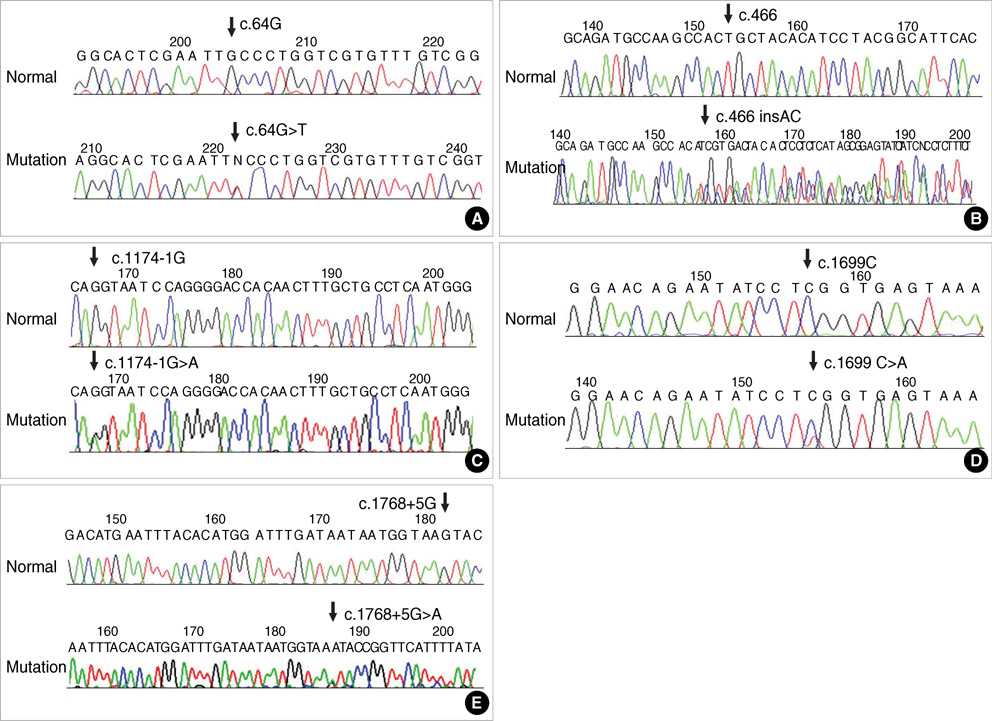
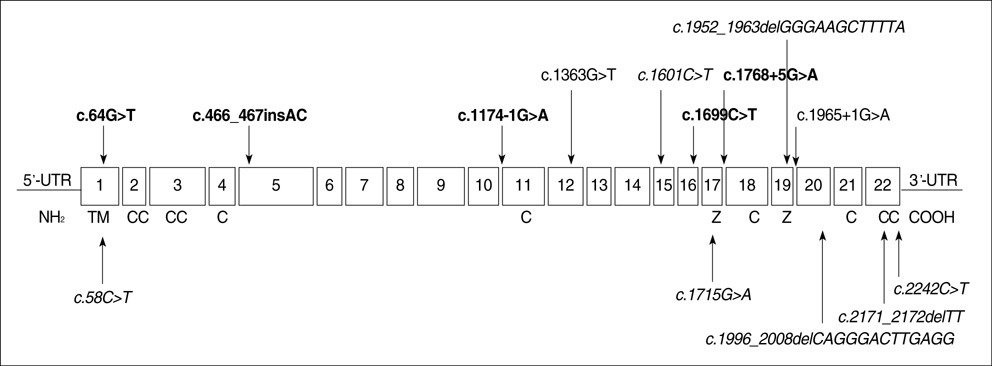
- X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets (XLH) results from mutations in the PHEX gene. Mutational analysis of the PHEX gene in 15 unrelated Korean patients with hypophosphatemic rickets revealed eight mutations, including five novel mutations, in nine patients: two nonsense mutations, two missense mutations, one insertion, and three splicing acceptor/donor site mutations. Of these, c.64G>T, c.1699C>T, c.466_467 insAC, c.1174-1G>A, and c.1768+5G>A were novel mutations. To analyze the correlation between genotype and phenotype, phenotypes were compared between groups with and without a mutation, in terms of mutation location, mutation type, and sex. Skeletal disease tended to be more severe in the group with a mutation in the C-terminal half of the PHEX gene, but no genotype-phenotype correlation was detected in other comparisons. Further extensive studies of the PHEX gene mutations and analyses of the genotype-phenotype relationships are required to understand PHEX function and the pathogenesis of XLH.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
A novel
de novo mutation withinPHEX gene in a young girl with hypophosphatemic rickets and review of literature
Chong Kun Cheon, Hoon Sang Lee, Su Yung Kim, Min Jung Kwak, Gu-Hwan Kim, Han-Wook Yoo
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2014;19(1):36-41. doi: 10.6065/apem.2014.19.1.36.A novel
de novo mosaic mutation inPHEX in a Korean patient with hypophosphatemic rickets
Misun Yang, Jinsup Kim, Aram Yang, Jahyun Jang, Tae Yeon Jeon, Sung Yoon Cho, Dong-Kyu Jin
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018;23(4):229-234. doi: 10.6065/apem.2018.23.4.229.Identification of a novel variant in the
PHEX gene using targeted gene panel sequencing in a 24-month-old boy with hypophosphatemic rickets
Ha Young Jo, Jung Hyun Shin, Hye Young Kim, Young Mi Kim, Heirim Lee, Mi Hye Bae, Kyung Hee Park, Ja-Hyun Jang, Min Jung Kwak
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020;25(1):63-67. doi: 10.6065/apem.2020.25.1.63.
Reference
-
1. Holm IA, Nelson AE, Robinson BG, Mason RS, Marsh DJ, Cowell CT, Carpenter TO. Mutational analysis and genotype-phenotype correlation of the PHEX gene in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:3889–3899.
Article2. Francis F, Strom TM, Hennig S, Boddrich A, Lorenz B, Brandau O, Mohnike KL, Cagnoli M, Steffens C, Klages S, Borzym K, Pohl T, Oudet C, Econs MJ, Rowe PS, Reinhardt R, Meitinger T, Lehrach H. Genomic organization of the human PEX gene mutated in X-linked dominant hypophosphatemic rickets. Genome Res. 1997. 7:573–585.3. Francis F, Hennig S, Korn B, Reinhardt R, de Jong P, Poustka A, Lehrach H, Rowe PSN, Goulding JN, Summerfield T, Mountford R, Read AP, Popowska E, Pronicka E, Davies KE, O'Riordan JL, Econs MJ, Nesbitt T, Drezner MK, Oudet C, Pannetier S, Hanauer A, Strom TM, Meindl A, Lorenz B, Cagnoli B, Mohnike KL, Murken J, Meitinger T. A gene (PEX) with homologies to endopeptidases in mutated in patients with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Nat Genet. 1995. 11:130–136.4. Quarles LD. FGF23, PHEX, and MEPE regulation of phosphate homeostasis and skeletal mineralization. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 285:E1–E9.5. Grieff M, Mumm S, Waeltz P, Mazzarella R, Whyte MP, Thakker RV, Schlessinger D. Expression and cloning of the human X-linked hypophosphatemia gene cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997. 231:635–639.
Article6. Nalla VK, Rogan PK. Automated splicing mutation analysis by information theory. Hum Mutat. 2005. 25:334–342.
Article7. Marsh DJ, Coulon V, Lunetta KL, Rocca-Serra P, Dahia PL, Zheng Z, Liaw D, Caron S, Duboue B, Lin AY, Richardson AL, Bonnetblanc JM, Bressieux JM, Cabarrot-Moreau A, Chompret A, Demange L, Eeles RA, Yahanda AM, Rearon ER, Fricker JP, Gorlin RJ, Hodgson SV, Huson S, Lacombe D, Leprat F, Odent S, Toulouse C, Olopade OI, Sobol H, Tishler S, Woods CG, Robinson BG, Weber HC, Parsons R, Peacocke M, Longy M, Eng C. Mutation spectrum and genotype-phenotype analyses in Cowden disease and Bannayan-Zonana syndrome, two hamartoma syndromes with germline PTEN mutation. Hum Mol Genet. 1998. 7:507–515.
Article8. Rowe PS, Oudet CL, Francis F, Sinding C, Pannetier S, Econs MJ, Strom TM, Meitinger T, Garabedian M, David A, Macher MA, Questiaux E, Popowska E, Pronicka E, Read AP, Mokrzycki A, Glorieux FH, Drezner MK, Hanauer A, Lehrach H, Goulding JN, O'Riordan JL. Distribution of mutations in the PEX gene in families with X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets (HYP). Hum Mol Genet. 1997. 6:539–549.
Article9. Dixon PH, Christie PT, Wooding C, Trump D, Grieff Mm, Holm I, Gertner JM, Schmidtke J, Shah B, Shaw N, Smith C, Tau C, Schlessinger D, Whyte MP, Thakker RV. Mutational analysis of PHEX gene in X-linked hypophosphatemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998. 83:3615–3623.
Article10. Cho HY, Lee BH, Kang JH, Ha IS, Cheong HI, Choi Y. A clinical and molecular genetic study of hypophosphatemic rickets in children. Pediatr Res. 2005. 58:329–333.
Article11. Tyynismaa H, Kaitila I, Nanto-Salonen K, Ala-Houhala M, Alitalo T. Identification of fifteen novel PHEX gene mutations in Finnish patients with hypophosphatemic rickets. Hum Mutat. 2000. 15:383–384.
Article12. Ritz E, Haxsen V, Zeier M. Disorders of phosphate metabolism pathomechanisms and management of hypophosphataemic disorders. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 17:547–558.13. Berezikov E, Cuppen E, Plasterk RH. Approaches to microRNA discovery. Nat Genet. 2006. 38:Suppl. S2–S7.
Article14. Popowska E, Pronicka E, Sulek A, Jurkiewicz D, Rowe E, Rowinska E, Krajewska-Walasek M. X-linked hypophosphatemia in Polish patients 1. Mutations in the PHEX gene. J Appl Genet. 2000. 41:293–302.15. Filisetti D, Ostermann G, Von Bredow M, Strom T, Filler G, Ehrich J, Pannetier S, Garnier JM, Rowe P, Francis F, Julienne A, Hanauer A, Econs MJ, Oudet C. Non-random distribution of mutations in the PHEX gene, and under-detected missense mutations at non-conserved residues. Eur J Hum Genet. 1999. 7:615–619.
Article16. Sabbagh Y, Boileau G, DesGroseillers L, Tenenhouse HS. Disease-causing missense mutations in the PHEX gene interfere with membrane targeting of the recombinant protein. Hum Mol Genet. 2001. 10:1539–1546.
Article17. Popowska E, Pronicka E, Sulek A, Jurkiewicz D, Rowinska E, Sykut-Cegielska J, Rump Z, Arasimowicz E, Krajewska-Walasek M. X-linked hypophosphatemia in Polish patients 2. Analysis of clinical features and genotype-phenotype correlation. J Appl Genet. 2001. 42:73–88.18. Orstavik KH, Orstavik RE, Halse J, Knudtzon J. X chromosome inactivation pattern in female carriers of X linked hypophosphataemic rickets. J Med Genet. 1996. 33:700–703.
Article19. Carrel L, Willard HF. X-inactivation profile reveals extensive variability in X-linked gene expression in females. Nature. 2005. 434:400–404.
Article20. Batra P, Tejani Z, Mars M. X-linked hypophosphatemia: dental and histologic findings. J Can Dent Assoc. 2006. 72:69–72.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A novel de novo mutation within PHEX gene in a young girl with hypophosphatemic rickets and review of literature
- A novel de novo mosaic mutation in PHEX in a Korean patient with hypophosphatemic rickets
- A Novel PHEX Gene Mutation in a Patient with Sporadic Hypophosphatemic Rickets
- X-linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets, del(2)(q37.1;q37.3) Deletion Syndrome and Mosaic Turner Syndrome, mos 45,X/46,X, del(2)(q37.1;q37.3) in a 3-year-old Female
- A pathogenic PHEX variant (c.1483-1G>C) in a Korean patient with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets