J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Jun;22(3):557-559. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.3.557.
A Case Report of a Patient Carrying CYP2C9*3/4 Genotype with Extremely Low Warfarin Dose Requirement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 50 Irwon-dong, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Korea. jwonk@smc.samsung.co.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1778371
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.3.557
Abstract
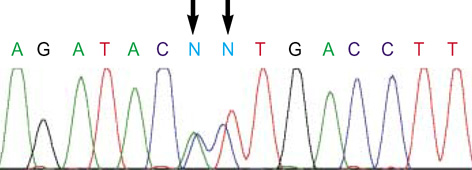
- We report a case of intolerance to warfarin dosing due to impaired drug metabolism in a patient with CYP2C9*3/*4. A 73-yr-old woman with atrial fibrilation was taking warfarin. She attained a high prothrombin time international normalized ratio (INR) at the standard doses during the induction of anticoagulation and extremely low dose of warfarin (6.5 mg/week) was finally chosen to reach the target INR. Genotyping for CYP2C9 revealed that this patient had a genotype CYP2C9*3/*4. This is the first Korean compound heterozygote for CYP2C9*3 and *4. This case suggests the clinical usefulness of pharmacogenetic testing for individualized dosage adjustments of warfarin.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kirchheiner J, Brockmoller J. Clinical consequences of cytochrome P450 2C9 polymorphisms. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005. 77:1–16.
Article2. Takahashi H, Echizen H. Pharmacogenetics of CYP2C9 and interindividual variability in anticoagulant response to warfarin. Pharmacogenomics J. 2003. 3:202–214.
Article3. Takahashi H, Echizen H. Pharmacogenetics of warfarin elimination and its clinical implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2001. 40:587–603.
Article4. Aithal GP, Day CP, Kesteven PJ, Daly AK. Association of polymorphisms in the cytochrome P450 CYP2C9 with warfarin dose requirement and risk of bleeding complications. Lancet. 1999. 353:717–719.
Article5. Lee JH, Park JS, Chung SW, Sohn DK, Kim SH, Lee HS. Warfarin toxicity patients in the Emergency Department. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2003. 14:145–149.6. Daly AK, King BP. Pharmacogenetics of oral anticoagulants. Pharmacogenetics. 2003. 13:247–252.
Article7. Higahi MK, Veenstra DL, Kondo LM, Wittkowsky AK, Srinouanprachanh SL, Farin FL, Rettie AE. Association between CYP2C9 genetic variants and anticoagulation-related outcomes during warfarin therapy. JAMA. 2002. 287:1690–1698.
Article8. Tabrizi AR, Zehnbauer BA, Borecki IB, McGrath SD, Buchman TG, Freeman BD. The frequency and effects of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C9 polymorphisms in patients receiving warfarin. J Am Coll Surg. 2002. 194:267–273.9. Takahashi H, Kashima T, Nomizo Y, Muramoto N, Shimizu T, Nasu K, Kubota T, Kimura S, Echizen H. Metabolism of warfarin enantiomers in Japanese patients with heart disease having different CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 genotypes. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1998. 63:519–528.
Article10. Scordo MG, Pengo V, Spina E, Dahl ML, Gusella M, Padrini R. Influence of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms on warfarin maintenance dose and metabolic clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002. 72:702–710.
Article11. Lee CR, Goldstein JA, Pieper JA. Cytochrome P450 2C9 polymorphisms: a comprehensive review of the in-vitro and human data. Pharmacogenetics. 2002. 12:251–263.
Article12. Stubbins MJ, Harries LW, Smith G, Tarbit MH, Wolf CR. Genetic analysis of the human cytochrome P450 CYP2C9 locus. Pharmacogenetics. 1996. 6:429–439.
Article13. Bhasker CR, Miners JO, Coulter S, Birkett DJ. Allelic and functional variability of cytochrome P4502C9. Pharmacogenetics. 1997. 7:51–58.
Article14. Ingelman-Sunberg M, Nebert DW, Daly AK. Human cytochrome P450 (CYP) genes. Accession date. 11/25/2005. Available from: URL: http://www.imm.ki.se/CYPalleles/cyp2c9.htm.15. Yoon YR, Shon JH, Kim MK, Lim YC, Lee HR, Park JY, Cha IJ, Shin JG. Frequency of cytochrome P450 2C9 mutant alleles in a Korean population. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2001. 51:277–280.
Article16. Imai J, Ieiri I, Mamiya K, Miyahara S, Furuumi H, Nanba E, Yamane M, Fukumaki Y, Ninomiya H, Tashiro N, Otsubo K, Higuchi S. Polymorphism of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C9 gene in Japanese epileptic patients: genetic analysis of the CYP2C9 locus. Pharmacogenetics. 2000. 10:85–89.
Article17. Voora D, McLeod HL, Eby C, Gage BF. Use of pharmacogenetics to guide warfarin therapy. Drugs Today. 2004. 40:247–257.
Article18. Gage BF, Eby C, Milligan PE, Banet GA, Ducan JR, McLeod HL. Use of pharmacogenetics and clinical factors to predict the maintenance dose of warfarin. Thromb Haemost. 2004. 91:87–94.
Article19. Lee BK, Lee JY, Jeong YM, Lee MK, Kim KB, Ahn H. Analysis of factors affecting nontherapeutic INRs in Korean outpatients with mechanical heart valves. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005. 38:746–760.20. Lee BK, Lee JY, Jeong YM, Lee MK, Kim KB, Ahn H. Determination of practical dosing of warfarin in Korean outpatients with mechanical heart valves. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005. 38:761–772.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Intolerance to Warfarin Dosing in an Intermediate Metabolizer of CYP2C9
- CYP2C9 Mutation Affecting the Individual Variability of Warfarin Dose Requirement
- Development and Comparison of Warfarin Dosing Algorithms in Stroke Patients
- Evaluation of the Verigene Warfarin Metabolism Nucleic Acid Test Kit for the Rapid Detection of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 Polymorphisms
- Extremely Elevated International Normalized Ratio of Warfarin in a Patient with CYP2C9*1/*3 and Thyrotoxicosis