Korean J Lab Med.
2009 Dec;29(6):594-600. 10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.6.594.
Application of a Diagnostic Method Using Reverse Transcription-PCR ELISA for the Diagnosis of Enteroviral Infections
- Affiliations
-
- 1Chungcheongnam-do Health & Environment Research Institute, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Food and Nutrition, College of Human Ecology, Chung-Ang University, Anseong, Korea.
- 3Department of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 4Department of Herbal Resources, Professional Graduate School of Oriental Medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea.
- 5Department of Life Science, Daejeon University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 6Division of Enteric and Hepatitis Viruses, Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Seoul, Korea. cheonds@korea.kr
- KMID: 1781616
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.6.594
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
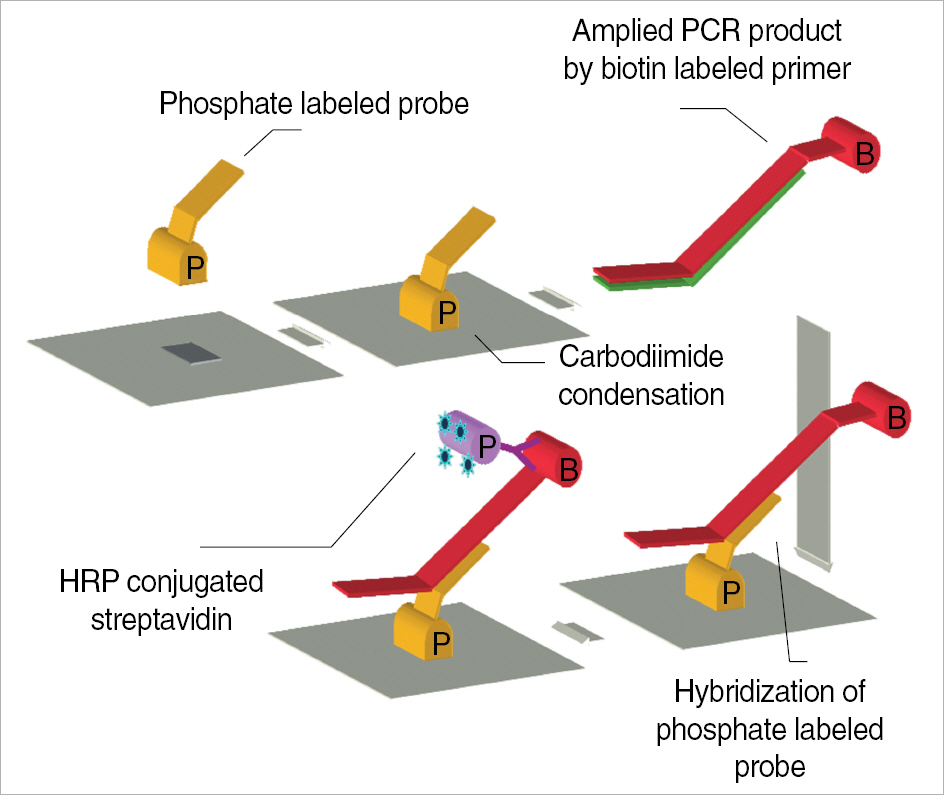
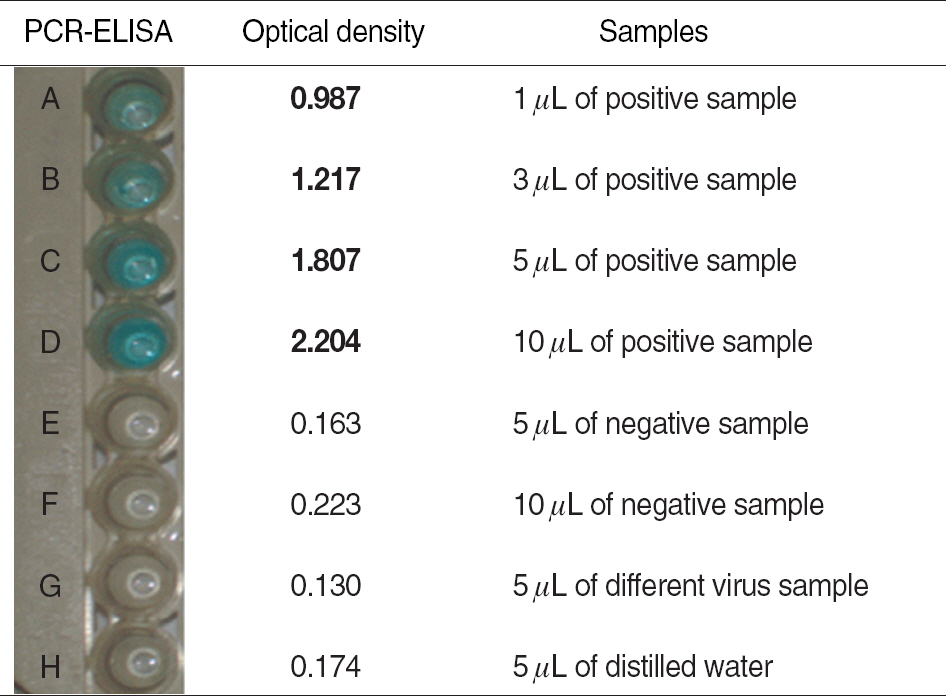
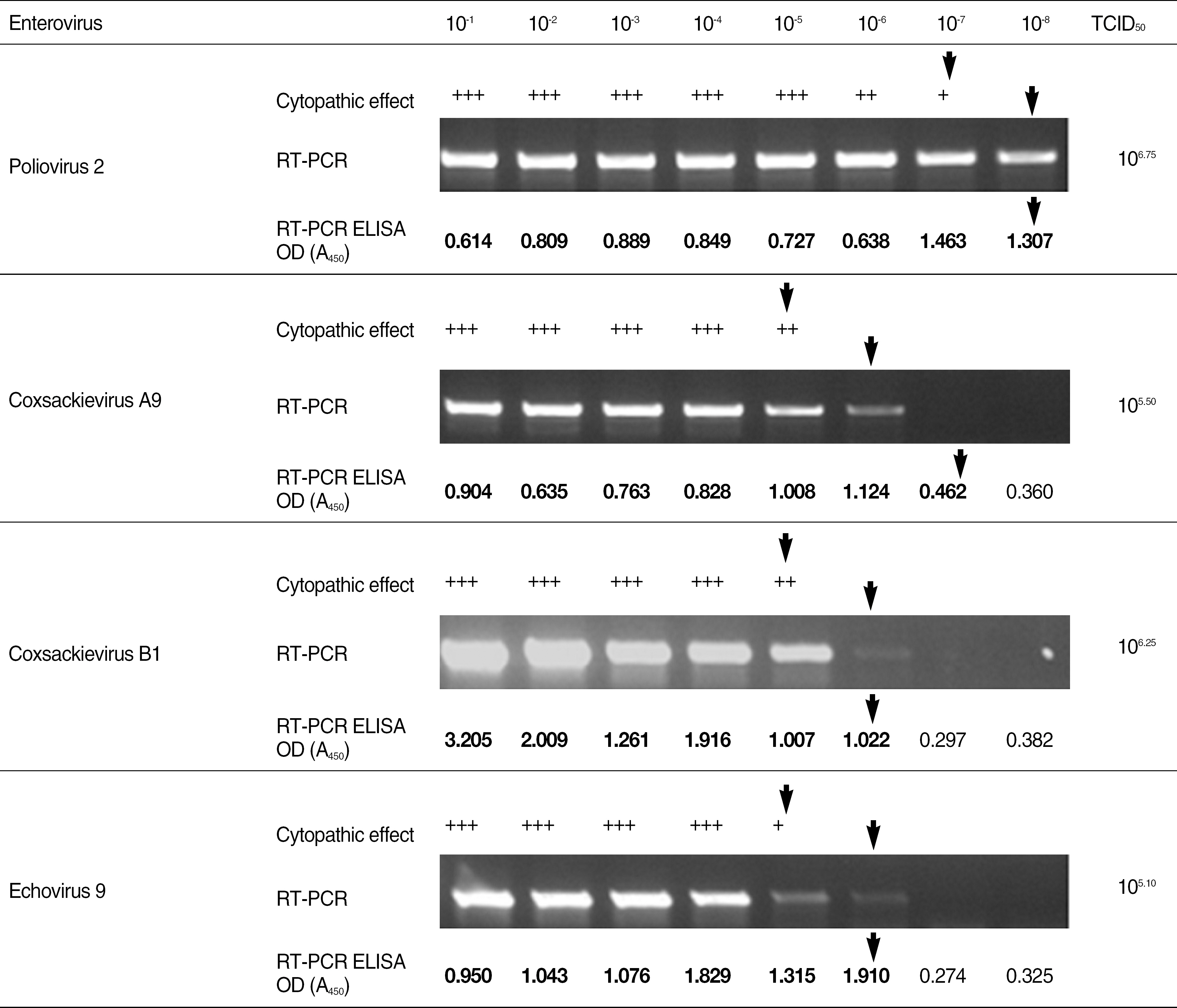
Enteroviruses are known as major pathogen for aseptic meningitis. Although rapid diagnosis for enteroviruses is very essential to exclude bacterial infections in patients with meningitis, classical diagnostic method based on virus isolation is not practicable for timely treatment of patients due to its laborious and time-consuming procedure. Recently molecular methodologies as alternatives are routinely used for rapid and sensitive diagnosis for enteroviruses infections. METHODS: Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR ELISA kit for targeting 5'non-coding region (NCR) with highly conserved genetic identity among all genotypes of enteroviruses was introduced in this investigation. RT-PCR ELISA was evaluated about sensitivity and specificity through virus isolation using clinical specimens from patients suspected of enteroviral infections and enteroviral isolates comparing with conventional RT-PCR identifying them. RESULTS: The detection limit of the RT-PCR ELISA was up to 10-100 folds higher than virus isolation using cell culture and conventional RT-PCR. On comparison between above two methods, the detection rate of RT-PCR ELISA for clinical specimens from patients with aseptic meningitis was 7% higher than that of conventional RT-PCR targeting 5'NCR (P=0.016). CONCLUSIONS: Our results suggest that RT-PCR ELISA developed in this study could be an alternative diagnostic method for the detection of enteroviral genome with high sensitivity and specificity.
MeSH Terms
-
5' Untranslated Regions
Adolescent
Child
Child, Preschool
Enterovirus/genetics/*isolation & purification
Enterovirus Infections/*diagnosis
*Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Humans
Infant
Meningitis, Aseptic/diagnosis
RNA, Viral/analysis
*Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
Rotavirus/genetics
Rotavirus Infections/diagnosis
Sensitivity and Specificity
Figure
Reference
-
1.Mayo M., Pringle CR. Virus taxonomy—1997. J Gen Virol. 1998. 79:649–57.
Article2.Pringle CR. Virus taxonomy at the XIth International Congress of Virology, Sydney, Australia, 1999. Arch Virol. 1999. 144:2065–70.
Article3.Zell R., Sidigi K., Henke A., Schmidt-Brauns J., Hoey E., Martin S, et al. Functional features of the bovine enterovirus 5′-non-translated region. J Gen Virol. 1999. 80:2299–309.
Article4.Melnick JL. Enteroviruses: polioviruses, coxsackieviruses, echo-viruses and newer enteroviruses. Fields BN, Knipe DM, editors. Fields virology. 3rd ed.Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven Publishers;1996. p. 655–712.5.Kocwa-Haluch R. Waterborne enteroviruses as a hazard for human health. Polish J Environ Studies. 2001. 10:485–7.6.Roivainen M. Enteroviruses: new findings on the role of enteroviruses in type 1 diabetes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. 38:721–5.
Article7.Yagi S., Schnurr D., Lin J. Spectrum of monoclonal antibodies to coxsackievirus B-3 includes type- and group-specific antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1992. 30:2498–501.
Article8.De Clercq K. Reduction of singleton reactors against swine vesicular disease virus by a combination of virus neutralisation test, monoclonal antibody-based competitive ELISA and isotype specific ELISA. J Virol Methods. 1998. 70:7–18.
Article9.Rotbart HA., Sawyer MH., Fast S., Lewinski C., Murphy N., Keyser EF, et al. Diagnosis of enteroviral meningitis by using PCR with a colorimetric microwell detection assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1994. 32:2590–2.
Article10.Egger D., Pasamontes L., Ostermayer M., Bienz K. Reverse transcription multiplex PCR for differentiation between polio- and entero-viruses from clinical and environmental samples. J Clin Microbiol. 1995. 33:1442–7.
Article11.Kim MB., Kim KS., Bae YB., Song CY., Yoon JD., Lee KH, et al. General primer-mediated PCR detection of enteroviruses causing aseptic meningitis. J Korean Soc Virol. 1996. 26:215–25. (김문보, 김기순, 배유병, 송철용, 윤재득, 이광호 등. General -primer를 이용한 무균성뇌막염원인바이러스분석. 대한바이러스학회지 1996;26:215-25.).12.Taggart EW., Byington CL., Hillyard DR., Robison JE., Carroll KC. Enhancement of the AMPLICOR enterovirus PCR test with a coprecipitant. J Clin Microbiol. 1998. 36:3408–9.
Article13.Ishiko H., Shimada Y., Yonaha M., Hashimoto O., Hayashi A., Sakae K, et al. Molecular diagnosis of human enteroviruses by phylogeny-based classification by use of the VP4 sequence. J Infect Dis. 2002. 185:744–54.
Article14.Zimmermann H., Eggers HJ., Zimmermann A., Kraus W. Nelsen-Salz B. Complete nucleotide sequence and biological properties of an infectious clone of prototype echovirus 9. Virus Res. 1995. 39:311–9.15.Chomczynski P. A reagent for the single-step simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA and proteins from cell and tissue samples. Biotechniques. 1993. 15:532–7.16.Jones ME., Fox AJ., Barnes AJ., Oppenheim BA., Balagopal P., Morgenstern GR, et al. PCR-ELISA for the early diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillus infection in neutropenic patients. J Clin Pathol. 1998. 51:652–6.
Article17.Chonmaitree T., Ford C., Sanders C., Lucia HL. Comparison of cell cultures for rapid isolation of enteroviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1998. 26:2576–80.
Article18.Zoll GJ., Melchers WJ., Kopecka H., Jambroes G., van der Poel HJ., Galama JM. General primer-mediated polymerase chain reaction for detection of enteroviruses: application for diagnosis routine and persistent infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1992. 30:160–5.19.Lomakina NF., Fallacara F., Pacciarini M., Amadori M., Lomakin AI., Timina AM, et al. Application of universal primers for identification of Foot-and-mouth disease virus and Swine vesicular disease virus by PCR and PCR-ELISA. Arch Virol. 2004. 149:1155–70.
Article20.Fong TT., Lipp EK. Enteric viruses humans and animals in aquatic environments: health risks, detection, and potential water quality assessment tools. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005. 69:357–71.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection of Enterovirus in Patients with Aseptic Meningitis by Reverse Transcription and Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Analysis of clinical information and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for early diagnosis of enteroviral meningitis
- The Development of Molecular Detection Method and Differentiation of Genotypes of Enterovirus
- Epidemiologic and Clinical features of Enteroviral Infections in Children, a Single Center Study in Korea: 2009
- Development of a novel reverse transcription PCR and its application to field sample testing for feline calicivirus prevalence in healthy stray cats in Korea