J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Feb;25(2):235-239. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.235.
Prognostic Value of p53 and bcl-2 Expression in Patients Treated with Breast Conservative Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. swha@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Institute of Radiation Medicine, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779253
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.235
Abstract
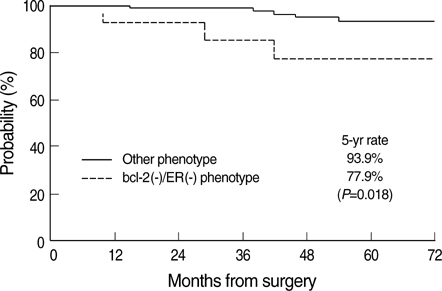
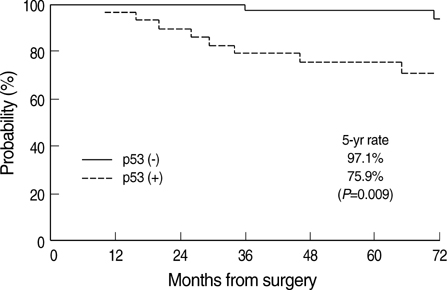
- Prognostic value of p53 and bcl-2 expression on treatment outcome in breast cancer patients has been extensively evaluated, but the results were inconclusive. We evaluated the prognostic significance of these molecular markers in patients treated with breast conserving surgery and radiotherapy. One hundred patients whose immunostaining of p53 and bcl-2 expression was available among 125 patients who underwent radiotherapy after breast conserving surgery and axillary lymph node dissection were enrolled into this study. Eighty-seven patients also received adjuvant chemotherapy and/or hormonal therapy. Conventional clinicopathologic variables and treatment-related factors were also considered. The 5-yr loco-regional relapse-free and distant metastasis-free survival rates were 91.7% and 90.9%, respectively. On univariate analysis, age, T stage and the absence of bcl-2 & estrogen receptor (ER) expression were associated with loco-regional relapse-free survival. When incorporating these variables into Cox proportional hazard model, only bcl-2(-)/ER(-) phenotype was an adverse prognostic factor (P=0.018). As for the distant metastasis-free survival, age, T stage, and p53 expression were significant on univariate analysis. However, p53 expression was the only prognosticator on multivariate analysis (P=0.009). A bcl-2(-)/ER(-) phenotype and p53 expression are useful molecular markers predicting loco-regional relapse-free and distant metastasis-free survival, respectively, in patients treated with breast conserving surgery and radiotherapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Breast Neoplasms/metabolism/radiotherapy/*surgery
Combined Modality Therapy
Disease-Free Survival
Female
Humans
*Mastectomy, Segmental
Middle Aged
Multivariate Analysis
Phenotype
Prognosis
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-bcl-2/genetics/*metabolism
Receptors, Estrogen/metabolism
Tumor Suppressor Protein p53/genetics/*metabolism
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-bcl-2
Receptors, Estrogen
Tumor Suppressor Protein p53
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Different Prognostic Significance of Bcl-2 Based on Cancer Molecular Subtype
Ju-Young Lee, Hyun-Ah Kim, Eun-Kyu Kim, Hoe-Min Yang, Kwan-il Kim, Jong Inn Lee, Jae Soo Koh, Eunyoung Ko, Nan Mo Moon, Min-Suk Kim, Nam-Sun Paik, Woo Chul Noh
J Breast Cancer. 2011;14(Suppl 1):S10-S16. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2011.14.S.S10.Analysis of the Potent Prognostic Factors in Luminal-Type Breast Cancer
Han-Sung Kim, Inseok Park, Hyun Jin Cho, Geumhee Gwak, Keunho Yang, Byung Noe Bae, Ki Whan Kim, Sehwan Han, Hong-Joo Kim, Young-Duck Kim
J Breast Cancer. 2012;15(4):401-406. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2012.15.4.401.
Reference
-
1. Cianfrocca M, Goldstein LJ. Prognostic and predictive factors in early-stage breast cancer. Oncologist. 2004. 9:606–616.
Article2. Alizadeh AA, Ross DT, Perou CM, van de Rijn M. Towards a novel classification of human malignancies based on gene expression patterns. J Pathol. 2001. 195:41–52.
Article3. Thor AD, Moore DH II, Edgerton SM, Kawasaki ES, Reihsaus E, Lynch HT, Marcus JN, Schwartz L, Chen LC, Mayall BH, Smith HS. Accumulation of p53 tumor suppressor gene protein: an independent marker of prognosis in breast cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992. 84:845–855.
Article4. Bergh J, Norberg T, Sjogren S, Lindgren A, Holmberg L. Complete sequencing of the p53 gene provides prognostic information in breast cancer patients, particularly in relation to adjuvant systemic therapy and radiotherapy. Nat Med. 1995. 1:1029–1034.
Article5. Silvestrini R, Veneroni S, Daidone MG, Benini E, Boracchi P, Mezzetti M, Di Fronzo G, Rilke F, Veronesi U. The Bcl-2 protein: a prognostic indicator strongly related to p53 protein in lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994. 86:499–504.
Article6. Zhang GJ, Tsuda H, Adachi I, Fukutomi T, Yamamoto H, Hirohashi S. Prognostic indicators for breast cancer patients with one to three regional lymph node metastases, with special reference to alterations in expression levels of bcl-2, p53 and c-erbB-2 proteins. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1997. 27:371–377.
Article7. Chen HH, Su WC, Guo HR, Chang TW, Lee WY. p53 and c-erbB-2 but not bcl-2 are predictive of metastasis-free survival in breast cancer patients receiving post-mastectomy adjuvant radiotherapy in Taiwan. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2002. 32:332–339.
Article8. Silvestrini R, Veneroni S, Benini E, Daidone MG, Luisi A, Leutner M, Maucione A, Kenda R, Zucali R, Veronesi U. Expression of p53, glutathione S-transferase-pi and Bcl-2 proteins and benefit from adjuvant radiotherapy in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997. 89:639–645.9. Noguchi S, Koyama H, Kasugai T, Tsukuma H, Tsuji N, Tsuda H, Akiyama F, Motomura K, Inaji H. A case-control study on risk factors for local recurrences of distant metastases in breast cancer patients treated with breast-conserving surgery. Oncology. 1997. 54:468–474.10. Elkhuizen PH, Voogd AC, van den Broek LC, Tan IT, van Houwelingen HC, Leer JW, van de Vijver MJ. Risk factors for local recurrence after breast-conserving therapy for invasive carcinomas: a case-control study of histological factors and alterations in oncogene expression. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999. 45:73–83.
Article11. Choi DH, Kim S, Rimm DL, Carter D, Haffty BG. Immunohistochemical biomarkers in patients with early-onset breast carcinoma by tissue microarray. Cancer J. 2005. 11:404–411.
Article12. Gasparini G, Barbareschi M, Doglioni C, Palma PD, Mauri FA, Boracchi P, Bevilacqua P, Caffo O, Morelli L, Verderio P, Pezzella F, Harris AL. Expression of bcl-2 protein predicts efficacy of adjuvant treatments in operable node-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1995. 1:189–198.13. Lê MG, Mathieu MC, Douc-Rasy S, Le Bihan ML, Adb El All H, Spielmann M, Riou G. c-myc, p53 and bcl-2, apoptosis-related genes in infiltrating breast carcinomas: evidence of a link between bcl-2 protein over-expression and a lower risk of metastasis and death in operable patients. Int J Cancer. 1999. 84:562–567.14. Neri A, Marrelli D, Roviello F, DeMarco G, Mariani F, DeStefano A, Megha T, Caruso S, Corso G, Cioppa T, Pinto E. Bcl-2 expression correlates with lymphovascular invasion and long-term prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006. 99:77–83.
Article15. Turner BC, Gumbs AA, Carbone CJ, Carter D, Glazer PM, Haffty BG. Mutant p53 protein overexpression in women with ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence following lumpectomy and radiation therapy. Cancer. 2000. 88:1091–1098.
Article16. Kim KJ, Huh SJ, Yang JH, Park W, Nam SJ, Kim JH, Lee JH, Kang SS, Lee JE, Kang MK, Park YJ, Nam HR. Treatment results and prognostic factors of early breast cancer treated with a breast conserving operation and radiotherapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2005. 35:126–133.
Article17. Rolland P, Spendlove I, Madjid Z, Rakha EA, Patel P, Ellis IO, Durrant L. The p53 positive Bcl-2 negative phenotype is an independent marker of prognosis in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007. 120:1311–1317.
Article18. Hellemans P, van Dam PA, Weyler J, van Oosterom AT, Buytaert P, van Marck E. Prognostic value of bcl-2 expression in invasive breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1995. 72:354–360.
Article19. Berardo MD, Elledge RM, de Moor C, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Allred DC. Bcl-2 and apoptosis in lymph node positive breast carcinoma. Cancer. 1998. 82:1296–1302.
Article20. Callagy GM, Pharoah PD, Pinder SE, Hsu FD, Nielsen TO, Ragaz J, Ellis IO, Huntsman D, Caldas C. Bcl-2 is a prognostic marker in breast cancer independently of the Nottingham Prognostic Index. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. 12:2468–2475.
Article21. Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M, Kearney T, Higgins SA, Weidhaas J, Harris L, Hait W, Toppmeyer D. Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:5652–5657.
Article22. Nguyen PL, Taghian AG, Katz MS, Niemierko A, Abi Raad RF, Boon WL, Bellon JR, Wong JS, Smith BL, Harris JR. Breast cancer subtype approximated by estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER-2 is associated with local and distant recurrence after breast-conserving therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2008. 26:2373–2378.
Article23. Freedman GM, Anderson PR, Li T, Nicolaou N. Locoregional recurrence of triple-negative breast cancer after breast-conserving surgery and radiation. Cancer. 2009. 115:946–951.
Article24. Tan DS, Marchio C, Jones RL, Savage K, Smith IE, Dowsett M, Reis-Filho JS. Triple negative breast cancer: molecular profiling and prognostic impact in adjuvant anthracycline-treated patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008. 111:27–44.
Article25. Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, Lee AH, Robertson JF, Ellis IO. Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer. 2007. 109:25–32.
Article26. Bidard FC, Matthieu MC, Chollet P, Raoefils I, Abrial C, Domont J, Spielmann M, Delaloge S, Andre F, Penault-Llorca F. p53 status and efficacy of primary anthracyclines/alkylating agent-based regimen according to breast cancer molecular classes. Ann Oncol. 2008. 19:1261–1265.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of p53, c-erbB2, bcl-2, Cathepsin D in Infiltrating Ductal Cancer of the Breast
- A Study of Apoptosis, and bcl-2 and p53 Expressions in Breast Cancer
- Expression of p53, c-erbB2, bcl-2, Cathepsin D in Infiltrating Ductal Cancer of the Breast
- Clinicopathological Correlation of Bcl-2 and p53 Immunohistochemistry in Breast Cancer
- Expression of p21, p53 and bcl-2 Proteins in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast