J Periodontal Implant Sci.
2010 Oct;40(5):239-243. 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.239.
The effect of implant shape and bone preparation on primary stability
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology and Research Institute for Oral Sciences, Gangneung-Wonju National University College of Dentistry, Gangneung, Korea. hsum@gwnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Periodontics, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1783565
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.239
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of implant shape and bone preparation on the primary stability of the implants using resonance frequency analysis.
METHODS
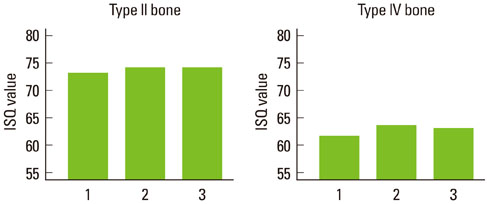
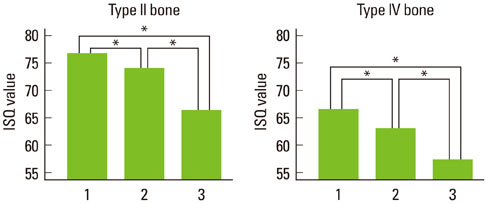
Sixty bovine rib blocks were used for soft and hard bone models. Each rib block received two types of dental implant fixtures; a straight-screw type and tapered-screw type. Final drilling was done at three different depths for each implant type; 1 mm under-preparation, standard preparation, and 1 mm over-preparation. Immediately after fixture insertion, the implant stability quotient (ISQ) was measured for each implant.
RESULTS
Regardless of the bone type, the ISQ values of the straight-screw type and tapered-screw type implants were not significantly different (P > 0.05). Depth of bone preparation had no significant effect on the ISQ value of straight-screw type implants (P > 0.05). For the tapered-screw type implants, under-preparation significantly increased the ISQ value (P < 0.05), whereas overpreparation significantly decreased the ISQ value (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Within the limitations of this study, it is concluded that bone density seemed to have a prevailing effect over implant shape on primary stability. The primary stability of the tapered-screw type implants might be enhanced by delicate surgical techniques.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Evaluation of the correlation between insertion torque and primary stability of dental implants using a block bone test
Dorjpalam Bayarchimeg, Hee Namgoong, Byung Kook Kim, Myung Duk Kim, Sungtae Kim, Tae-Il Kim, Yang Jo Seol, Yong Moo Lee, Young Ku, In-Chul Rhyu, Eun Hee Lee, Ki-Tae Koo
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2013;43(1):30-36. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2013.43.1.30.Histomorphometric analysis of microcrack healing after the installation of mini-implants
Soobin Shin, Pan-Soo Park, Seung-Hak Baek, Il-Hyung Yang
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2015;45(2):62-68. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2015.45.2.62.
Reference
-
1. Friberg B, Jemt T, Lekholm U. Early failures in 4,641 consecutively placed Branemark dental implants: a study from stage 1 surgery to the connection of completed prostheses. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1991. 6:142–146.2. Lioubavina-Hack N, Lang NP, Karring T. Significance of primary stability for osseointegration of dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006. 17:244–250.
Article3. Martinez H, Davarpanah M, Missika P, Celletti R, Lazzara R. Optimal implant stabilization in low density bone. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001. 12:423–432.
Article4. O'Sullivan D, Sennerby L, Meredith N. Influence of implant taper on the primary and secondary stability of osseointegrated titanium implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004. 15:474–480.5. Glauser R, Sennerby L, Meredith N, Ree A, Lundgren A, Gottlow J, et al. Resonance frequency analysis of implants subjected to immediate or early functional occlusal loading. Successful vs. failing implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004. 15:428–434.
Article6. Garber DA, Salama H, Salama MA. Two-stage versus one-stage--is there really a controversy? J Periodontol. 2001. 72:417–421.
Article7. Olsson M, Friberg B, Nilson H, Kultje C. MkII--a modified self-tapping Branemark implant: 3-year results of a controlled prospective pilot study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1995. 10:15–21.8. Turkyilmaz I, Aksoy U, McGlumphy EA. Two alternative surgical techniques for enhancing primary implant stability in the posterior maxilla: a clinical study including bone density, insertion torque, and resonance frequency analysis data. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2008. 10:231–237.
Article9. Lekholm U, Zarb G. Branemark PI, Zarb GA, Albrektsson T, editors. Patient selection and preparation. Tissue-integrated prostheses: osseointegration in clinical dentistry. 1985. Chicago: Quintessence;199–209.10. Meredith N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int J Prosthodont. 1998. 11:491–501.11. Pattijn V, Jaecques SV, De Smet E, Muraru L, Van Lierde C, Van der Perre G, et al. Resonance frequency analysis of implants in the guinea pig model: influence of boundary conditions and orientation of the transducer. Med Eng Phys. 2007. 29:182–190.
Article12. Sennerby L, Thomsen P, Ericson LE. A morphometric and biomechanic comparison of titanium implants inserted in rabbit cortical and cancellous bone. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1992. 7:62–71.13. O'Sullivan D, Sennerby L, Meredith N. Measurements comparing the initial stability of five designs of dental implants: a human cadaver study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2000. 2:85–92.14. Akca K, Chang TL, Tekdemir I, Fanuscu MI. Biomechanical aspects of initial intraosseous stability and implant design: a quantitative micro-morphometric analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006. 17:465–472.
Article15. Andres-Garcia R, Vives NG, Climent FH, Palacin AF, Santos VR, Climent MH, et al. In vitro evaluation of the influence of the cortical bone on the primary stability of two implant systems. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2009. 14:E93–E97.16. O'Sullivan D, Sennerby L, Jagger D, Meredith N. A comparison of two methods of enhancing implant primary stability. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2004. 6:48–57.17. Akkocaoglu M, Uysal S, Tekdemir I, Akca K, Cehreli MC. Implant design and intraosseous stability of immediately placed implants: a human cadaver study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005. 16:202–209.
Article18. Oh GY, Park SH, Kim SG. Influence of implant fixture design on implant primary stability. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2007. 45:98–106.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effect of osteotome technique on primary implant stability according to implant fixture diameter
- The effect of undersizing and tapping on bone to implant contact and implant primary stability: A histomorphometric study on bovine ribs
- Effect of preparation methods of recipient site on primary implant stability in various bone qualities
- Influence of implant fixture design on implant primary stability
- The evaluation of implant stability measured by resonance frequency analysis in different bone types