J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Feb;25(2):203-210. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.203.
Comparison of Four Pancreatic Islet Implantation Sites
- Affiliations
-
- 1Xenotransplantation Research Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. chgpark@snu.ac.kr
- 2Cancer Research Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Transplantation Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779248
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.203
Abstract
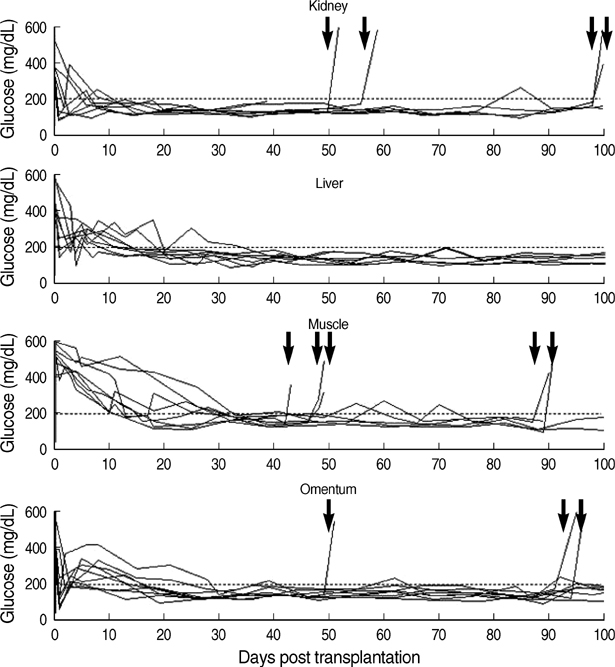
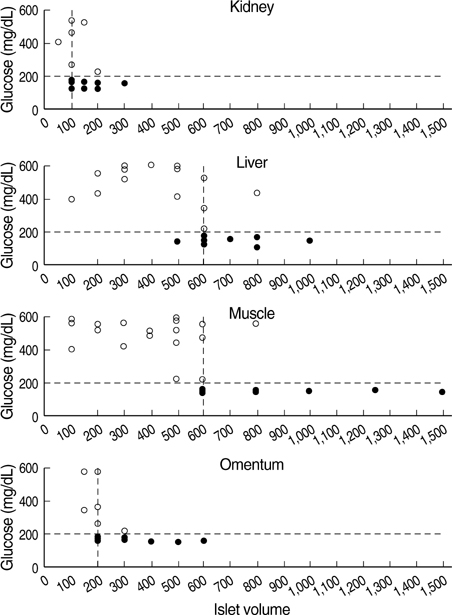
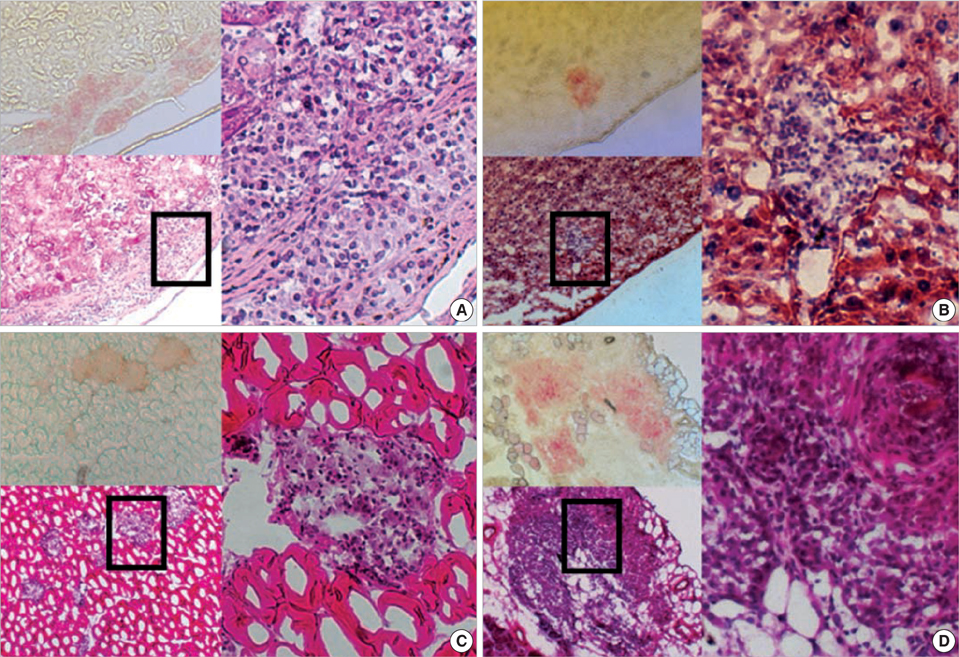
- Although the liver is the most common site for pancreatic islet transplantation, it is not optimal. We compared kidney, liver, muscle, and omentum as transplantation sites with regard to operative feasibility, and the efficiency of implantation and glycemic control. Islets from C57BL/6 mice were transplanted into diabetic syngeneic recipients. The mean operative time and mortality were measured to assess feasibility. To assess implantation efficiency, the marginal mass required to cure diabetes and the mean time taken to achieve normoglycemia were measured. A glucose tolerance test was performed to assess glycemic control efficiency. The data are listed in the order of the kidney, liver, muscle, and omentum, respectively. The mean mortality rate was 6.7, 20.0, 7.1, and 12.5%; the mean operative time was 10.2, 27.4, 11.2, and 19.8 min; the marginal islet mass was 100, 600, 600, and 200 islet equivalence units and the mean time to reach euglycemia was 3.0, 15.1, 26.6, and 13.9 days. The glucose kinetics of omental pouch islets was the most similar to controls. Thus, a strategic approach is required for deciding on the best transplantation recipient sites after considering donor sources and islet volume. Alternatives can be chosen based on safety or efficacy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, Korbutt GS, Toth E, Warnock GL, Kneteman NM, Rajotte RV. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000. 343:230–238.
Article2. Ryan EA, Paty BW, Senior PA, Bigam D, Alfadhli E, Kneteman NM, Lakey JR, Shapiro AM. Five-year follow-up after clinical islet transplantation. Diabetes. 2005. 54:2060–2069.
Article3. Bennet W, Sundberg B, Groth CG, Brendel MD, Brandhorst D, Brandhorst H, Bretzel RG, Elgue G, Larsson R, Nilsson B, Korsgren O. Incompatibility between human blood and isolated islets of Langerhans: a finding with implications for clinical intraportal islet transplantation? Diabetes. 1999. 48:1907–1914.
Article4. Caiazzo R, Gmyr V, Hubert T, Delalleau N, Lamberts R, Moerman E, Kerr-Conte J, Pattou F. Evaluation of alternative sites for islet transplantation in the minipig: interest and limits of the gastric submucosa. Transplant Proc. 2007. 39:2620–2623.
Article5. Korsgren O, Lundgren T, Felldin M, Foss A, Isaksson B, Permert J, Persson NH, Rafael E, Ryden M, Salmela K, Tibell A, Tufveson G, Nilsson B. Optimising islet engraftment is critical for successful clinical islet transplantation. Diabetologia. 2008. 51:227–232.
Article6. Mellgren A, Schnell Landstrom AH, Petersson B, Andersson A. The renal subcapsular site offers better growth conditions for transplanted mouse pancreatic islet cells than the liver or spleen. Diabetologia. 1986. 29:670–672.
Article7. Hiller WF, Klempnauer J, Luck R, Steiniger B. Progressive deterioration of endocrine function after intraportal but not kidney subcapsular rat islet transplantation. Diabetes. 1991. 40:134–140.
Article8. Kemp CB, Knight MJ, Scharp DW, Ballinger WF, Lacy PE. Effect of transplantation site on the results of pancreatic islet isografts in diabetic rats. Diabetologia. 1973. 9:486–491.
Article9. Axen KV, Pi-Sunyer FX. Long-term reversal of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats by intramuscular islet implantation. Transplantation. 1981. 31:439–441.
Article10. Yasunami Y, Lacy PE, Finke EH. A new site for islet transplantation--a peritoneal-omental pouch. Transplantation. 1983. 36:181–182.
Article11. Juang JH, Hsu BR, Kuo CH. Islet transplantation at subcutaneous and intramuscular sites. Transplant Proc. 2005. 37:3479–3481.
Article12. Kin T, Korbutt GS, Rajotte RV. Survival and metabolic function of syngeneic rat islet grafts transplanted in the omental pouch. Am J Transplant. 2003. 3:281–285.
Article13. Tchervenivanov N, Yuan S, Lipsett M, Agapitos D, Rosenberg L. Morphological and functional studies on submucosal islet transplants in normal and diabetic hamsters. Cell Transplant. 2002. 11:529–537.
Article14. Ao Z, Matayoshi K, Lakey JR, Rajotte RV, Warnock GL. Survival and function of purified islets in the omental pouch site of outbred dogs. Transplantation. 1993. 56:524–529.
Article15. Gray DW, Sutton R, McShane P, Peters M, Morris PJ. Exocrine contamination impairs implantation of pancreatic islets transplanted beneath the kidney capsule. J Surg Res. 1988. 45:432–442.
Article16. Jindal RM, Sidner RA, McDaniel HB, Johnson MS, Fineberg SE. Intraportal vs kidney subcapsular site for human pancreatic islet transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1998. 30:398–399.
Article17. Kamei T, Yasunami Y. Demonstration of donor specific unresponsiveness in rat islet allografts: importance of transplant site for induction by cyclosporin A and maintenance. Diabetologia. 1989. 32:779–785.
Article18. Bennet W, Bjorkland A, Sundberg B, Brandhorst D, Brendel MD, Richards A, White DJ, Nilsson B, Groth CG, Korsgren O. Expression of complement regulatory proteins on islets of Langerhans: a comparison between human islets and islets isolated from normal and hDAF transgenic pigs. Transplantation. 2001. 72:312–319.19. Dombrowski F, Mathieu C, Evert M. Hepatocellular neoplasms induced by low-number pancreatic islet transplants in autoimmune diabetic BB/Pfd rats. Cancer Res. 2006. 66:1833–1843.
Article20. Alejandro R, Cutfield RG, Shienvold FL, Polonsky KS, Noel J, Olson L, Dillberger J, Miller J, Mintz DH. Natural history of intrahepatic canine islet cell autografts. J Clin Invest. 1986. 78:1339–1348.
Article21. Hughes SJ, Davies SE, Powis SH, Press M. Hyperoxia improves the survival of intraportally transplanted syngeneic pancreatic islets. Transplantation. 2003. 75:1954–1959.
Article22. Yonekawa Y, Okitsu T, Wake K, Iwanaga Y, Noguchi H, Nagata H, Liu X, Kobayashi N, Matsumoto S. A new mouse model for intraportal islet transplantation with limited hepatic lobe as a graft site. Transplantation. 2006. 82:712–715.
Article23. al-Abdullah IH, Anil Kumar MS, Kelly-Sullivan D, Abouna GM. Site for unpurified islet transplantation is an important parameter for determination of the outcome of graft survival and function. Cell Transplant. 1995. 4:297–305.
Article24. Kaufman DB, Morel P, Field MJ, Munn SR, Sutherland DE. Purified canine islet autografts. Functional outcome as influenced by islet number and implantation site. Transplantation. 1990. 50:385–391.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current status of pancreatic islet xenotransplantation
- Pancreatic islet-cell adenoma
- Immunohistochemical Study on the Distribution of Carbonic Anhydrase Isozymes in Pancreatic Islet of Rat
- A Case of Nonfunctioning Pancreatic Islet Cell Carcinomas in Adolescence
- History, current status and perspective of islet transplantation