J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Feb;26(2):312-315. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.2.312.
Haddad Syndrome with PHOX2B Gene Mutation in a Korean Infant
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute for Medical Genetics, Keimyung University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. dkkimmd@kmu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anatomy, Keimyung University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Division of Pediatric Surgery, Department of Surgery, Keimyung University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Keimyung University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 5Hanvit Institute for Medical Genetics, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 1782126
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.2.312
Abstract
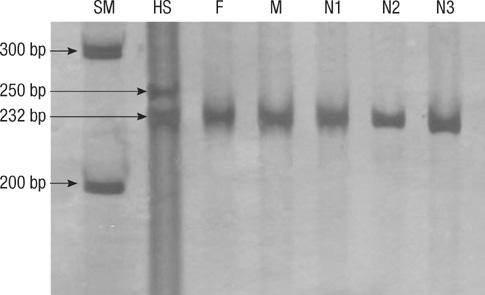
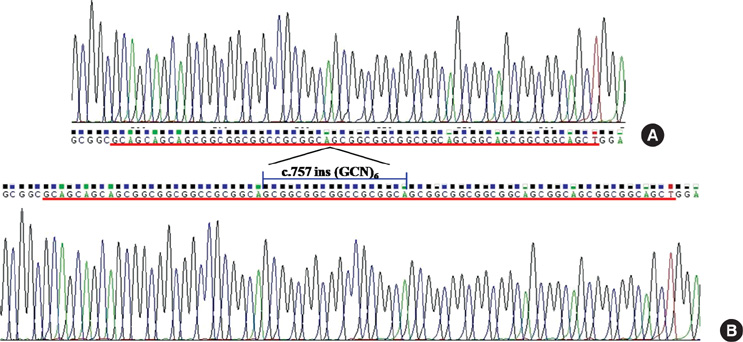
- Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome with Hirschsprung's disease, also known as Haddad syndrome, is an extremely rare disorder with variable symptoms. Recent studies described that congenital central hypoventilation syndrome had deep relation to the mutation of the PHOX2B gene in its diagnosis and phenotype. We report a newborn male infant with clinical manifestations of recurrent hypoventilation with hypercapnea and bowel obstruction. These clinical manifestations were compatible with congenital central hypoventilation syndrome and Hirschsprung's disease, and polyalanine 26 repeats in the PHOX2B gene supported the diagnosis of congenital central hypoventilation. We described a first case of Haddad syndrome in Korean and its clinical and genetic characteristics were discussed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Base Sequence
DNA Mutational Analysis
Hirschsprung Disease/diagnosis/genetics/pathology
Homeodomain Proteins/*genetics
Humans
Hypoventilation/congenital/diagnosis/genetics
Infant, Newborn
Male
Molecular Sequence Data
*Mutation
Sleep Apnea, Central/diagnosis/genetics
Transcription Factors/*genetics
Figure
Reference
-
1. Haddad GG, Mazza NM, Defendini R, Blanc WA, Driscoll JM, Epstein MA, Epstein RA, Mellins RB. Congenital failure of automatic control of ventilation, gastrointestinal motility and heart rate. Medicine (Baltimore). 1978. 57:517–526.2. Tomycz ND, Haynes RL, Schmidt EF, Ackerson K, Kinney HC. Novel neuropathologic findings in the Haddad syndrome. Acta Neuropathol. 2010. 119:261–269.3. Amiel J, Laudier B, Attié-Bitach T, Trang H, de Pontual L, Gener B, Trochet D, Etchevers H, Ray P, Simonneau M, Vekemans M, Munnich A, Gaultier C, Lyonnet S. Polyalanine expansion and frameshift mutations of the paired-like homeobox gene PHOX2B in congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Nat Genet. 2003. 33:459–461.4. Matera I, Bachetti T, Puppo F, Di Duca M, Morandi F, Casiraghi GM, Cilio MR, Hennekam R, Hofstra R, Schöber JG, Ravazzolo R, Ottonello G, Ceccherini I. PHOX2B mutations and polyalanine expansions correlate with the severity of the respiratory phenotype and associated symptoms in both congenital and late onset Central Hypoventilation syndrome. J Med Genet. 2004. 41:373–380.5. Sasaki A, Kanai M, Kijima K, Akaba K, Hashimoto M, Hasegawa H, Otaki S, Koizumi T, Kusuda S, Ogawa Y, Tuchiya K, Yamamoto W, Nakamura T, Hayasaka K. Molecular analysis of congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Hum Genet. 2003. 114:22–26.6. Weese-Mayer DE, Berry-Kravis EM, Zhou L, Maher BS, Silvestri JM, Curran ME, Marazita ML. Idiopathic congenital central hypoventilation syndrome: analysis of genes pertinent to early autonomic nervous system embryologic development and identification of mutations in PHOX2b. Am J Med Genet A. 2003. 123A:267–278.7. Lee MK, Kim JS, Park SJ, Kim KS, Kim IK, Yoon CH, Kim KM. A case of Haddad syndrome. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. 8:252–256.8. Ha TW, Han KH, Son DG, Kim SP, Kim DK. Analysis of loss of heterozygosity in Korean patients with keratoacanthoma. J Korean Med Sci. 2005. 20:340–343.9. Croaker GD, Shi E, Simpson E, Cartmill T, Cass DT. Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome and Hirschsprung's disease. Arch Dis Child. 1998. 78:316–322.10. Trochet D, O'Brien LM, Gozal D, Trang H, Nordenskjöld A, Laudier B, Svensson PJ, Uhrig S, Cole T, Niemann S, Munnich A, Gaultier C, Lyonnet S, Amiel J. PHOX2B genotype allows for prediction of tumor risk in congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2005. 76:421–426.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Haddad Syndrome with 27 Polyalanine Repeats in PHOX2B Gene in a Korean Infant
- Haddad Syndrome with a Germ-Line Mutation in the PHOX2B Gene in a Korean Neonate
- Haddad Syndrome: A Case of Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome Combined with Hirschsprung Disease
- Molecular genetics of congenital central hypoventilation syndrome and Haddad syndrome
- A Case of Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome with PHOX2B Gene Mutation in a Korean Neonate