J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Aug;25(8):1237-1240. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.8.1237.
A Case of Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome with PHOX2B Gene Mutation in a Korean Neonate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. psepse@naver.com
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1714051
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.8.1237
Abstract
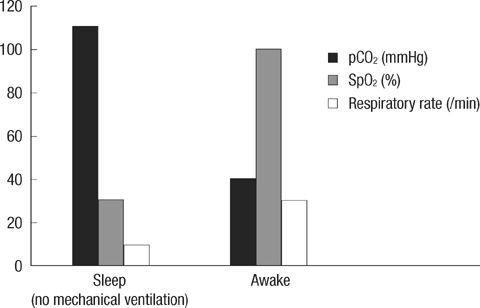
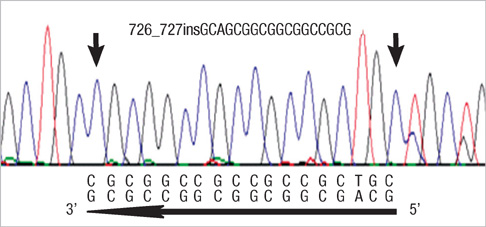
- Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (CCHS) is a life-threatening disorder with apnea and cyanosis during sleep requiring immediate endotracheal intubation during the first day of life. The PHOX2B gene has been identified as the major gene involved in CCHS. This is the first report of a Korean neonate with CCHS confirmed to have a PHOX2B mutation with expanded alleles containing 20 polyalanine repeats that is a relatively small number compared to previous cases. The patient required intermittent ventilator support during sleep only and did not suffer from any other disorders of the autonomic nerve system. He consistently needs ventilator support during sleep and remains alive. Analysis of PHOX2B gene is useful for diagnosis and appropriate therapeutic intervention of CCHS patients.
MeSH Terms
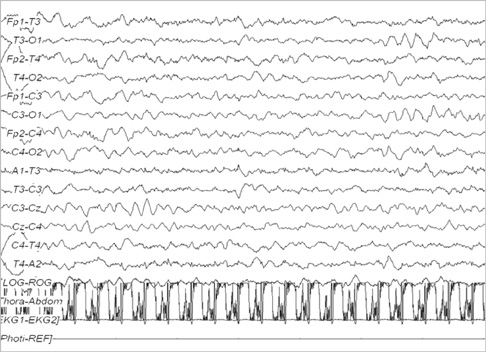
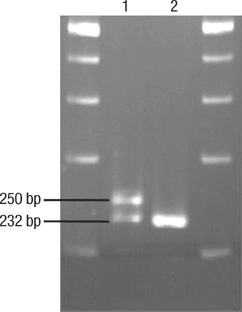
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gozal D. Congenital hypoventilation syndrome: An update. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1998. 26:273–282.2. Or SF, Tong MF, Lo FM, Law CW, Miu TY, Trochet D, Lam TS. PHOX2B mutations in three Chinese patients with congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Chin Med J (Engl). 2006. 119:1749–1752.3. Choi JH, Oh JH, Kim JH, Koh DK, Hong SC. Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome combined with Hirschsprung disease diagnosed in the neonatal period. Korean J Pediatr. 2006. 49:446–450.
Article4. Lee MK, Kim JS, Park SJ, Kim KS, Kim IK, Yoon CH, Kim KM. A Case of Haddad Syndrome. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. 8:252–256.
Article5. Hwang IO, Lee ES. A case of Ondine's curse with Hirschsprung disease. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2004. 11:72–76.6. Jung SE, Kim DY, Kim KH, Lee SC, Park KW, Kim WK. The neurocristopathy in a newborn with congenital central hypoventilation syndrome, Hirschsprung's disease and ganglioneuroblastoma. J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg. 1999. 5:146–151.7. Ahn YM, Choi HR, Lee HJ, Dong ES. A case of congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (ondine's curse) with Hirschsprung's disease. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 1993. 3:113–120.8. Rohrer T, Trachsel D, Engelcke G, Hammer J. Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome associated with Hirschsprung's disease and neuroblastoma: case of multiple neurocristopathies. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2002. 33:71–76.
Article9. Weese-Mayer DE, Berry-Kravis EM, Zhou L, Maher BS, Silvestri JM, Curran ME, Marazita ML. Idiopathic congenital central hypoventilation syndrome: analysis of genes pertinent to early autonomic nerve system embryologic development and identification of mutations in PHOX2b. Am J Med Genet A. 2003. 123A:267–278.10. Amiel J, Laudier B, Attié-Bitach T, Trang H, de Pontual L, Gener B, Trochet D, Etchevers H, Ray P, Simonneau M, Vekemans M, Munnich A, Gaultier C, Lyonnet S. Polyalanine expansion and frameshift mutations of the paired-like homeobox gene PHOX2B in congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Nat Gene. 2003. 33:459–461.
Article11. Pattyn A, Morin X, Cremer H, Goridis C, Brunet JF. The homeobox gene Phox2B is essential for the development of autonomic neural crest derivatives. Nature. 1999. 399:366–370.
Article12. Benailly HK, Lapierre JM, Laudier B, Amiel J, Attié T, De Blois MC, Vekemans M, Romana SP. PMX2B, a new candidate gene for Hirschsprung's disease. Clin Genet. 2003. 64:204–209.
Article13. Trang H, Dehan M, Beaufils F, Zaccaria I, Amiel J, Gaultier C. French CCHS Working Group. The French Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome Registry: general data, phenotype, and genotype. Chest. 2005. 127:72–79.14. Coleman M, Boros SJ, Huseby TL, Brennom WS. Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome; a report of successful experience with bilateral diaphragmatic pacing. Arch Dis Child. 1980. 55:901–903.
Article15. Trochet D, O'Brien LM, Gozal D, Trang H, Nordenskjöld A, Laudier B, Svensson PJ, Uhrig S, Cole T, Niemann S, Munnich A, Gaultier C, Lyonnet S, Amiel J. PHOX2B genotype allows for prediction of tumor risk in congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2005. 76:421–426.
Article16. Sasaki A, Kanai M, Kijima K, Akaba K, Hashimoto M, Hasegawa H, Otaki S, Koizumi T, Kusuda S, Ogawa Y, Tuchiya K, Yamamoto W, Nakamura T, Hayasaka K. Molecular analysis of congenital central hyoventilation syndome. Hum Genet. 2003. 114:22–26.17. Matera I, Bachetti T, Puppo F, Di Duca M, Morandi F, Casiraghi GM, Cilio MR, Hennekam R, Hofstra R, Schober JG, Ravazzolo R, Ottonello G, Ceccherini I. PHOX2B mutations and polyalanine expansions correlate with the severity of the respiratory phenotype and associated symptoms in both congenital and late onset central hypoventilation syndrome. J Med Genet. 2004. 41:373–380.
Article18. Bajaj R, Smith J, Trochet D, Pitkin J, Ouvrier R, Graf N, Sillence D, Kluckow M. Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome and Hirschsprung's disease in an extremely preterm infant. Pediatrics. 2005. 115:e737–e738.
Article19. Holzinger A, Mittal RA, Kachel W, Priessmann H, Hammel M, Ihrler S, Till H, Munch HG. A novel 17 bp deletion in the PHOX2B gene causes congenital central hypoventilation syndrome with total aganglionosis of the small and large intestine. Am J Med Genet A. 2005. 139:50–51.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Haddad Syndrome with PHOX2B Gene Mutation in a Korean Infant
- Haddad Syndrome with a Germ-Line Mutation in the PHOX2B Gene in a Korean Neonate
- Haddad Syndrome with 27 Polyalanine Repeats in PHOX2B Gene in a Korean Infant
- Haddad Syndrome: A Case of Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome Combined with Hirschsprung Disease
- Molecular genetics of congenital central hypoventilation syndrome and Haddad syndrome