J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Jan;24(Suppl 1):S63-S68. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S63.
N-terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels Predict Left Ventricular Systolic Function in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yoongoo.kim@samsung.com
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1778142
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S63
Abstract
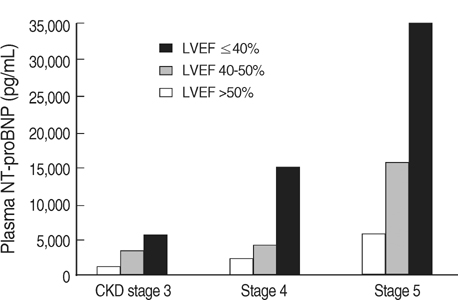
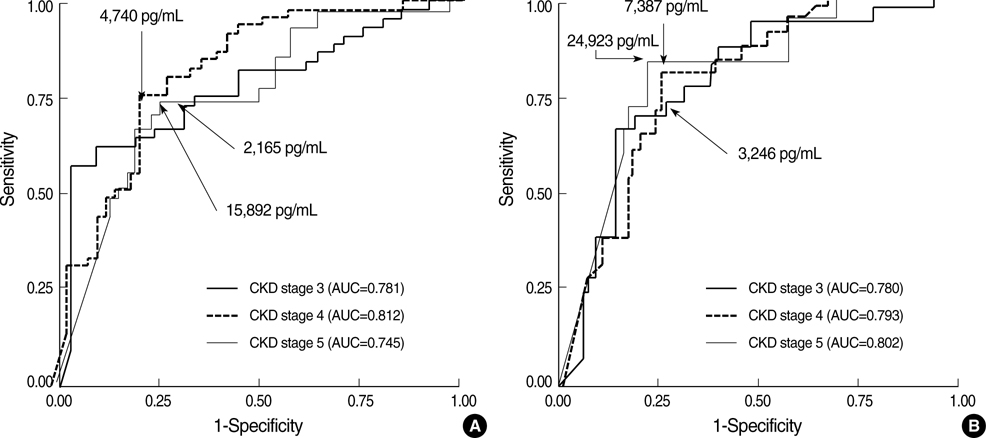
- N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) can be a useful marker for left ventricular (LV) dysfunction in patients without kidney disease. This study was conducted to clarify the relationship between NT-proBNP and LV systolic function in patients with decreased renal function. We studied 256 chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients, patients on dialysis were excluded. The median glomerular filtration rate was 24 (13-36) mL/min/1.73 m(2) and the median NT-proBNP was 4,849 (1,310- 19,009) pg/mL. The prevalence of LV systolic dysfunction increased from the lower to the upper NT-proBNP quartiles (I, 17%; II, 34%; III, 61%; and IV, 72%; p<0.001 for trend). The NT-proBNP quartile was an independent predictor of LV systolic dysfunction after adjustment for renal function, compared with quartile I: II, odds ratio (OR) 3.99 (95% confidence interval [CI],1.34-11.93); III, OR 11.28 (95% CI, 3.74-33.95); and IV, OR 36.97 (95% CI, 11.47-119.1). Area under the curve and optimum cut points for NT-proBNP to detect LV systolic dysfunction were 0.781 and 2,165 pg/mL in CKD stage 3, 0.812 and 4,740 pg/mL in CKD stage 4, and 0.745 and 15,892 pg/ mL in CKD stage 5. The NT-proBNP level was a predictor of LV systolic dysfunction in CKD patients. Optimum cut points should be stratified according to renal function.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Area Under Curve
Female
Glomerular Filtration Rate
Humans
Kidney Failure, Chronic/*complications/pathology
Male
Middle Aged
Natriuretic Peptide, Brain/*blood
Peptide Fragments/diagnostic use
Prevalence
Protein Structure, Tertiary
Sensitivity and Specificity
Ventricular Dysfunction, Left/complications/diagnosis
*Ventricular Function, Left
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002. 39:2 Suppl 1. S1–S266.2. Mann JF, Gerstein HC, Pogue J, Bosch J, Yusuf S. Renal insufficiency as a predictor of cardiovascular outcomes and the impact of ramipril: the HOPE randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2001. 134:629–636.
Article3. K/DOQI Workgroup. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005. 45:4 Suppl 3. S1–S153.4. Stevenson LW, Perloff JK. The limited reliability of physical signs for estimating hemodynamics in chronic heart failure. JAMA. 1989. 261:884–888.
Article5. Maisel AS, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Duc P, Omland T, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Wu AH, Clopton P, Steg PG, Westheim A, Knudsen CW, Perez A, Kazanegra R, Herrmann HC, McCullough PA. Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002. 347:161–167.
Article6. Groenning BA, Raymond I, Hildebrandt PR, Nilsson JC, Baumann M, Pedersen F. Diagnostic and prognostic evaluation of left ventricular systolic heart failure by plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide concentrations in a large sample of the general population. Heart. 2004. 90:297–303.
Article7. Hobbs FD, Davis RC, Roalfe AK, Hare R, Davies MK, Kenkre JE. Reliability of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide assay in diagnosis of heart failure: cohort study in representative and high risk community populations. BMJ. 2002. 324:1498.
Article8. Davis M, Espiner E, Richards G, Billings J, Town I, Neill A, Drennan C, Richards M, Turner J, Yandle T. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide in assessment of acute dyspnoea. Lancet. 1994. 343:440–444.
Article9. Kragelund C, Gronning B, Kober L, Hildebrandt P, Steffensen R. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and long-term mortality in stable coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 2005. 352:666–675.
Article10. Luchner A, Hengstenberg C, Lowel H, Trawinski J, Baumann M, Riegger GA, Schunkert H, Holmer S. N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide after myocardial infarction: a marker of cardio-renal function. Hypertension. 2002. 39:99–104.11. Devereux RB, Casale PN, Kligfield P, Eisenberg RR, Miller D, Campo E, Alonso DR. Performance of primary and derived M-mode echocardiographic measurements for detection of left ventricular hypertrophy in necropsied subjects and in patients with systemic hypertension, mitral regurgitation and dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 1986. 57:1388–1393.
Article12. Hartmann F, Packer M, Coats AJ, Fowler MB, Krum H, Mohacsi P, Rouleau JL, Tendera M, Castaigne A, Anker SD, Amann-Zalan I, Hoersch S, Katus HA. Prognostic impact of plasma N-terminal probrain natriuretic peptide in severe chronic congestive heart failure: a substudy of the Carvedilol Prospective Randomized Cumulative Survival (COPERNICUS) trial. Circulation. 2004. 110:1780–1786.13. Ndrepepa G, Braun S, Mehilli J, von Beckerath N, Vogt W, Schomig A, Kastrati A. Plasma levels of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in patients with coronary artery disease and relation to clinical presentation, angiographic severity, and left ventricular ejection fraction. Am J Cardiol. 2005. 95:553–557.
Article14. James SK, Lindahl B, Siegbahn A, Stridsberg M, Venge P, Armstrong P, Barnathan ES, Califf R, Topol EJ, Simoons ML, Wallentin L. N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and other risk markers for the separate prediction of mortality and subsequent myocardial infarction in patients with unstable coronary artery disease: a Global Utilization of Strategies To Open occluded arteries (GUSTO)-IV substudy. Circulation. 2003. 108:275–281.15. Mutlu B, Bayrak F, Kahveci G, Degertekin M, Eroglu E, Basaran Y. Usefulness of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide to predict clinical course in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 2006. 98:1504–1506.
Article16. Vickery S, Price CP, John RI, Abbas NA, Webb MC, Kempson ME, Lamb EJ. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and amino-terminal proBNP in patients with CKD: relationship to renal function and left ventricular hypertrophy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005. 46:610–620.
Article17. Khan IA, Fink J, Nass C, Chen H, Christenson R, deFilippi CR. N-terminal pro-b-type natriuretic peptide and b-type natriuretic peptide for identifying coronary artery disease and left ventricular hypertrophy in ambulatory chronic kidney disease patients. Am J Cardiol. 2006. 97:1530–1534.
Article18. DeFilippi CR, Fink JC, Nass CM, Chen H, Christenson R. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide for predicting coronary disease and left ventricular hypertrophy in asymptomatic CKD not requiring dialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005. 46:35–44.
Article19. DeFilippi C, van Kimmenade RR, Pinto YM. Amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide testing in renal disease. Am J Cardiol. 2008. 101:82–88.
Article20. Baek H, Kim JA, Choi SY, Do YS, Jang EH, Kim JI, Do JH, Choi SC, Lee JE, Huh W, Kim DJ, Oh HY, Park SW, Ki CS, Kim YG. Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP) and cardiac troponin T (cTnT) as markers of cardiac diseases in stable hemodialysis patients. Korean J Nephrol. 2007. 26:212–219.21. Choi SY, Kim JA, Lee JE, Do YS, Jang EH, Bae HJ, Kim JI, Do JH, Choi SC, Kim DJ, Huh W, Oh HY, Park SW, Jeon E, Ki CS, Kim YG. Plasma levels of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and left ventricular function in patients with chronic renal failure. Korean J Nephrol. 2006. 25:413–421.22. Takami Y, Horio T, Iwashima Y, Takiuchi S, Kamide K, Yoshihara F, Nakamura S, Nakahama H, Inenaga T, Kangawa K, Kawano Y. Diagnostic and prognostic value of plasma brain natriuretic peptide in non-dialysis-dependent CRF. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004. 44:420–428.
Article23. Ambrosi P, Oddoze C, Habib G. Utility of B-natriuretic peptide in detecting diastolic dysfunction: comparison with Doppler velocity recordings. Circulation. 2002. 106:e70.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation of N-Terminal Pro-Brain Type Natriuretic Peptide Level and Echocardiographic Parameters
- Changes in N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in a neonate with symptomatic isolated left ventricular noncompaction
- Serial Monitoring of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Heart Failure Patients
- Plasma Levels of N-terminal pro-brain Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP) and Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure
- Clinical Implication of B-type Natriuretic Peptide in the Elderly