J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Apr;26(4):528-533. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.4.528.
B-cell Complement Dependent Cytotoxic Crossmatch Positivity is an Independent Risk Factor for Long-term Renal Allograft Survival
- Affiliations
-
- 1Transplantation Research Center, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. yangch@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1777883
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.4.528
Abstract
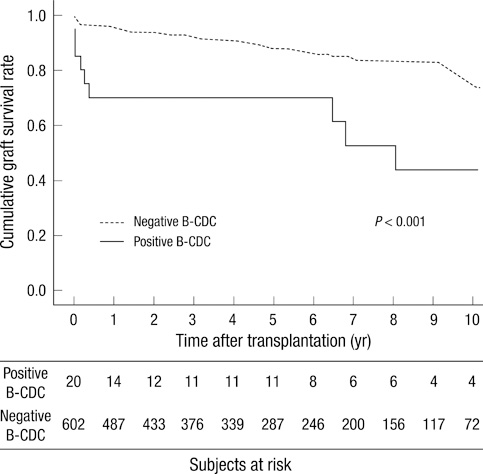
- The clinical significance of positive B-cell complement-dependent cytotoxicity crossmatching (B-CDC) in renal transplant recipients remains unclear. We reviewed 20 recipients with isolated B-CDC positivity at the time of transplantation. We compared the clinical characteristics, acute rejection and long-term graft survival between positive and negative B-CDC patients (n = 602). The number of retransplant recipients and positivity for T- and B-flowcytometric crossmatch was greater in positive B-CDC patients than in negative B-CDC patients. The overall acute rejection rate of positive B-CDC patients was significantly higher (P < 0.001), and Banff grade II or III cellular rejection was more frequently observed in positive B-CDC patients (P = 0.037). Compared with negative B-CDC patients, acute cellular rejection as a cause of graft loss was more prevalent (P = 0.020) and rescue rejection therapy was more frequently needed in positive B-CDC patients (P = 0.007). The allograft survival rate of positive B-CDC patients was significantly lower than that of negative B-CDC patients (P < 0.001), and B-CDC positivity independently increased the risk of allograft failure 2.31-fold (95% CI 1.15-4.67; P = 0.019) according to multivariate analysis. In conclusion, isolated B-CDC positivity is an independent long-term prognostic factor for allograft survival.
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Disease
Adult
Aged
B-Lymphocytes/*immunology
Complement Activation
Cytotoxicity Tests, Immunologic
Female
Graft Survival/*immunology
Histocompatibility Testing/*methods
Humans
*Kidney Transplantation/immunology
Male
Middle Aged
Prognosis
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Survival Analysis
T-Lymphocytes/immunology
Transplantation, Homologous
Figure
Reference
-
1. Patel R, Terasaki PI. Significance of the positive crossmatch test in kidney transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1969. 280:735–739.2. Girnita AL, Webber SA, Zeevi A. Anti-HLA alloantibodies in pediatric solid organ transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 2006. 10:146–153.3. Gebel HM, Bray RA, Nickerson P. Pre-transplant assessment of donor-reactive, HLA-specific antibodies in renal transplantation: contraindication vs. risk. Am J Transplant. 2003. 3:1488–1500.4. Ahern AT, Artruc SB, DellaPelle P, Cosimi AB, Russell PS, Colvin RB, Fuller TC. Hyperacute rejection of HLA-AB-identical renal allografts associated with B lymphocyte and endothelial reactive antibodies. Transplantation. 1982. 33:103–106.5. Scornik JC, LeFor WM, Cicciarelli JC, Brunson ME, Bogaard T, Howard RJ, Ackermann JR, Mendez R, Shires DL Jr, Pfaff WW. Hyperacute and acute kidney graft rejection due to antibodies against B cells. Transplantation. 1992. 54:61–64.6. Ettinger RB, Terasaki PI, Opelz G, Malekzadeh M, Uittenbogaart C, Pennisi AJ, Fine R. Successful renal allografts across a positive cross-match for donor B-lymphocyte alloantigens. Lancet. 1976. 2:56–58.7. Jeannet M, Benzonana G, Arni I. Donor-specific B and T lymphocyte antibodies and kidney graft survival. Transplantation. 1981. 31:160–163.8. Ting A. Positive crossmatches --when is it safe to transplant? Transpl Int. 1989. 2:2–7.9. Guerin C, Pomier G, Fleuru H, Laverne S, Le Petit JC, Berthoux FC. Renal transplantation with positive allocrossmatch (B/T; historical/current) but current T negative. Transplant Proc. 1991. 23:417–418.10. Jendrisak M, Phelan D, Marsh J, McCullough C, So S, Mohanakumar T, Rush T, Michalski S, Hanto D. Significance of B-cell crossmatch on outcome in renal transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1991. 23:434–436.11. Hourmant M, Bignon JD, Cesbron A, Soulillou J. Terasaki PI, editor. Effect of a positive crossmatch against donor B lymphocytes in cadaver kidney transplantation. A prospective one-center study. Clinical Transplants, UCLA Histocompatibility Typing. 1990. Los Angeles: Laboratory Press;301–309.12. Ting A, Morris PJ. Renal transplantation and B-cell cross-matches with autoantibodies and alloantibodies. Lancet. 1977. 2:1095–1097.13. Hwang HS, Hyoung BJ, Lee SY, Jeon YJ, Yoon HE, Kim JY, Choi BS, Oh EJ, Kim YS, Bang BK, Yang CW. Comparison of antibody monitoring system with flow cytometric crossmatch test in renal transplant recipients with high panel-reactive antibody. Nephron Clin Pract. 2009. 111:c260–c264.14. Yang CW, Oh EJ, Lee SB, Moon IS, Kim DG, Choi BS, Park SC, Choi YJ, Park YJ, Han K. Detection of donor-specific anti-HLA class I and II antibodies using antibody monitoring system. Transplant Proc. 2006. 38:2803–2806.15. Yoon HE, Hyoung BJ, Hwang HS, Lee SY, Jeon YJ, Song JC, Oh EJ, Park SC, Choi BS, Moon IS, Kim YS, Yang CW. Successful renal transplantation with desensitization in highly sensitized patients: a single center experience. J Korean Med Sci. 2009. 24:Suppl 1. S148–S155.16. Racusen LC, Solez K, Colvin RB, Bonsib SM, Castro MC, Cavallo T, Croker BP, Demetris AJ, Drachenberg CB, Fogo AB, Furness P, Gaber LW, Gibson IW, Glotz D, Goldberg JC, Grande J, Halloran PF, Hansen HE, Hartley B, Hayry PJ, Hill CM, Hoffman EO, Hunsicker LG, Lindblad AS, Yamaguchi Y. The Banff 97 working classification of renal allograft pathology. Kidney Int. 1999. 55:713–723.17. Karpinski M, Rush D, Jeffery J, Exner M, Regele H, Dancea S, Pochinco D, Birk P, Nickerson P. Flow cytometric crossmatching in primary renal transplant recipients with a negative anti-human globulin enhanced cytotoxicity crossmatch. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001. 12:2807–2814.18. Gloor JM, Winters JL, Cornell LD, Fix LA, DeGoey SR, Knauer RM, Cosio FG, Gandhi MJ, Kremers W, Stegall MD. Baseline donor-specific antibody levels and outcomes in positive crossmatch kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2010. 10:582–589.19. Feucht HE, Opelz G. The humoral immune response towards HLA class II determinants in renal transplantation. Kidney Int. 1996. 50:1464–1475.20. Le Bas-Bernardet S, Hourmant M, Valentin N, Paitier C, Giral-Classe M, Curry S, Follea G, Soulillou JP, Bignon JD. Identification of the antibodies involved in B-cell crossmatch positivity in renal transplantation. Transplantation. 2003. 75:477–482.21. Issa N, Cosio FG, Gloor JM, Sethi S, Dean PG, Moore SB, DeGoey S, Stegall MD. Transplant glomerulopathy: risk and prognosis related to anti-human leukocyte antigen class II antibody levels. Transplantation. 2008. 86:681–685.22. Kooijmans-Coutinho MF, Hermans J, Schrama E, Ringers J, Daha MR, Bruijn JA, van der Woude FJ. Interstitial rejection, vascular rejection, and diffuse thrombosis of renal allografts. Predisposing factors, histology, immunohistochemistry, and relation to outcome. Transplantation. 1996. 61:1338–1344.23. Salmela KT, von Willebrand EO, Kyllönen LE, Eklund BH, Höckerstedt KA, Isoniemi HM, Krogerus L, Taskinen E, Ahonen PJ. Acute vascular rejection in renal transplantation--diagnosis and outcome. Transplantation. 1992. 54:858–862.24. Eng HS, Bennett G, Tsiopelas E, Lake M, Humphreys I, Chang SH, Coates PT, Russ GR. Anti-HLA donor-specific antibodies detected in positive B-cell crossmatches by Luminex predict late graft loss. Am J Transplant. 2008. 8:2335–2342.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Hypercholesterolemia and Hypertension on Long-term Renal Allograft Survival
- Plasmapheresis in a Renal Transplant Patient with Positive Crossmatch only Detected by Flow Cytometry
- Flow Cytometric AHG-CDC for HLA Crossmatch: A Pilot Study
- Post-Renal Transplantation Dyslipidemia
- Impact of the Pattern of Acute Rejection Episodes on Graft Survival