J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Feb;20(1):150-152. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.1.150.
Neostigmine for the Treatment of Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy with Acute Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction in a Cirrhotic Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. p1052ccy@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1781744
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.1.150
Abstract
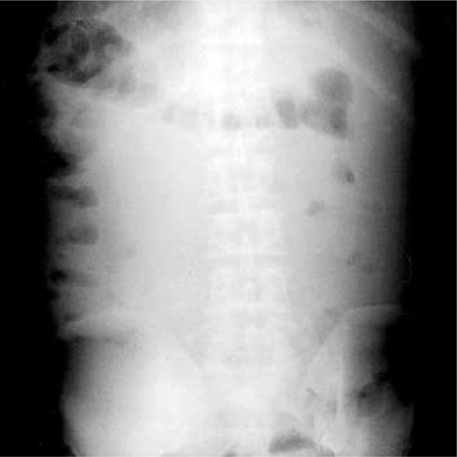
- We treated a 49-yr-old man with neostigmine, who had liver cirrhosis, acute hepatic encephalopathy, and acute intestinal pseudoobstruction. He was admitted in a state of hepatic confusion. On physical examination, the abdomen was distended; and bowel sound was absent. Plain abdomen film revealed multiple airfluid levels and distention of bowel loops. Initially, we gave him lactulose enemas every 6 hr for one day without improvement in his mental state. Furthermore, he became to a state of coma. Therefore, we gave him 0.5 mg of neostigmine subcutaneously to improve his peristaltic movement, and 2 L of polyethylene glycol electrolyte solution through a nasogastric tube for 4 hr to reduce the production and absorption of gutderived toxins of nitrogenous compounds. After these treatments, the venous ammonia level decreased to the normal range within 12 hr, and the coma disappeared after 2 days. We suggest that neostigmine may be one of the most effective treatments to initiate peristaltic movement and bowel cleansing in cirrhotic patients with acute hepatic encephalopathy and acute intestinal pseudoobstruction.
MeSH Terms
-
Air
Ammonia/metabolism
Blood Pressure
Cholinesterase Inhibitors/*pharmacology
Electrolytes/pharmacology
Enema
Fibrosis/*drug therapy
Hepatic Encephalopathy/*diagnosis/*drug therapy/radiography
Humans
Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction/*diagnosis/*drug therapy/radiography
Lactulose/pharmacology
Liver/metabolism
Male
Middle Aged
Neostigmine/*pharmacology
Peristalsis
Polyethylene Glycols/pharmacology
Time Factors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Blei AT, Cordoba J. Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001. 96:1968–1976.
Article2. Kiba T, Numata K, Saito S. Neostigmine and polyethylene glycol electrolyte solution for the therapy of acute hepatic encephalopathy with liver cirrhosis and ascites. Hepatogastroenterology. 2003. 50:823–826.3. Runyon BA. Fatal bacterial peritonitis secondary to nonobstructive colonic dilatation (Ogilvie's syndrome) in cirrhotic ascites. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1986. 8:687–689.
Article4. Morgan MY, Hawley KE. Lactitol vs. lactulose in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients: a double-blind, randomized trial. Hepatology. 1987. 7:1278–1284.
Article5. Strauss E, da Costa MF. The importance of bacterial infections as precipiting factors of chronic hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 1998. 45:900–904.6. Malbrain ML. Abdominal pressure in the critically ill: measurement and clinical relevance. Intensive Care Med. 1999. 25:1453–1458.
Article7. Paran H, Silverberg D, Mayo A, Shwartz I, Neufeld D, Freund U. Treatment of acute colonic pseudo-obstruction with neostigmine. J Am Coll Surg. 2000. 190:315–318.8. Amaro R, Rogers AI. Neostigmine infusion: New standard of care for acute colonic pseudo-obstruction? Am J Gastroenterol. 2000. 95:304–305.9. Ponec RJ, Saunders MD, Kimmey MB. Neostigmine for the treatment of acute colonic pseudo-obstruction. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:137–141.10. Trevisani GT, Hyman NH, Church JM. Neostigmine: safe and effective treatment for acute colonic pseudo-obstruction. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000. 43:599–603.11. Delgado-Aros S, Camilleri M. Pseudo-obstruction in the critically ill. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2003. 17:427–444.
Article12. Beck DE, Fazio VW, Jagelman DG. Comparison of oral lavage methods for preoperative colonic cleansing. Dis Colon Rectum. 1986. 29:699–703.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Pseudo-obstruction Responding to Neostigmine
- Eosinophilic Peritonitis Followed by Acute Colonic Pseudo-obstruction (Ogilvie's syndrome) in an ESRD Patient on CAPD
- Treatment of Acute Colonic Pseudo-obstruction (Ogilvie's Syndrome) with Intravenous Neostigmine
- Acute Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction in a Patient with MELAS Syndrome
- Effective and Safe Use of Neostigmine in Treatment of Acute Kidney Injury Associated with Colonic Pseudo-obstruction after Cardiac Surgery