J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Apr;21(2):188-192. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.188.
Synergy of Arbekacin-based Combinations Against Vancomycin Hetero-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Asian-Pacific Research Foundation for Infectious Diseases (ARFID), Korea. jhsong@ansorp.org
- 2Division of Infectious Diseases, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781820
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.188
Abstract
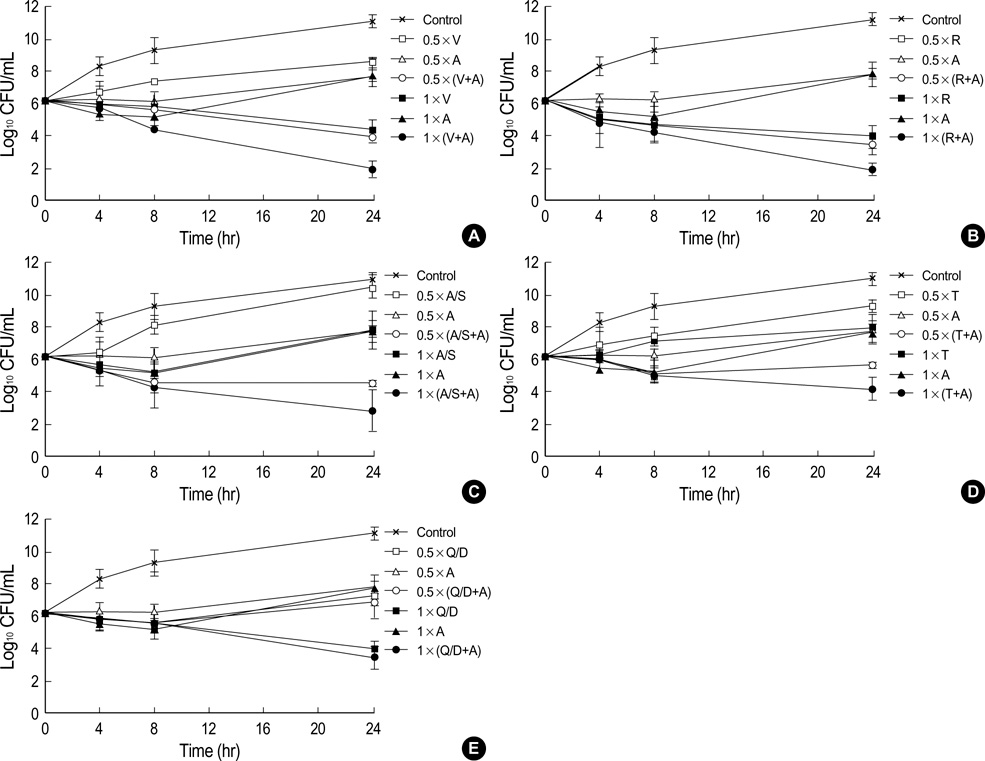
- This study was undertaken to evaluate the in vitro activities of arbekacin-based combination regimens against vancomycin hetero-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (hetero-VISA). Combinations of arbekacin with vancomycin, rifampin, ampicillin-sulbactam, teicoplanin, or quinipristin-dalfopristin against seven hetero-VISA strains and two methicillin-resistant S. aureus strains were evaluated by the time-kill assay. The combinations of arbekacin with vancomycin, teicoplanin, or ampicillinsulbactam showed the synergistic interaction against hetero-VISA strains. Data suggest that these arbekacin-based combination regimens may be useful candidates for treatment options of hetero-VISA infections.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Virginiamycin/administration & dosage
Vancomycin/*administration & dosage
Teicoplanin/administration & dosage
Sulbactam/administration & dosage
Staphylococcus aureus/*drug effects/isolation & purification
Staphylococcal Infections/drug therapy/microbiology
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
Methicillin Resistance
Humans
Drug Synergism
Drug Resistance, Bacterial
Dibekacin/administration & dosage/*analogs & derivatives
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*administration & dosage
Ampicillin/administration & dosage
Aminoglycosides/*administration & dosage
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Efficacy of the Arbekacin and Teicoplanin Combination on Glycopeptide Intermediate Staphylococcus aureus in a Rabbit Model of Endocarditis
Cheong Ho Cho, Jun Yong Choi, Sang Hoon Han, Han Sung Lee, Suk Hoon Choi, Bum Sik Chin, Hee Kyoung Choi, Su Jin Jeoung, Myung Soo Kim, Chang Oh Kim, Chang Ki Kim, Dongeun Yong, Young Goo Song, Kyungwon Lee, June Myung Kim
Infect Chemother. 2008;40(2):102-106. doi: 10.3947/ic.2008.40.2.102.Clinical Usefulness of Arbekacin
Jae Hoon Lee, Chang-Seop Lee
Infect Chemother. 2016;48(1):1-11. doi: 10.3947/ic.2016.48.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Hiramatsu K, Hanaki H, Ino T, Yabuta K, Oguri T, Tenover FC. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical strain with reduced vancomycin susceptibility. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997. 40:135–136.
Article2. Walsh TR, Howe RA. The prevalence and mechanisms of vancomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2002. 56:657–675.3. Chang S, Sievert DM, Hageman JC, Boulton ML, Tenover FC, Downes FP, Shah S, Rudrik JT, Pupp GR, Brown WJ, Cardo D, Fridkin SK. Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Investigative Team. Infection with vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus containing the vanA resistance gene. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:1342–1347.4. Weigel LM, Clewell DB, Gill SR, Clark NC, McDougal LK, Flannagan SE, Kolonay JF, Shetty J, Killgore GE, Tenover FC. Genetic analysis of a high-level vancomycin-resistant isolate of Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 2003. 302:1569–1701.
Article5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus - New York, 2004. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2004. 53:322–323.6. Ariza J, Pujol M, Cabo J, Pena C, Fernandez N, Linares J, Ayats J, Gudiol F. Vancomycin in surgical infections due to methicillin-resistance Staphylococcus aureus with heterogeneous resistance to vancomycin. Lancet. 1999. 353:1587–1588.7. Howe RA, Bowker KE, Walsh TR, Feest TG, MacGowan AP. Vancomycin resistance Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1998. 351:602.8. Kim MN, Pai CH, Woo JH, Ryu JS, Hiramatsu K. Vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus in Korea. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:3879–3881.
Article9. Ploy MC, Grelaud C, Martin C, de Lumely L, Denis F. First clinical isolate of vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus in a French hospital. Lancet. 1998. 351:1212.
Article10. Wong SS, Ho PL, Woo PC, Yuen KY. Bacteremia caused by staphylococci with inducible vancomycin heteroresistance. Clin Infect Dis. 1999. 29:760–767.
Article11. Bert F, Clarissou J, Durand F, Delefosse D, Chauvet C, Lefebvre P, Lambert N, Branger C. Prevalence, molecular epidemiology, and clinical significance of heterogeneous glycopeptide-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus in live transplant recipients. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:5147–5152.12. Moore MR, Perdreau-Remington F, Chambers HF. Vancomycin treatment failure associated with heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus in a patient with endocarditis and in the rabbit model of endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. 47:1262–1266.
Article13. Naimi TS, Anderson D, O'Boyle C, Boxrud DJ, Johnson SK, Tenover FC, Lynfield R. Vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus with phenotypic susceptibility to methicillin in a patient with recurrent bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis. 2003. 36:1609–1612.
Article14. Watanabe T, Ohashi K, Matsui K, Kubota T. Comparative studies of the bactericical, morphological and post-antibiotic effects of arbekacin and vancomycin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997. 39:471–476.15. Hiramatsu K. Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a new model of antibiotic resistance. Lancet Infect Dis. 2001. 1:147–155.16. Kondo S, Iinuma K, Yamamoto H, Maeda K, Umezawa H. Synthesis of 1-N-(S-4-amino-2-hydroxybutyryl)-kanamycin B and 3'-, 4'-dideoxykanamycin B active against kanamycin-resistant bacteria. J Antibiotics. 1973. 26:412–415.17. Kondo S, Tamura A, Gomi S, Ikeda Y, Takeuchi T, Mitsuhashi S. Structures of enzymatically modified products of arbekacin by meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antibiotics. 1993. 46:310–315.18. Osakabe Y, Takahashi Y, Narihara K. The utility and dosage and administration of arbekacin in patients with MRSA infection. Antibiot Chemother. 1996. 12:120–127.19. Hamilton-Miller MT, Shah S. Activity of the semi-synthetic kanamycin B derivative, arbekacin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1995. 35:865–868.20. You I, Kariyama R, Zervos MJ, Kumon H, Chow JW. In-vitro activity of arbekacin alone and in combination with vancomycin against gentamicin- and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000. 36:37–41.
Article21. NCCLS. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 13th Informational Supplement. 2003. M100-S13.22. Eliopoulos GM, Moellering RC. Lorian V, editor. Antimicrobial combinations. Antibiotics in Laboratory Medicine. 1996. 4th edn. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;330–396.23. LaPante KL, Rybak MJ. Clinical glycopeptide-intermediate staphylococci tested against arbekacin, daptomycin, and tigecycline. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2004. 50:125–130.24. Wong SS, Ho PL, Woo PC, Yuen KY. Bacteremia caused by staphylococci with inducible vancomycin heteroresistance. Clin Infect Dis. 1999. 29:760–767.
Article25. Tenover FC, Weigel LM, Appelbaum PC, McDougal LK, Chaitram J, McAllister S, Clark N, Killgore G, O'Hara CM, Jevitt L, Patel JB, Bozdogan B. Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolate from a patient in Pennsylvania. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. 48:275–280.
Article26. Whitener CJ, Park SY, Browne FA, Parent LJ, Julian K, Bozdogan B, Appelbaum PC, Chaitram J, Weigel LM, Jernigan J, McDougal LK, Tenover FC, Fridkin SK. Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the absence of vancomycin exposure. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 38:1049–1055.27. Hotta K, Zhu CB, Ogata T, Sunada A, Ishikawa J, Mizuno S, Ikeda Y, Kondo S. Enzymatic 2''-N-acetylation of arbekacin and antibiotic activity of its product. J Antibiotics. 1996. 49:458–464.
Article28. Suzuki K. Efficacy and safety of arbekacin for staphylococcal infection in the NICU. Pediatr Int. 2003. 45:301–306.
Article29. Akins PL, Rybak MJ. In vitro activities of daptomycin, arbekacin, vancomycin, and gentamicin alone and/or in combination against glycopeptide intermediate-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an infection model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000. 44:1925–1929.
Article30. Lee DG, Chun HS, Yim DS, Choi SM, Choi JH, Yoo JH, Shin WS, Kang MW. Efficacies of vancomycin, arbekacin, and gentamicin alone or in combination against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro infective endocarditis model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. 47:3768–3773.31. Kumon H, Mizuno A, Nasu Y, Tsugawa M, Kishi M, Ohmori H. Pharmacokinetics of arbekacin in healthy volunteers and patients with renal insufficiency. Jpn J Antibiotics. 1989. 42:200–207.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Vancomycin Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus in Korean Primary Hospitals
- Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- Combination Effects of Various Beta-Lactam Antibiotics with Vancomycin or Teicoplanin against Staphylococcus aureus with Reduced Susceptibility to Vancomycin
- Efficacy of Vancomycin-beta-lactam Combinations Against Heterogeneously Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (hetero-VRSA)
- Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus with Reduced Susceptibility to Vancomycin in a Tertiary Hospital