Korean J Radiol.
2009 Aug;10(4):407-410. 10.3348/kjr.2009.10.4.407.
Primary Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor of the Breast: a Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Hospital and Research Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang-city 410-769, Korea.
- 2Department of Surgery, Medical College, Korea University, Seoul 136-705, Korea. eslee@korea.ac.kr
- 3Department of Pathology, Hospital and Research Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang-city 410-769, Korea.
- KMID: 1777271
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2009.10.4.407
Abstract
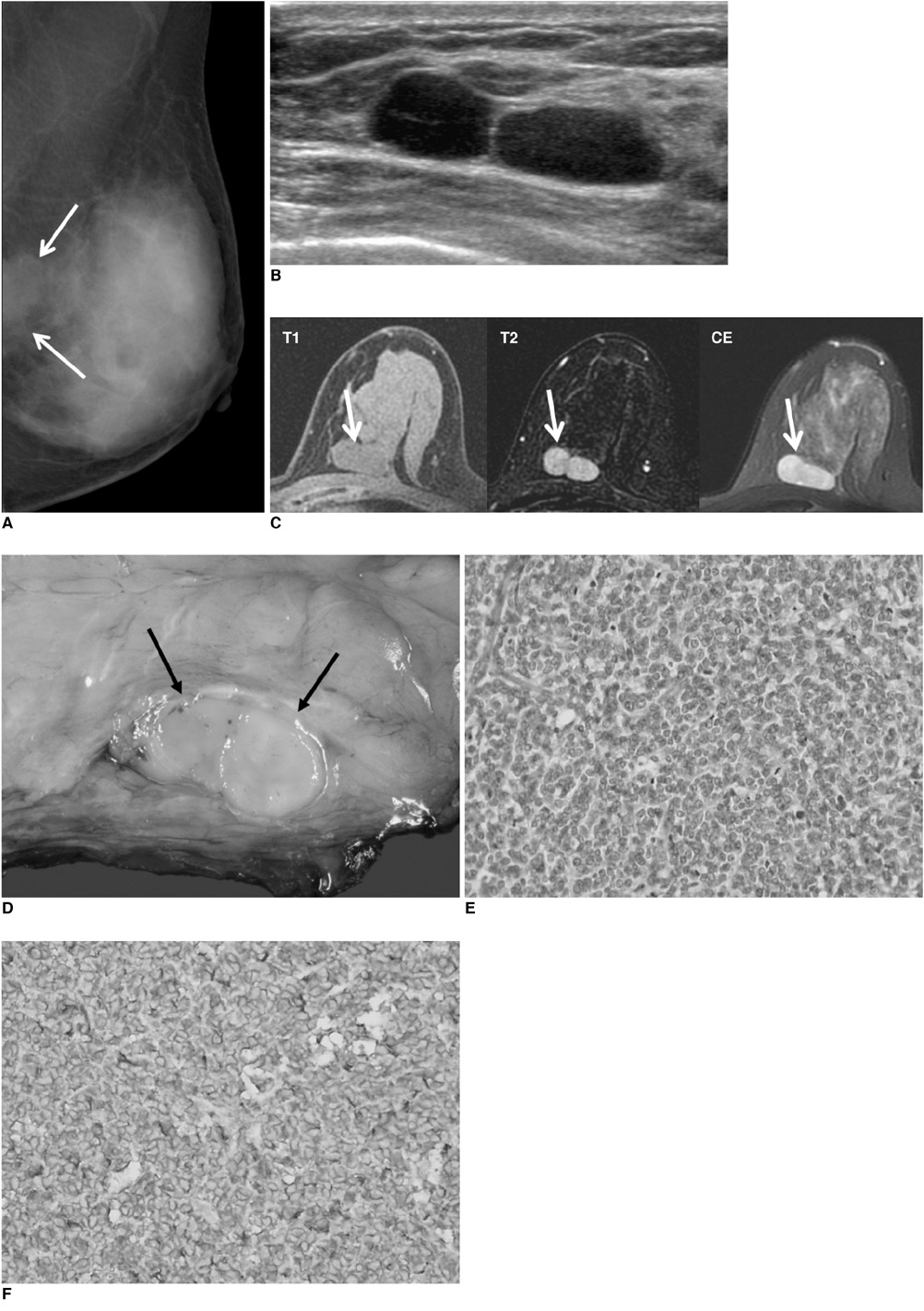
- Primary primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNET) are rare malignant tumors, affecting mostly children and adolescents. Only three cases of primary breast PNETs have been reported in the medical literature, with none in Korea. We present a case of a primary PNET of the breast in a 33-year-old woman, with imaging and immunohistopathology findings.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tefft M, Vawter GF, Mitus A. Paravertebral "round cell" tumors in children. Radiology. 1969. 92:1501–1509.2. da Silva BB, Lopes-Costa PV, Pires CG, Borges RS, da Silva RG Jr. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the breast. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2008. 137:248–249.3. Maxwell RW, Ghate SV, Bentley RC, Soo MS. Primary primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the breast. J Ultrasound Med. 2006. 25:1331–1333.4. Tamura G, Sasou S, Kudoh S, Kikuchi J, Ishikawa A, Tsuchiya T, et al. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the breast: immunohistochemistry and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Pathol Int. 2007. 57:509–512.5. Ibarburen C, Haberman JJ, Zerhouni EA. Peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors. CT and MRI evaluation. Eur J Radiol. 1996. 21:225–232.6. Chung CH, Wang CH, Wang TY, Huang JK, Leu YS. Extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma mimicking a thyroid nodule. Thyroid. 2006. 16:1065–1066.7. Danner DB, Hruban RH, Pitt HA, Hayashi R, Griffin CA, Perlman EJ. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor arising in the pancreas. Mod Pathol. 1994. 7:200–204.8. Hart MN, Earle KM. Primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the brain in children. Cancer. 1973. 32:890–897.9. Jimenez RE, Folpe AL, Lapham RL, Ro JY, O'Shea PA, Weiss SW, et al. Primary Ewing's sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 11 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002. 26:320–327.10. Kang MS, Yoon HK, Choi JB, Eum JW. Extraskeletal Ewing's sarcoma of the hard palate. J Korean Med Sci. 2005. 20:687–690.11. Lee YY, Kim do H, Lee JH, Choi JS, In KH, Oh YW, et al. Primary pulmonary Ewing's sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor in a 67-year-old man. J Korean Med Sci. 2007. 22:S159–S163.12. Winer-Muram HT, Kauffman WM, Gronemeyer SA, Jennings SG. Primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the chest wall (Askin tumors): CT and MR findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993. 161:265–268.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor of Mediastinum in an Adult: A Case Report
- A Case of Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor in the Nasal Cavity
- A Case of Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor in the Maxillary Sinus
- Primary Epidural Peripheral Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor of the Lumbar Spine: A Case Report
- A Case of Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor of the Uterus