A novel de novo mutation within PHEX gene in a young girl with hypophosphatemic rickets and review of literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Children's Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea. chongkun@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Medical Genetics Clinic and Laboratory, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1702662
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2014.19.1.36
Abstract
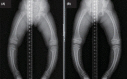
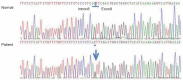
- X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) is the most common form of familial hypophosphatemic rickets and it is caused by loss-of-function mutations in the PHEX gene. Recently, a wide variety of PHEX gene defects in XLH have been revealed; these include missense mutations, nonsense mutations, splice site mutations, insertions, and deletions. Recently, we encountered a 2-year-9-month-old female with sporadic hypophosphatemic rickets. She underwent osteotomy, dental abscess was evident, and there was severe bowing of the legs. A low serum phosphorus level in combination with elevated serum alkaline phosphatase activity and normal serum calcium is suggestive of hypophosphatemic rickets. PHEX gene analysis revealed a splice acceptor site mutation, c.934-1G>T (IVS8-1G>T), at the intron8 and exon9 junction. To the best of our knowledge, this mutation is novel and has not been reported. The results of this study expand and improve our understanding of the clinical and molecular characteristics and the global pool of patients with sporadic hypophosphatemic rickets.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
X-linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets, del(2)(q37.1;q37.3) Deletion Syndrome and Mosaic Turner Syndrome, mos 45,X/46,X, del(2)(q37.1;q37.3) in a 3-year-old Female
Alaina P. Vidmar, Brian Miyazaki, Pedro A. Sanchez-Lara, Pisit Pitukcheewanont
J Bone Metab. 2017;24(4):257-261. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2017.24.4.257.A novel
de novo mosaic mutation inPHEX in a Korean patient with hypophosphatemic rickets
Misun Yang, Jinsup Kim, Aram Yang, Jahyun Jang, Tae Yeon Jeon, Sung Yoon Cho, Dong-Kyu Jin
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018;23(4):229-234. doi: 10.6065/apem.2018.23.4.229.Identification of a novel variant in the
PHEX gene using targeted gene panel sequencing in a 24-month-old boy with hypophosphatemic rickets
Ha Young Jo, Jung Hyun Shin, Hye Young Kim, Young Mi Kim, Heirim Lee, Mi Hye Bae, Kyung Hee Park, Ja-Hyun Jang, Min Jung Kwak
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020;25(1):63-67. doi: 10.6065/apem.2020.25.1.63.
Reference
-
1. Kienitz T, Ventz M, Kaminsky E, Quinkler M. Novel PHEX nonsense mutation in a patient with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets and review of current therapeutic regimens. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2011; 119:431–435. PMID: 21553362.
Article2. Ichikawa S, Traxler EA, Estwick SA, Curry LR, Johnson ML, Sorenson AH, et al. Mutational survey of the PHEX gene in patients with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Bone. 2008; 43:663–666. PMID: 18625346.
Article3. Kim J, Yang KH, Nam JS, Choi JR, Song J, Chang M, et al. A novel PHEX mutation in a Korean patient with sporadic hypophosphatemic rickets. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2009; 39:182–187. PMID: 19429806.4. Holm IA, Nelson AE, Robinson BG, Mason RS, Marsh DJ, Cowell CT, et al. Mutational analysis and genotypephenotype correlation of the PHEX gene in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:3889–3899. PMID: 11502829.
Article5. Kang QL, Xu J, Zhang Z, He JW, Lu LS, Fu WZ, et al. Three novel PHEX gene mutations in four Chinese families with X-linked dominant hypophosphatemic rickets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 423:793–798. PMID: 22713460.
Article6. Song HR, Park JW, Cho DY, Yang JH, Yoon HR, Jung SC. PHEX gene mutations and genotype-phenotype analysis of Korean patients with hypophosphatemic rickets. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:981–986. PMID: 18162710.
Article7. Durmaz E, Zou M, Al-Rijjal RA, Baitei EY, Hammami S, Bircan I, et al. Novel and de novo PHEX mutations in patients with hypophosphatemic rickets. Bone. 2013; 52:286–291. PMID: 23079138.
Article8. Tyynismaa H, Kaitila I, Nanto-Salonen K, Ala-Houhala M, Alitalo T. Identification of fifteen novel PHEX gene mutations in Finnish patients with hypophosphatemic rickets. Hum Mutat. 2000; 15:383–384. PMID: 10737991.
Article9. Owen C, Chen F, Flenniken AM, Osborne LR, Ichikawa S, Adamson SL, et al. A novel Phex mutation in a new mouse model of hypophosphatemic rickets. J Cell Biochem. 2012; 113:2432–2441. PMID: 22573557.10. Cho HY, Lee BH, Kang JH, Ha IS, Cheong HI, Choi Y. A clinical and molecular genetic study of hypophosphatemic rickets in children. Pediatr Res. 2005; 58:329–333. PMID: 16055933.
Article11. Dixon PH, Christie PT, Wooding C, Trump D, Grieff M, Holm I, et al. Mutational analysis of PHEX gene in X-linked hypophosphatemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998; 83:3615–3623. PMID: 9768674.
Article12. Gaucher C, Walrant-Debray O, Nguyen TM, Esterle L, Garabedian M, Jehan F. PHEX analysis in 118 pedigrees reveals new genetic clues in hypophosphatemic rickets. Hum Genet. 2009; 125:401–411. PMID: 19219621.
Article13. Sato K, Tajima T, Nakae J, Adachi M, Asakura Y, Tachibana K, et al. Three novel PHEX gene mutations in Japanese patients with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Pediatr Res. 2000; 48:536–540. PMID: 11004247.
Article14. Quinlan C, Guegan K, Offiah A, Neill RO, Hiorns MP, Ellard S, et al. Growth in PHEX-associated X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: the importance of early treatment. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012; 27:581–588. PMID: 22101457.
Article15. Chou YY, Chao SC, Tsai SC, Lin SJ. Novel PHEX gene mut ations in two Taiwanes e patients wit h hypophosphatemic rickets. J Formos Med Assoc. 2005; 104:198–202. PMID: 15818436.16. Morey M, Castro-Feijoo L, Barreiro J, Cabanas P, Pombo M, Gil M, et al. Genetic diagnosis of X-linked dominant Hypophosphatemic Rickets in a cohort study: tubular reabsorption of phosphate and 1,25(OH)2D serum levels are associated with PHEX mutation type. BMC Med Genet. 2011; 12:116. PMID: 21902834.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A novel de novo mosaic mutation in PHEX in a Korean patient with hypophosphatemic rickets
- PHEX Gene Mutations and Genotype-Phenotype Analysis of Korean Patients with Hypophosphatemic Rickets
- A Novel PHEX Gene Mutation in a Patient with Sporadic Hypophosphatemic Rickets
- A novel variant of PHEX in a Korean family with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets
- A pathogenic PHEX variant (c.1483-1G>C) in a Korean patient with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets