Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2021 Jun;26(2):130-133. 10.6065/apem.2040186.093.
A pathogenic PHEX variant (c.1483-1G>C) in a Korean patient with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2517592
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2040186.093
Abstract
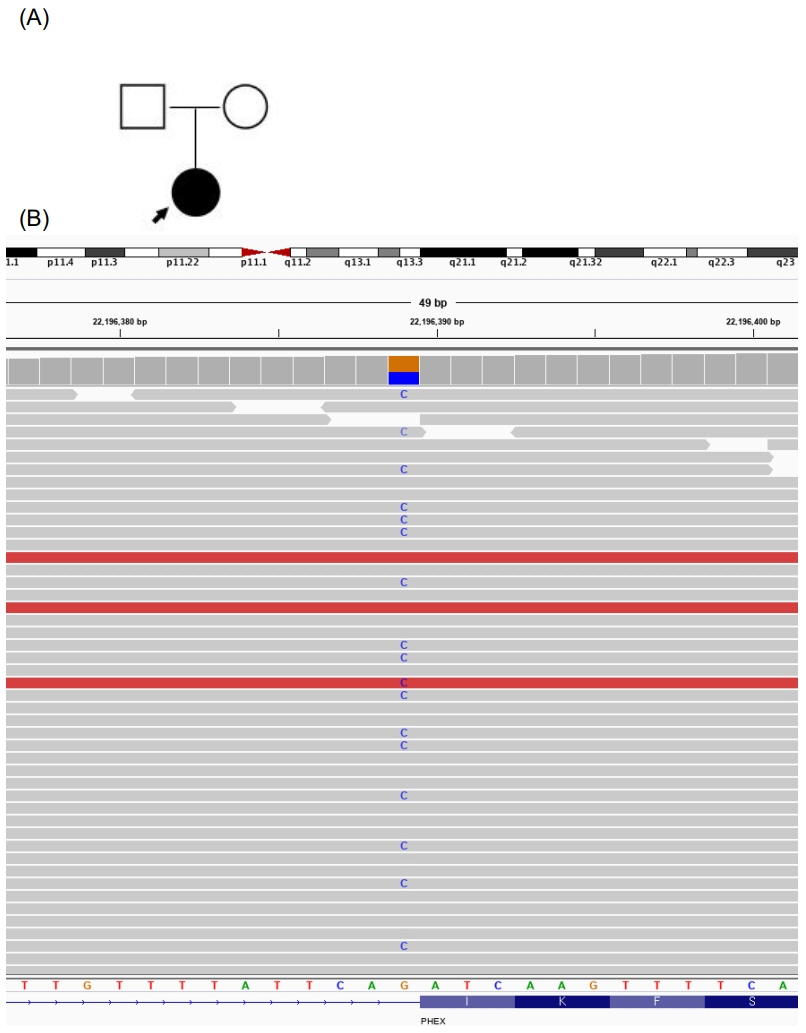
- X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets is an X-linked dominantly inherited disorder characterized by defects in renal phosphate transport leading to phosphate wasting and hypophosphatemia. In this report, we describe a case of X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets in a patient with a rare pathogenic PHEX variant. The 25-year-old female patient came to our clinic for genetic counseling regarding presumed genetic disease and pregnancy. When she was 9 years old, she had been diagnosed with vitamin D-resistant rickets based on laboratory results and symptoms. She had undergone orthopedic surgery due to bowing leg deformities. Since then, she was intermittently self-prescribing oral phosphate and calcium supplements. At 25 years old, she was diagnosed with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets with a rare pathogenic PHEX variant (c.1483-1G>C) by next-generation sequencing. This is the second report of the c.1483-1G>C variant to date, and her pathogenicity was confirmed based on the most recent guideline. Traditionally, the disease had been diagnosed mostly based on clinical findings. However, with advancements in genetic testing, genetic confirmation has become an imperative part of diagnostic workup. Herein, we report a 25-year-old female Korean patient diagnosed with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets harboring a rare pathogenic PHEX variant.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Holm IA, Nelson AE, Robinson BG, Mason RS, Marsh DJ, Cowell CT, et al. Mutational analysis and genotype-phenotype correlation of the PHEX gene in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:3889–99.
Article2. Roetzer KM, Varga F, Zwettler E, Nawrot-Wawrzyniak K, Haller J, Forster E, et al. Novel PHEX mutation associated with hypophosphatemic rickets. Nephron Physiol. 2007; 106:p8–12.
Article3. Jonsson KB, Zahradnik R, Larsson T, White KE, Sugimoto T, Imanishi Y, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 in oncogenic osteomalacia and X-linked hypophosphatemia. New Engl J Med. 2003; 348:1656–63.
Article4. Carpenter TO, Imel EA, Holm IA, Jan de Beur SM, Insogna KL. A clinician's guide to X-linked hypophosphatemia. J Bone Miner Res. 2011; 26:1381–8.
Article5. Li SS, Gu JM, Yu WJ, He JW, Fu WZ, Zhang ZL. Seven novel and six de novo PHEX gene mutations in patients with hypophosphatemic rickets. Int J Mol Med. 2016; 38:1703–14.
Article6. Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015; 17:405–23.
Article7. Capelli S, Donghi V, Maruca K, Vezzoli G, Corbetta S, Brandi ML, et al. Clinical and molecular heterogeneity in a large series of patients with hypophosphatemic rickets. Bone. 2015; 79:143–9.
Article8. Zhao Y, Yang F, Wang L, Che H. Familial hypophosphatemic rickets caused by a PHEX gene mutation accompanied by a NPR2 missense mutation. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020; 32:305–11.9. Cho HY, Lee BH, Kang JH, Ha IS, Cheong HI, Choi Y. A clinical and molecular genetic study of hypophosphatemic rickets in children. Pediatr Res. 2005; 58:329–33.
Article10. Kang YE, Hong JH, Kim J, Joung KH, Kim HJ, Ku BJ, et al. A novel PHEX gene mutation in a patient with sporadic hypophosphatemic rickets. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2014; 29:195–201.
Article11. Clausmeyer S, Hesse V, Clemens P, Engelbach M, Kreuzer M, Becker-Rose P, et al. Mutational analysis of the PHEX gene: novel point mutations and detection of large deletions by MLPA in patients with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Calcif Tissue Int. 2009; 85:211–20.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- PHEX Gene Mutations and Genotype-Phenotype Analysis of Korean Patients with Hypophosphatemic Rickets
- A novel de novo mutation within PHEX gene in a young girl with hypophosphatemic rickets and review of literature
- A Novel PHEX Gene Mutation in a Patient with Sporadic Hypophosphatemic Rickets
- A novel de novo mosaic mutation in PHEX in a Korean patient with hypophosphatemic rickets
- A novel variant of PHEX in a Korean family with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets