J Periodontal Implant Sci.
2010 Oct;40(5):220-226. 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.220.
Periodontal regeneration capacity of equine particulate bone in canine alveolar bone defects
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology and Dental Research Institute, Seoul National University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. ccpperio@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Seoul National University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Craniomaxillofacial Reconstructive Science, Seoul National University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Dental Biomaterials Science, Seoul National University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1783562
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.220
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was performed to evaluate the periodontal wound healing effect of particulate equine bone mineral on canine alveolar bone defects.
METHODS
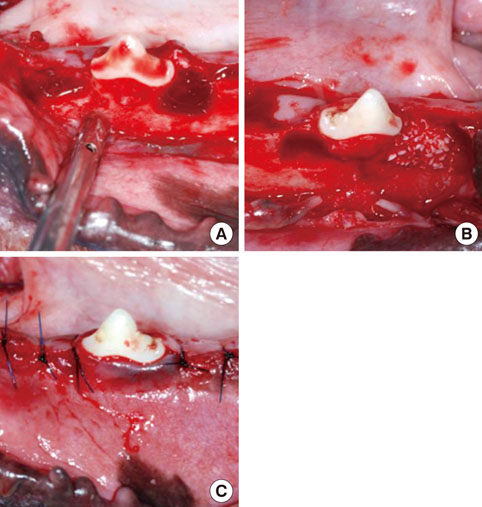
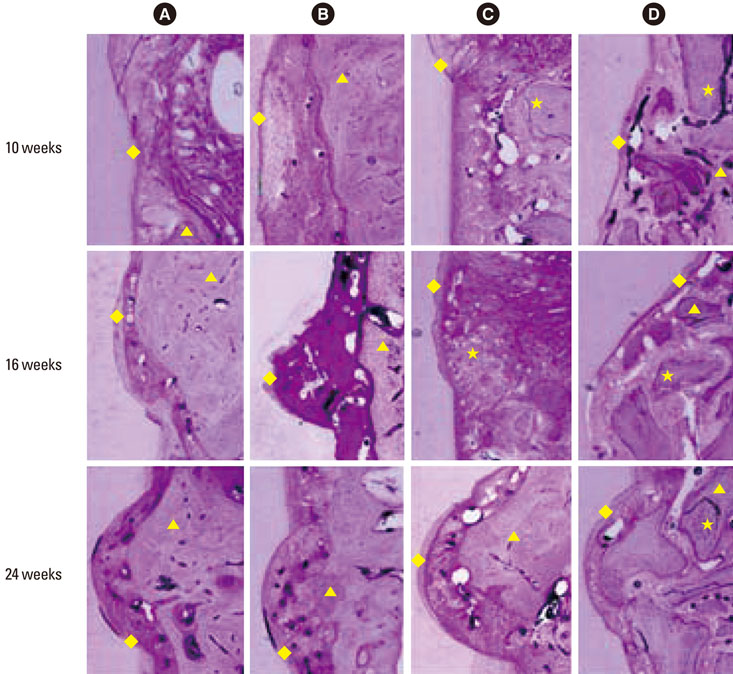
Twelve adult male beagle dogs were used as study subjects. The mandibular second and fourth premolars were extracted prior to the experimental surgery, and the extraction sites were allowed to heal for 8 weeks. After periodontal probing, two-walled defects were created at the mesial and distal sides of the mandibular third premolars bilaterally, and the defects were filled with equine particulate bone with collagen membrane or bovine particulate bone with collagen membrane, or collagen membrane alone. The defects without any treatment served as negative controls. After probing depth measurement, animals were sacrificed at 10, 16, and 24 post-surgery weeks for micro-computed tomographic and histomorphometric analysis.
RESULTS
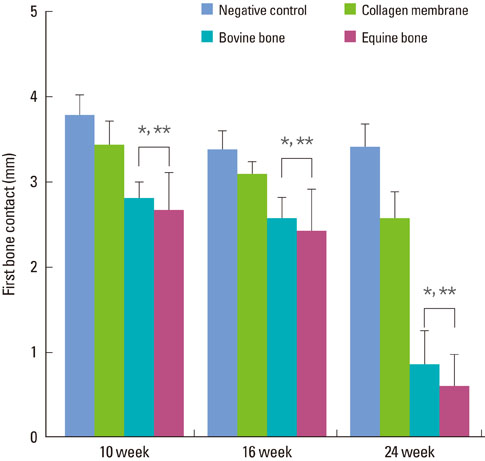
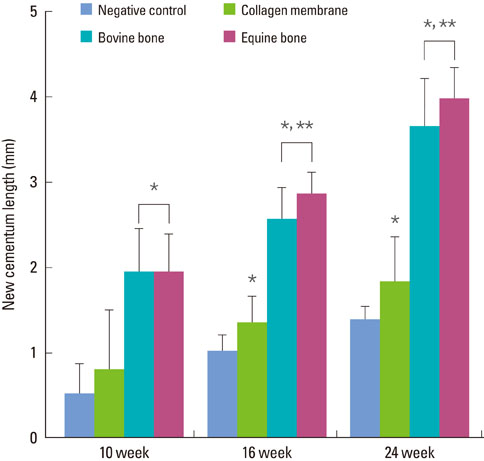
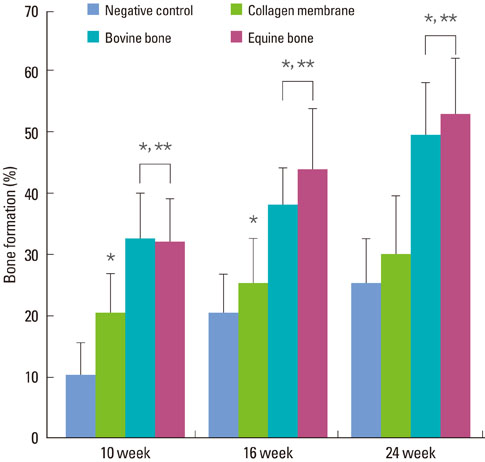
The equine particulate bone-inserted group showed significantly decreased values of probing depth and first bone contact compared to the negative control and collagen membrane alone groups at weeks 10, 16, and 24 (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in the new cementum length, newly-formed bone area, or newly-formed bone volume between equine particulate bone- and bovine particulate bone-inserted groups, both of which showed significantly increased values compared to the negative control and collagen membrane alone groups (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Equine particulate bone showed significant differences in probing depth, first bone contact, new cementum length, newly formed bone area, and bone volume fraction values when compared to the negative control and collagen membrane alone groups. There were no significant differences between equine and bovine particulate bone substitutes in these parameters; therefore, we can conclude that equine particulate bone is equivalent to bovine bone for periodontal regeneration.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Herold RW, Pashley DH, Cuenin MF, Niagro F, Hokett SD, Peacock ME, et al. The effects of varying degrees of allograft decalcification on cultured porcine osteoclast cells. J Periodontol. 2002; 73:213–219.
Article2. Dragoo MR, Sullivan HC. A clinical and histological evaluation of autogenous iliac bone grafts in humans. I. Wound healing 2 to 8 months. J Periodontol. 1973; 44:599–613.
Article3. Hiatt WH, Schallhorn RG. Intraoral transplants of cancellous bone and marrow in periodontal lesions. J Periodontol. 1973; 44:194–208.
Article4. Valentini P, Abensur D. Maxillary sinus floor elevation for implant placement with demineralized freeze-dried bone and bovine bone (Bio-Oss): a clinical study of 20 patients. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1997; 17:232–241.5. Valentini P, Abensur D, Densari D, Graziani JN, Hammerle C. Histological evaluation of Bio-Oss in a 2-stage sinus floor elevation and implantation procedure. A human case report. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1998; 9:59–64.6. Wang M. Developing bioactive composite materials for tissue replacement. Biomaterials. 2003; 24:2133–2151.
Article7. Brugnami F, Then PR, Moroi H, Leone CW. Histologic evaluation of human extraction sockets treated with demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft (DFDBA) and cell occlusive membrane. J Periodontol. 1996; 67:821–825.
Article8. Schwartz Z, Goldstein M, Raviv E, Hirsch A, Ranly DM, Boyan BD. Clinical evaluation of demineralized bone allograft in a hyaluronic acid carrier for sinus lift augmentation in humans: a computed tomography and histomorphometric study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007; 18:204–211.
Article9. Whittaker JM, James RA, Lozada J, Cordova C, GaRey DJ. Histological response and clinical evaluation of heterograft and allograft materials in the elevation of the maxillary sinus for the preparation of endosteal dental implant sites. Simultaneous sinus elevation and root form implantation: an eight-month autopsy report. J Oral Implantol. 1989; 15:141–144.10. Schmitt JM, Buck DC, Joh SP, Lynch SE, Hollinger JO. Comparison of porous bone mineral and biologically active glass in critical-sized defects. J Periodontol. 1997; 68:1043–1053.
Article11. Artzi Z, Tal H, Dayan D. Porous bovine bone mineral in healing of human extraction sockets: 2. Histochemical observations at 9 months. J Periodontol. 2001; 72:152–159.
Article12. Carmagnola D, Adriaens P, Berglundh T. Healing of human extraction sockets filled with Bio-Oss. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003; 14:137–143.13. Wenz B, Oesch B, Horst M. Analysis of the risk of transmitting bovine spongiform encephalopathy through bone grafts derived from bovine bone. Biomaterials. 2001; 22:1599–1606.
Article14. Milthorpe BK. Xenografts for tendon and ligament repair. Biomaterials. 1994; 15:745–752.
Article15. Sogal A, Tofe AJ. Risk assessment of bovine spongiform encephalopathy transmission through bone graft material derived from bovine bone used for dental applications. J Periodontol. 1999; 70:1053–1063.
Article16. Traini T, Valentini P, Iezzi G, Piattelli A. A histologic and histomorphometric evaluation of anorganic bovine bone retrieved 9 years after a sinus augmentation procedure. J Periodontol. 2007; 78:955–961.
Article17. Yildirim M, Spiekermann H, Biesterfeld S, Edelhoff D. Maxillary sinus augmentation using xenogenic bone substitute material Bio-Oss in combination with venous blood. A histologic and histomorphometric study in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000; 11:217–229.
Article18. Maiorana C, Sigurta D, Mirandola A, Garlini G, Santoro F. Sinus elevation with alloplasts or xenogenic materials and implants: an up-to-4-year clinical and radiologic follow-up. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2006; 21:426–432.19. Simion M, Nevins M, Rocchietta I, Fontana F, Maschera E, Schupbach P, et al. Vertical ridge augmentation using an equine block infused with recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB: a histologic study in a canine model. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2009; 29:245–255.20. Di Stefano DA, Artese L, Iezzi G, Piattelli A, Pagnutti S, Piccirilli M, et al. Alveolar ridge regeneration with equine spongy bone: a clinical, histological, and immunohistochemical case series. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2009; 11:90–100.
Article21. Caton J, Nyman S, Zander H. Histometric evaluation of periodontal surgery. II. Connective tissue attachment levels after four regenerative procedures. J Clin Periodontol. 1980; 7:224–231.
Article22. Dragoo MR, Kaldahl WB. Clinical and histological evaluation of alloplasts and allografts in regenerative periodontal surgery in humans. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1983; 3:8–29.23. Froum SJ. Human histologic evaluation of HTR polymer and freeze-dried bone allograft. A case report. J Clin Periodontol. 1996; 23:615–620.
Article24. Murphy KG, Gunsolley JC. Guided tissue regeneration for the treatment of periodontal intrabony and furcation defects. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol. 2003; 8:266–302.
Article25. Luo G, Kinney JH, Kaufman JJ, Haupt D, Chiabrera A, Siffert RS. Relationship between plain radiographic patterns and three-dimensional trabecular architecture in the human calcaneus. Osteoporos Int. 1999; 9:339–345.
Article26. Misch KA, Yi ES, Sarment DP. Accuracy of cone beam computed tomography for periodontal defect measurements. J Periodontol. 2006; 77:1261–1266.
Article27. Reddy MS. Radiographic alveolar bone change as an outcome measure for therapies that inhibit bone loss or foster bone gain. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2005; 7:175–188.28. Sant'Anna EF, Gomez DF, Sumner DR, Williams JM, Figueroa AA, Ostric SA, et al. Micro-computed tomography evaluation of the glenoid fossa and mandibular condyle bone after bilateral vertical ramus mandibular distraction in a canine model. J Craniofac Surg. 2006; 17:611–619.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reconstruction of alveolar clefts with iliac cancellous particulate or block bone grafts: a comparative study
- Regenerative capacity of augmented bone in rat calvarial guided bone augmentation model
- The Effect of Demineralized Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft in Guided Bone Regeneration on Supra-Alveolar Peri-Implant Defects in Dogs
- Bone Augmentation with Fibrin Sealant during Guided Bone Regeneration for Implant Surgery
- Guided bone regeneration using K-incision technique