Yonsei Med J.
2014 Jan;55(1):209-215. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.209.
Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Sevoflurane Requirements and Emergence Agitation in Children Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hkkil@yuhs.ac
- 2Anesthesia and Pain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779908
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.209
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Dexmedetomidine, a potent selective alpha2-adrenergic agonist, produces sedation and analgesia. This study was conducted to assess the effect of dexmedetomidine infusion on sevoflurane requirements, recovery profiles, and emergence agitation in children undergoing ambulatory surgery.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty children undergoing ambulatory hernioplasty or orchiopexy were randomized into two groups. The dexmedetomidine group (Group D, n=20) received dexmedetomidine 1 microg/kg, followed by 0.1 microg/kg/h until the end of surgery, whereas the saline group (Group S, n=20) received volume-matched normal saline. Sevoflurane was used for induction and maintenance of anesthesia and caudal block was performed in all children. End-tidal sevoflurane concentration (ET-sevo), the incidence of emergence agitation, pain scores, and sedation scores were recorded. Hemodynamic changes and other adverse effects were assessed in the perioperative period.
RESULTS
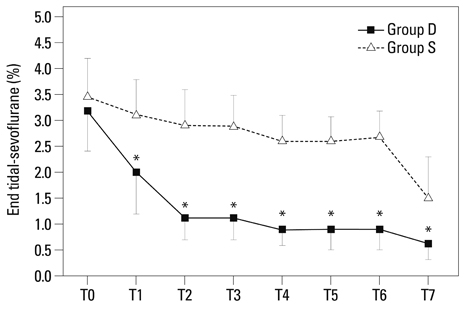
ET-sevo of Group D was significantly reduced in 23.8-67% compared to Group S during surgery. The incidence of emergence agitation was lower in Group D than in Group S (5% vs. 55%, p=0.001). Postoperative pain was comparable, and discharge time was not different between the groups. Mean arterial pressure and heart rate were significantly lower in Group D during surgery.
CONCLUSION
Intraoperative infusion of dexmedetomidine reduced sevoflurane requirements and decreased emergence agitation without delaying discharge in children undergoing ambulatory surgery. However, caution should be taken in regard to bradycardia and hypotension.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Emergence agitation: current knowledge and unresolved questions
Seok-Jin Lee, Tae-Yun Sung
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2020;73(6):471-485. doi: 10.4097/kja.20097.
Reference
-
1. Su F, Hammer GB. Dexmedetomidine: pediatric pharmacology, clinical uses and safety. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2011; 10:55–66.
Article2. Mason KP, Lerman J. Review article: dexmedetomidine in children: current knowledge and future applications. Anesth Analg. 2011; 113:1129–1142.3. Hall JE, Uhrich TD, Barney JA, Arain SR, Ebert TJ. Sedative, amnestic, and analgesic properties of small-dose dexmedetomidine infusions. Anesth Analg. 2000; 90:699–705.
Article4. Patel A, Davidson M, Tran MC, Quraishi H, Schoenberg C, Sant M, et al. Dexmedetomidine infusion for analgesia and prevention of emergence agitation in children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome undergoing tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. Anesth Analg. 2010; 111:1004–1010.
Article5. Al-Zaben KR, Qudaisat IY, Al-Ghanem SM, Massad IM, Al-Mustafa MM, Al-Oweidi AS, et al. Intraoperative administration of dexmedetomidine reduces the analgesic requirements for children undergoing hypospadius surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2010; 27:247–252.
Article6. Lili X, Jianjun S, Haiyan Z. The application of dexmedetomidine in children undergoing vitreoretinal surgery. J Anesth. 2012; 26:556–561.
Article7. Lerman J, Davis PJ, Welborn LG, Orr RJ, Rabb M, Carpenter R, et al. Induction, recovery, and safety characteristics of sevoflurane in children undergoing ambulatory surgery. A comparison with halothane. Anesthesiology. 1996; 84:1332–1340.
Article8. Bock M, Kunz P, Schreckenberger R, Graf BM, Martin E, Motsch J. Comparison of caudal and intravenous clonidine in the prevention of agitation after sevoflurane in children. Br J Anaesth. 2002; 88:790–796.
Article9. Cravero J, Surgenor S, Whalen K. Emergence agitation in paediatric patients after sevoflurane anaesthesia and no surgery: a comparison with halothane. Paediatr Anaesth. 2000; 10:419–424.
Article10. Moore JK, Moore EW, Elliott RA, St Leger AS, Payne K, Kerr J. Propofol and halothane versus sevoflurane in paediatric day-case surgery: induction and recovery characteristics. Br J Anaesth. 2003; 90:461–466.
Article11. Guler G, Akin A, Tosun Z, Ors S, Esmaoglu A, Boyaci A. Single-dose dexmedetomidine reduces agitation and provides smooth extubation after pediatric adenotonsillectomy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2005; 15:762–766.
Article12. Shukry M, Clyde MC, Kalarickal PL, Ramadhyani U. Does dexmedetomidine prevent emergence delirium in children after sevoflurane-based general anesthesia? Paediatr Anaesth. 2005; 15:1098–1104.
Article13. Sato M, Shirakami G, Tazuke-Nishimura M, Matsuura S, Tanimoto K, Fukuda K. Effect of single-dose dexmedetomidine on emergence agitation and recovery profiles after sevoflurane anesthesia in pediatric ambulatory surgery. J Anesth. 2010; 24:675–682.
Article14. Na HS, Song IA, Hwang JW, Do SH, Oh AY. Emergence agitation in children undergoing adenotonsillectomy: a comparison of sevoflurane vs. sevoflurane-remifentanil administration. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2013; 57:100–105.
Article15. Aouad MT, Yazbeck-Karam VG, Nasr VG, El-Khatib MF, Kanazi GE, Bleik JH. A single dose of propofol at the end of surgery for the prevention of emergence agitation in children undergoing strabismus surgery during sevoflurane anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 2007; 107:733–738.
Article16. Cohen IT, Finkel JC, Hannallah RS, Hummer KA, Patel KM. The effect of fentanyl on the emergence characteristics after desflurane or sevoflurane anesthesia in children. Anesth Analg. 2002; 94:1178–1181.
Article17. Meng QT, Xia ZY, Luo T, Wu Y, Tang LH, Zhao B, et al. Dexmedetomidine reduces emergence agitation after tonsillectomy in children by sevoflurane anesthesia: a case-control study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; 76:1036–1041.
Article18. Isik B, Arslan M, Tunga AD, Kurtipek O. Dexmedetomidine decreases emergence agitation in pediatric patients after sevoflurane anesthesia without surgery. Paediatr Anaesth. 2006; 16:748–753.
Article19. Weldon BC, Watcha MF, White PF. Oral midazolam in children: effect of time and adjunctive therapy. Anesth Analg. 1992; 75:51–55.20. Weldon BC, Bell M, Craddock T. The effect of caudal analgesia on emergence agitation in children after sevoflurane versus halothane anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2004; 98:321–326.
Article21. Watcha MF, Ramirez-Ruiz M, White PF, Jones MB, Lagueruela RG, Terkonda RP. Perioperative effects of oral ketorolac and acetaminophen in children undergoing bilateral myringotomy. Can J Anaesth. 1992; 39:649–654.
Article22. McGrath PJ, Johnson G, Schillinger JT. The Children of Eastern Ontario Pain Scale CHEOPS: a behavioral scale for rating postoperative pain in children. In : Fields HL, Dubner R, Cervero F, editors. Advances in Pain Research and Therapy, Volume 9: Proceedings of the Fourth World Congress on Pain. New York: Raven Press;1985. p. 395–402.23. Voepel-Lewis T, Zanotti J, Dammeyer JA, Merkel S. Reliability and validity of the face, legs, activity, cry, consolability behavioral tool in assessing acute pain in critically ill patients. Am J Crit Care. 2010; 19:55–61.
Article24. Ramsay MA, Savege TM, Simpson BR, Goodwin R. Controlled sedation with alphaxalone-alphadolone. Br Med J. 1974; 2:656–659.
Article25. Magalhães E, Govêia CS, Ladeira LC, Espíndola BV. [Relationship between dexmedetomidine continuous infusion and end-tidal sevoflurane concentration, monitored by bispectral analysis.]. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2004; 54:303–310.26. Guo TZ, Jiang JY, Buttermann AE, Maze M. Dexmedetomidine injection into the locus ceruleus produces antinociception. Anesthesiology. 1996; 84:873–881.
Article27. Tufanogullari B, White PF, Peixoto MP, Kianpour D, Lacour T, Griffin J, et al. Dexmedetomidine infusion during laparoscopic bariatric surgery: the effect on recovery outcome variables. Anesth Analg. 2008; 106:1741–1748.
Article28. Fragen RJ, Fitzgerald PC. Effect of dexmedetomidine on the minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) of sevoflurane in adults age 55 to 70 years. J Clin Anesth. 1999; 11:466–470.
Article29. Ohtani N, Kida K, Shoji K, Yasui Y, Masaki E. Recovery profiles from dexmedetomidine as a general anesthetic adjuvant in patients undergoing lower abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg. 2008; 107:1871–1874.
Article30. Drummond JC. Monitoring depth of anesthesia: with emphasis on the application of the bispectral index and the middle latency auditory evoked response to the prevention of recall. Anesthesiology. 2000; 93:876–882.31. Nunes RR, Cavalcante SL. Influence of dexmedetomidine upon sevoflurane end-expiratory concentration. Evaluation by bispectral index, suppression rate and electroencephalographic power spectral analysis. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2002; 52:133–145.32. Dawson C, Ma D, Chow A, Maze M. Dexmedetomidine enhances analgesic action of nitrous oxide: mechanisms of action. Anesthesiology. 2004; 100:894–904.33. Aantaa R, Jaakola ML, Kallio A, Kanto J. Reduction of the minimum alveolar concentration of isoflurane by dexmedetomidine. Anesthesiology. 1997; 86:1055–1060.
Article34. Komatsu H, Taie S, Endo S, Fukuda K, Ueki M, Nogaya J, et al. Electrical seizures during sevoflurane anesthesia in two pediatric patients with epilepsy. Anesthesiology. 1994; 81:1535–1537.
Article35. Woodforth IJ, Hicks RG, Crawford MR, Stephen JP, Burke DJ. Electroencephalographic evidence of seizure activity under deep sevoflurane anesthesia in a nonepileptic patient. Anesthesiology. 1997; 87:1579–1582.
Article36. Kim JM, Lee JH, Lee HJ, Koo BN. Comparison of emergence time in children undergoing minor surgery according to anesthetic: desflurane and sevoflurane. Yonsei Med J. 2013; 54:732–738.
Article37. Dahmani S, Stany I, Brasher C, Lejeune C, Bruneau B, Wood C, et al. Pharmacological prevention of sevoflurane- and desflurane-related emergence agitation in children: a meta-analysis of published studies. Br J Anaesth. 2010; 104:216–223.
Article38. Pestieau SR, Quezado ZM, Johnson YJ, Anderson JL, Cheng YI, McCarter RJ, et al. High-dose dexmedetomidine increases the opioid-free interval and decreases opioid requirement after tonsillectomy in children. Can J Anaesth. 2011; 58:540–550.
Article39. Hammer GB, Drover DR, Cao H, Jackson E, Williams GD, Ramamoorthy C, et al. The effects of dexmedetomidine on cardiac electrophysiology in children. Anesth Analg. 2008; 106:79–83.
Article40. Sikich N, Lerman J. Development and psychometric evaluation of the pediatric anesthesia emergence delirium scale. Anesthesiology. 2004; 100:1138–1145.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Combined Use of Remifentanil on Postoperative Recovery Time and Emergence Agitation during Sevoflurane Anesthesia in Children
- The Effect of Ondansetron on the Emergence Agitation after Sevoflurane Anesthesia in Pediatric Patients Undergoing Tonsillectomy
- The Effect of Ketamine and Fentanyl on the Incidence of Emergence Agitation after Sevoflurane Anesthesia in Children undergoing Tonsillectomy
- Effects of propofol and nalbuphine on emergence agitation after sevoflurane anesthesia in children for strabismus surgery
- Appropriate Dose of Fentanyl for the Prevention of Emergence Agitation after Sevoflurane Anesthesia in Pediatric Patients undergoing Tonsillectomy