J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Apr;24(2):357-359. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.357.
Massive Empyema Associated With Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy and IgA Deficiency
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Cadiovascular Surgery, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. leekyungyil@catholic.ac.kr
- 3Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779147
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.357
Abstract
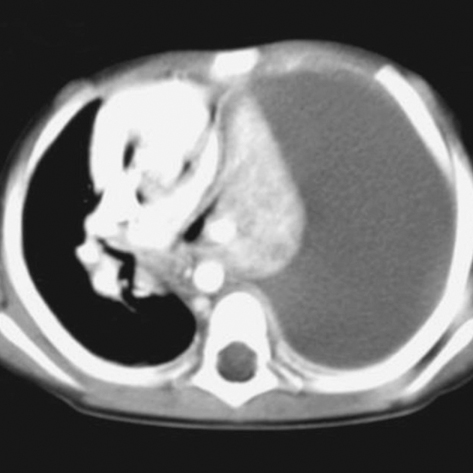
- Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy (THI) is originally defined as a physiological maturation defect of immunoglobulin G (IgG) production that occurs at 3-6 months of age and lasts until 18 to 36 months of age. We report here on a 22-month-old child with THI and IgA deficiency, who had massive pneumococcal empyema. Her depressed IgG level returned to normal within 6 months, but IgA level was still low at 6 yr of age. Although THI is an age-dependent and self-limiting disorder, severe infection that includes an atypical presentation of an infection may occur in some patients and this requires evaluation with immunologic study.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Agammaglobulinemia/complications/*diagnosis/immunology
Anti-Bacterial Agents/therapeutic use
Ceftriaxone/therapeutic use
Drug Resistance, Bacterial
Empyema, Pleural/*diagnosis/etiology/radiography
Female
Humans
IgA Deficiency/*diagnosis/immunology
Immunoglobulin A/blood
Immunoglobulin G/blood
Infant
Staphylococcal Infections/*diagnosis/drug therapy/microbiology
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shen YH, Hwang KP, Niu CK. Complicated parapneumonic effusion and empyema in children. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2006. 39:483–488.2. McGeady SJ. Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy; need to reconsider name and definition. J Pediatr. 1987. 110:47–50.
Article3. Kilic SS, Tezcan I, Sanal O, Metin A, Ersoy F. Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy: clinical and immunological features of 40 new cases. Pediatr Int. 2000. 42:647–650.4. Kidon MI, Handzel ZT, Schwartz R, Altboum I, Stein M, Zan-Bar I. Symptomatic hypogammaglobulinemia in infancy and childhood: clinical outcome and in vitro immune responses. BMC Fam Pract. 2004. 5:23.
Article5. Whelan MA, Hwan WH, Beausoleil J, Hauck WW, MaGeady SJ. Infants presenting with recurrent infections and low immunoglobulins: characteristics and analysis of normalization. J Clin Immunol. 2006. 26:7–11.
Article6. Koff RS. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of hepatitis A virus infection. Vaccine. 1992. 10:Suppl 1. S15–S17.
Article7. Lee KY, Han JW, Lee JS. Kawasaki disease may be a hyperimmune reaction of genetically susceptible children to variants of normal environmental flora. Med Hypotheses. 2007. 69:642–651.
Article8. Cherrick I, Karayalcin G, Lanzkowsky P. Transient erythroblastopenia of childhood. Prospective study of fifty patients. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1994. 16:320–324.9. Bux J, Behrens G, Jaeger G, Welte K. Diagnosis and clinical course of autoimmune neutropenia in infancy: analysis of 240 cases. Blood. 1998. 91:181–186.
Article10. Blanchette VS, Carcao M. Childhood acute immune thrombocytopenic purpura: 20 years later. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2003. 29:605–617.
Article11. Siegel RL, Issekutz T, Schwaber J, Rosen FS, Geha RS. Deficiency of T helper cells in transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy. N Engl J Med. 1981. 305:1307–1313.
Article12. Kowalczyk D, Mytar B, Zembala M. Cytokine production in transient hypogammaglobulinemia and isolated IgA deficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997. 100:556–562.13. Ballow M. Primary immunodeficiencincy disorders: antibody deficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002. 109:581–591.14. Benderly A, Pollack S, Etzioni A. Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy with severe bacterial infections and persistent IgA deficiency. Isr J Med Sci. 1986. 22:393–396.15. Smart JM, Kemp AS, Armstrong DS. Pneumocyctitis carinii pneumonia in an infant with transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy. Arch Dis Child. 2002. 87:449–450.16. Hsueh KC, Chiu HH, Lin HC, Hsu CH, Tsai FJ. Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy presenting as Staphylococcus aureus sepsis with deep neck infection. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2005. 38:141–144.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Chronic Intractable Diarrhea with IgA, IgG2 and IgG4 Deficiency
- A Case of Prolonged Hypogammaglobulinemia after Rituximab-Containing Chemotherapy in a Patient with Lymphoma
- Iron Deficiency and Brain Development in Infancy
- A Case of IgA, IgG2, IgG4 Deficiency with Recurrent Infection and Erythematous Indurated Nodules
- Two Cases of Malignant Lymphomas in Children with Selective IgA and IgG Subclass Deficiency