Korean J Lab Med.
2008 Oct;28(5):325-331. 10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.5.325.
Assessment of Hemorheological Deformability of Human Red Cells Exposed to tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide, Verapamil and Ascorbate by Ektacytometer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Pathology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. suhjs@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Mechanical Engineering, School of Engineering, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781563
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.5.325
Abstract
-
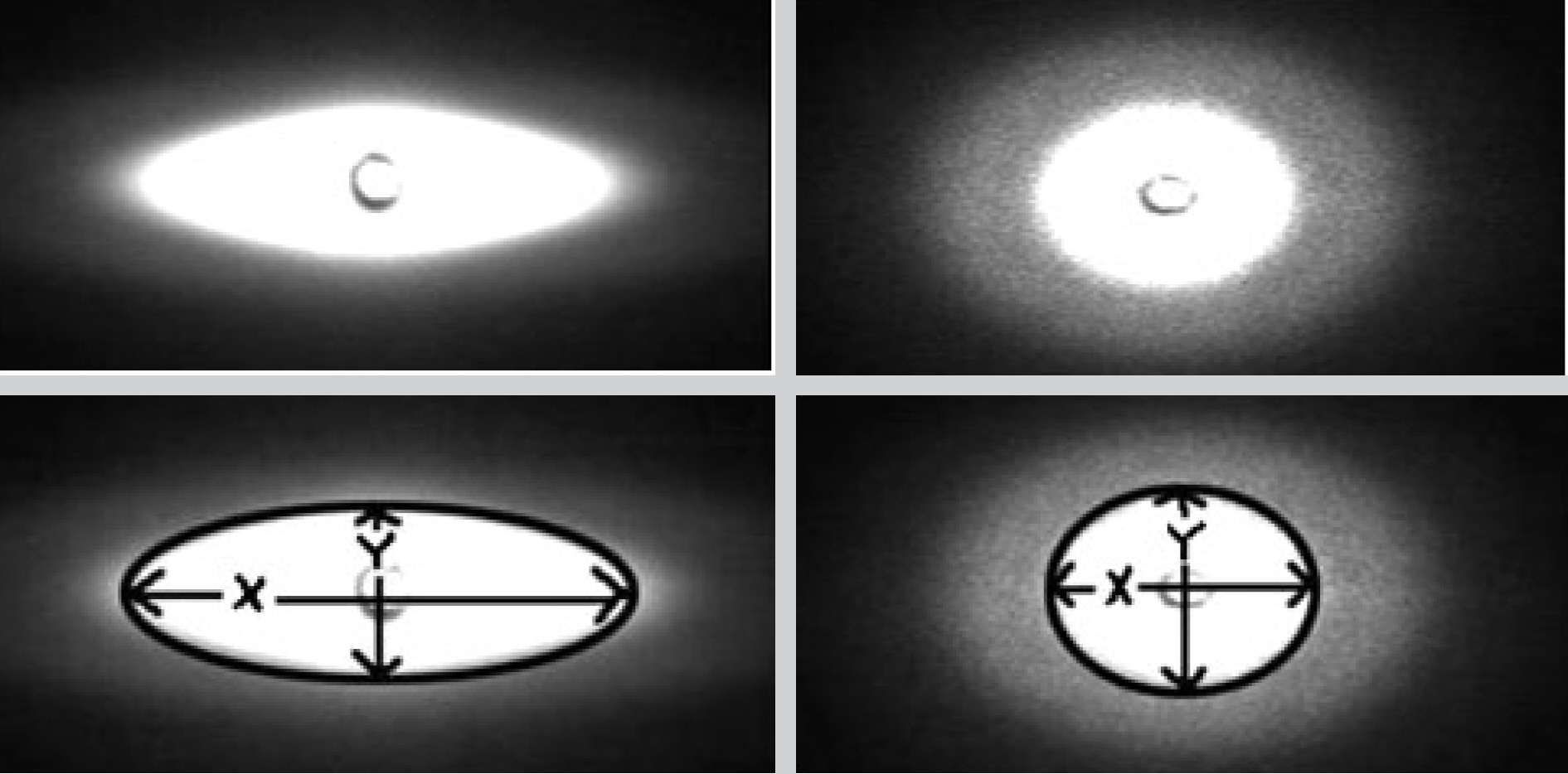
BACKGROUND: Normal erythrocyte is deformable and this facilitates blood flow in the capillaries. Oxidative stress reduces the deformability of erythrocytes, and influences on blood flow in microcirculation. The objective of this study was to investigate the deformability of erythrocytes exposed to oxidative stress, the protective effects of verapamil and ascorbic acid against oxidative damages in erythrocytes, and the value of the microfluidic ektacytometer, RheoScan-D (RheoMeditech, Korea) in clinical application.
METHODS
Effects of oxidative stress on erythrocytes were investigated using tert-butyl hydroperoxide (tBHP). Before exposure to tBHP, the erythrocytes were pretreated with verapamil and ascorbic acid to examine their protective effect against oxidative damages. The deformability of erythrocytes was measured by the microfluidic ektacytometer, RheoScan-D.
RESULTS
When treated with tBHP, the deformability of erythrocytes was decreased (P<0.01) and methemoglobin (metHb) formation and mean corpuscular volume (MCV) of erythrocytes were increased (P<0.01, P<0.05) compared to those of the untreated control cells. Compared to the tBHP treated cells, pretreatment with verapamil increased the deformability of erythrocytes (P<0.01) and decreased metHb formation (P<0.01) and MCV (P<0.05). Likewise, pretreatment with ascorbic acid increased the deformability of erythrocytes (P<0.01) and decreased metHb formation (P<0.01).
CONCLUSIONS
Oxidative stress reduces the deformability of erythrocytes and the deformability could be one of markers for oxidative damage. Verapamil and ascorbic acid have protective role against tBHP induced oxidative stress. The ektacytometer, RheoScan-D used in this study is convenient for clinical measurement and could be used in various fields of clinical medicine.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Antioxidants/pharmacology
Ascorbic Acid/*pharmacology
Calcium Channel Blockers/pharmacology
Erythrocyte Deformability/*drug effects
Erythrocytes/drug effects/physiology
Humans
Male
Microfluidic Analytical Techniques/*instrumentation
Oxidative Stress
Statistics, Nonparametric
Verapamil/*pharmacology
tert-Butylhydroperoxide/*pharmacology
Figure
Reference
-
1.Aleksander SP., Paul CJ. Microcirculation and hemorheology. Fluid Mech. 2005. 37:43–69.2.Carrell RW., Winterbourn CC., Rachmilewitz EA. Activated oxygen and haemolysis. Br J Haematol. 1975. 30:259–64.3.Lynch RE., Fridovich I. Effects of superoxide on the erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1978. 253:1838–45.
Article4.Kong S., Davison AJ. The relative effectiveness of OH, H2O2, O2-, and reducing free radicals in causing damage to biomembranes. A study of radiation damage to erythrocyte ghosts using selective free radical scavengers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981. 640:313–25.5.Davies KJ., Goldberg AL. Oxygen radicals stimulate intracellular proteolysis and lipid peroxidation by independent mechanisms in erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987. 262:8220–6.
Article6.Morgan DL., Furlow TL., Menzel DB. Ozone-initiated changes in erythrocyte membrane and loss of deformability. Environ Res. 1988. 45:108–17.
Article7.Morgan DL., Dorsey AF., Menzel DB. Erythrocytes from ozone-exposed mice exhibit decreased deformability. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1985. 5:137–43.
Article8.Dobbe JG., Streekstra GJ., Hardeman MR., Ince C., Grimbergen CA. Measurement of the distribution of the red blood cell deformability using an automated rheoscope. Cytometry. 2002. 50:313–25.9.Dobbe JG., Hardeman MR., Streekstra GJ., Grimbergen CA. Validation and application of an automated rheoscope for measuring red blood cell deformability distributions in different species. Biorheology. 2004. 41:65–77.10.Hardeman MR., Goedhart PT., Dobbe JGG., Lettinga KP. Laser-assisted optical rotational cell analyser (LOCRA): 1. a new instrument for measurement of various structural hemorheological parameters. Clin Hemorheol. 1994. 14:605–18.11.Kim YK., Ku Y., Shin S., Suh JS., Song KE. Association between oxidative stress and RBC deformability. Korean J Lab Med. 2005. 25(S2):S659. (김유경, 구윤희, 신세현, 서장수, 송경은. 산화 스트레스와 적혈구가변형성의관련성. 대한진단검사의학회지 2005;25 (S2): S659.).12.Shin S., Ku Y., Park MS., Jang JH., Suh JS. Rapid cell-deformability sensing system based on slit-flow laser diffractometry with decreasing pressure differential. Biosens Bioelectron. 2005. 20:1291–7.
Article13.Corry WD., Meiselman HJ., Hochstein P. t-Butyl hydroperoxide induced changes in the physicochemical properties of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980. 597:224–34.14.Trotta RJ., Sullivan SG., Stern A. Lipid peroxidation and haemoglobin degradation in red blood cells exposed to t-butyl hydroperoxide. The relative roles of haem- and glutathione-dependent decomposition of t-butyl hydroperoxide and membrane lipid hydroperoxides in lipid peroxidation and haemolysis. Biochem J. 1983. 212:759–72.
Article15.Dise CA., Goodman DB. t-Butyl hydroperoxide alters fatty acid incorporation into erythrocyte membrane phospholipid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986. 859:69–78.
Article16.Deuticke B., Heller KB., Haest CW. Progressive oxidative membrane damage in erythrocytes after pulse treatment with t-butyl hydroperoxide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987. 899:113–24.17.Moore RB., Bamberg AD., Wilson LC., Jenkins LD., Mankad VN. Ascorbate protects against tert-butyl hydroperoxide inhibition of erythrocyte membrane Ca2+ + Mg2 (+)-ATPase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990. 278:416–24.18.Rohb TT., Hinds TR., Vincenzi FF. Inhibition of the Ca2+ pump of intact red blood cells by t-butyl hydroperoxide: importance of glutathione peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993. 1153:67–76.19.Van der Zee J., Van Steveninck J., Koster JF., Dubbelman TM. Inhibition of enzymes and oxidative damage of red blood cells induced by t-butyl hydroperoxide derived radicals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989. 980:175–80.20.Simmons A, editor. Technical Hematology. 3rd ed.Philadelphia: J. B. Lippincott Company;1983. p. 13–8.21.Hanss M. Erythrocyte filtrability measurement by the initial flow rate method. Biorheology. 1983. 20:199–211.
Article22.Koutsouris D., Guillet R., Lelievre JC., Guillemin MT., Bertholom P., Beuzard Y, et al. Determination of erythrocyte transit times through micropores. I–Basic operational principles. Biorheology. 1988. 25:763–72.
Article23.Baskurt OK. Deformability of red blood cells from different species studied by resistive pulse shape analysis technique. Biorheology. 1996. 33:169–79.
Article24.Schmid-Schoenbein H., Wells R., Schildkraut R. Microscopy and viscometry of blood flowing under uniform shear rate (rheoscopy). J Appl Physiol. 1969. 26:674–8.25.Nakamura T., Hasegawa S., Shio H., Uyesaka N. Rheologic and pathophysiologic significance of red cell passage through narrow pores. Blood Cells. 1994. 20:151–65.26.Jarolim P., Lahav M., Liu SC., Palek J. Effect of hemoglobin oxidation products on the stability of red cell membrane skeletons and the associations of skeletal proteins: correlation with a release of hemin. Blood. 1990. 76:2125–31.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of Ca2+ influx in the tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced apoptosis of HepG2 human hepatoblastoma cellse
- Antioxidant effects of serotonin and L-DOPA on oxidative damages of brain synaptosomes
- Changes in the Physical Properties of Irradiated Red Blood Cells
- Usefulness of Frozen-thawed-deglycerolized Red Blood Cells as Quality Control Materials for Red Blood Cell Deformability Test
- Effect of Dipyridamole on the Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress in Trabecular Meshwork Cells