J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Oct;20(5):759-763. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.5.759.
Additive Effect of Diesel Exhaust Particulates and Ozone on Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Asthma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. jas877@schbc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Tokyo, Japan.
- KMID: 1781757
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.5.759
Abstract
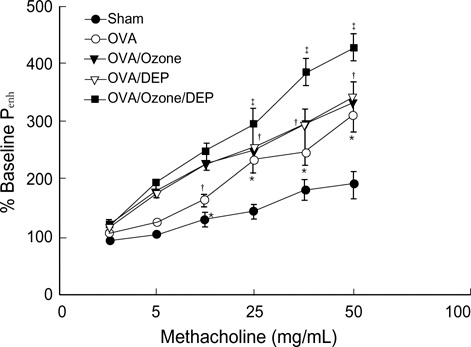
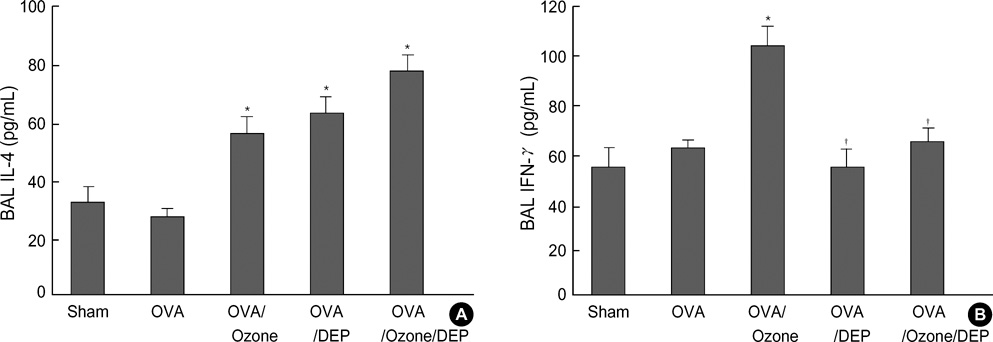
- Allergic airway diseases are related to exposure to atmospheric pollutants, which have been suggested to be one factor in the increasing prevalence of asthma. Little is known about the effect of ozone and diesel exhaust particulates (DEP) on the development or aggravation of asthma. We have used a mouse asthma model to determine the effect of ozone and DEP on airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation. Methacholine enhanced pause (P(enh)) was measured. Levels of IL-4 and IFN-gamma were quantified in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids by enzyme immunoassays. The OVA-sensitized-challenged and ozone and DEP exposure group had higher P(enh) than the OVA-sensitized-challenged group and the OVA-sensitized-challenged and DEP exposure group, and the OVA-sensitized-challenged and ozone exposure group. Levels of IFN-gamma were decreased in the OVA-sensitized-challenged and DEP exposure group and the OVA-sensitized-challenged and ozone and DEP exposure group compared to the OVA-sensitized-challenged and ozone exposure group. Levels of IL-4 were increased in the OVA-sensitized-challenged and ozone exposure group and the OVA-sensitized-challenged and DEP exposure group, and the OVA-sensitized-challenged and ozone and DEP exposure group compared to OVA-sensitized-challenged group. Co-exposure of ozone and DEP has additive effect on airway hyperresponsiveness by modulation of IL-4 and IFN-gamma suggesting that DEP amplify Th2 immune response.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Air Pollutants, Environmental/toxicity
Animals
Asthma/*chemically induced/*immunology
Disease Models, Animal
Drug Combinations
Drug Synergism
Female
Hypersensitivity/complications/*etiology/*immunology
Interferon Type II/immunology
Interleukin-4/immunology
Mice
Mice, Inbred BALB C
Ovalbumin
Ozone/*toxicity
Pneumonia/*chemically induced/complications/*immunology
Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
Respiratory Hypersensitivity/chemically induced/complications/immunology
Vehicle Emissions/*toxicity
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Effects of Ammonium Chloride on Ozone-induced Airway Inflammation: the Role of Slc26a4 in the Lungs of Mice
Jong-Uk Lee, Hyeon Ju Lee, Ji-Na Kim, Min Kyung Kim, Sung Roul Kim, Hun-Soo Chang, Choon-Sik Park, Jong-Sook Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(32):e272. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e272.The Effects of On-site Measured Ozone Concentration on Pulmonary Function and Symptoms of Asthmatics
Doh Hyung Kim, Youn Seup Kim, Jae Seuk Park, Ho Jang Kwon, Kye Young Lee, Sang-Rok Lee, Young Koo Jee
J Korean Med Sci. 2007;22(1):30-36. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.1.30.Past, Present, and Future of Allergy in Korea
You-Young Kim
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2010;2(3):155-164. doi: 10.4168/aair.2010.2.3.155.
Reference
-
1. Scruetzle D, Lewtas J. Bioassy-directed chemical analysis in environmental research. Anal Chem. 1986. 58:1060A–1075A.2. Draper W. Quantification of nitro and dinitropolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in diesel exhaust particulate matter. Chromosphere. 1986. 15:437–447.3. McClellan RO, Brooks AL, Cuddihy RG, Jones RK, Mauderly JL, Wolff RK. Lewtas IJ, editor. Inhalation toxicology of diesel exhaust particles. Toxicological effects of emissions from diesel engines. 1982. New York: Elsevier Scientific Publications;99–120.4. Mauderly JL, Jones RK, Griffith WC, Henderson RF, McClellan RO. Diesel exhaust is a pulmonary carcinogen in rats exposed chronically by inhalation. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1987. 9:208–221.
Article5. McClellan RO. Health effects of exposure to diesel exhaust particles. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987. 27:279–300.
Article6. Ichinose T, Furuyama A, Sagai M. Biological effects of diesel exhaust particles (DEP) II. Acute toxicity of DEP introduced into lung by intratracheal instillation. Toxicology. 1995. 99:153–167.
Article7. Strachan DP, Anderson HR. Trends in hospital admission rates for asthma in children. BMJ. 1992. 304:819–820.
Article8. Haahtela T, Lindholm H, Bjorksten F, Koskenvuo K, Laitinen LA. Prevalence of asthma in Finnish young men. BMJ. 1990. 301:266–268.
Article9. Committee of the Environmental and Occupational Health Assembly of the American Thoracic Society. Health effects of outdoor air pollution. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996. 153:3–50.10. Holtzman MJ, Fabbri LM, O'Byrne PM, Gold BD, Aizawa K, Walters EH, Alpert SE, Nadel JA. Importance of airway inflammation for hyperresponsiveness induced by ozone in dogs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983. 127:686–690.11. Gordon T, Taylor BF, Amdur MO. Ozone inhibition of tissue cholinesterase in guinea pigs. Arch Environ Health. 1981. 36:284–288.
Article12. Basha MA, Gross KB, Gwizdala CJ, Haidar AH, Popovich J Jr. Bronchoalveolar lavage neutrophilia in asthmatic and healthy volunteers after controlled exposure to ozone and filtered purified air. Chest. 1994. 106:1757–1765.
Article13. Seltzer J, Bigby BG, Stulbarg M, Holtzman MJ, Nadel JA, Ureki IF, Leikauf GD, Goetzl EJ, Boushey HA. O3-induced change in bronchial reactivity to methacholine and airway inflammation in humans. J Appl Physiol. 1986. 60:1321–1326.
Article14. Koren HS, Devlin RB, Graham DE, Mann R, McGee MP, Horstman DH, Kozumbo WJ, Becker S, House DE, McDonnell WF, Blomberg PA. Ozone-induced inflammation in the lower airways of human subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989. 139:407–415.
Article15. Jakab GJ, Hemenway DR. Concomitant exposure to carbon black particulates enhances ozone-induced lung inflammation and suppression of alveolar macrophage phagocytosis. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1994. 41:221–231.
Article16. Vincent R, Bjarnason SG, Adamson IY, Hedgecock C, Kumarathasan P, Guenette J, Potvin M, Goegan P, Bouthillier L. Acute pulmonary toxicity of urban particulate matter and ozone. Am J Pathol. 1997. 151:1563–1570.17. Brusselle GG, Kips JC, Tavernier JH, van der Heyden JG, Cuvelier CA, Pauwels RA, Bluethmann H. Attenuation of allergic airway inflammation in IL-4 deficient mice. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994. 24:73–80.
Article18. Anderson AA. A sampler for respiratory health hazard assessment. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1966. 27:160–165.19. Sagai M, Furuyama A, Ichinose T. Biologic effects of diesel exhaust particles (DEP): III. Pathogenesis of asthma-like symptoms in mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 1996. 21:199–209.20. Ohtoshi T, Takizawa H, Okazaki H, Kawasaki S, Takeuchi N, Ohta K, Ito K. Diesel exhaust particles stimulate human airway epithelial cells to produce cytokines relevant to airway inflammation in vitro. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998. 101:778–785.
Article21. Hamelmann E, Schwarze J, Takeda K, Oshiba A, Larsen GL, Irvin CG, Gelfand EW. Noninvasive measurement of airway responsiveness in allergic mice using barometric plethysmography. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997. 156:766–775.
Article22. Ohta K, Yamashita N, Tajima M, Miyasaka T, Nakano J, Nakajima M, Ishii A, Horiuchi T, Mano K, Miyamoto T. Diesel exhaust particulate induces airway hyperresponsiveness in a murine model: essential role of GM-CSF. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999. 104:1024–1030.
Article23. Fahy O, Hammad H, Senechal S, Pestel J, Tonnel AB, Wallaert B, Tsicopoulos A. Synergistic effect of diesel organic extracts and allergen Der p 1 on the release of chemokines by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from allergic subjects: involvement of the map kinase pathway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2000. 23:247–254.24. Jang AS, Choi IS, Kim SW, Song BC, Yeum CH, Jung JY. Airway obstruction after acute ozone exposure in BALB/c mice using barometric plethysmography. Korean J Intern Med. 2003. 18:1–5.
Article25. Jang AS, Choi IS, Koh YI, Park CS, Lee JS. The relationship between alveolar epithelial proliferation and airway obstruction after ozone exposure. Allergy. 2002. 57:737–740.
Article26. Fujimaki H, Nohara O, Ichinose T, Watanabe N, Saito S. IL-4 production in mediastinal lymph node cells in mice intratracheally instilled with diesel exhaust particulates and antigen. Toxicology. 1994. 92:261–268.
Article27. Fujimaki H, Saneyoshi K, Shiraishi F, Imai T, Endo T. Inhalation of diesel exhaust enhances antigen-specific IgE antibody production in mice. Toxicology. 1997. 116:227–233.
Article28. Diaz-Sanchez D, Tsien A, Fleming J, Saxon A. Combined diesel exhaust particulate and ragweed allergen challenge markedly enhances in vivo nasal ragweed specific IgE and shews cytokine production to a T helper cell-type pattern. J Immunol. 1997. 158:2406–2413.29. van Zijverden M, van der Pijl A, Bol M, van Pinxteren FA, de Haar C, Penninks AH, van Loveren H, Pieters R. Diesel exhaust, carbon black, and silica particles display distinct Th1/Th2 modulating activity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2000. 168:131–139.
Article30. Takano H, Yoshikawa T, Ichinose T, Miyabara Y, Imaoka K, Sagai M. Diesel exhaust particles enhance antigen induced airway inflammation and local cytokine expression in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997. 156:36–42.31. Ichinose T, Takano H, Miyabara Y, Yanagisawa R, Sagai R. Murine strain differences in allergic airway inflammation and immunoglobulin production by a combination of antigen and diesel exhaust particles. Toxicology. 1997. 122:183–192.
Article32. Terada N, Maesako K, Hiruma K, Hamano N, Houki G, Konno A, Ikeda T, Sai M. Diesel exhaust particulates enhance eosinophil adhesion to nasal epithelial cells and cause degranulation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997. 114:167–174.
Article33. Madden MC, Richards JH, Dailey LA, Hatch GE, Ghio AJ. Effect of ozone on diesel exhaust particle toxicity in rat lung. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2000. 168:140–148.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of ozone on influenza virus-induced airway hyperreactivity in rats
- Effect of DHEA on airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in murine model of asthma
- Effect of ozone on nasal mucosa inflammation
- Effects of Diesel Exhaust Particles on Airway Inflammation and Hyperresponsiveness in a Murine Model
- Long-Term Effects of Diesel Exhaust Particles on Airway Inflammation and Remodeling in a Mouse Model