Outbreaks of Imipenem Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii Producing OXA-23 beta-Lactamase in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. leehejo@khmc.or.kr
- 2Division of Antimicrobial Resistance, National Institute of Health, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1777088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2009.50.6.764
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Since November 2006, imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates have increased in Kyung Hee University Hospital in Seoul, Korea. The purpose of this study was to determine the genetic basis and molecular epidemiology of outbreak isolates.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
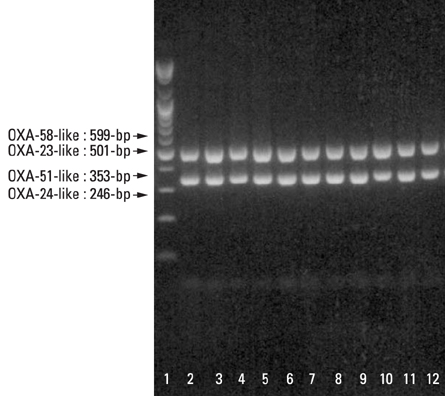
Forty-nine non-repetitive isolates of the 734 IRAB strains were investigated in order to determine their characteristics. The modified Hodge and the ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA)-disk synergy test were performed for the screening of carbapenemase and metallo-beta-lactamase production. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays were performed for the detection of genes encoding for OXA-23-like, OXA-24-like, OXA-58-like and OXA-51-like carbapenemase. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) was performed for strain identification.
RESULTS
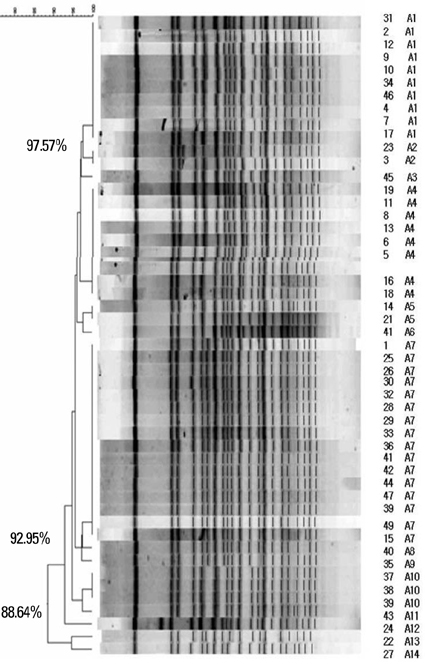
All isolates showed 100% resistance to ciprofloxacin and gentamicin, 97.9% resistance to cefepime, piperacillin/tazobactam, aztreonam, ceftazidime and piperacillin, 93.9% resistance to tobramycin and 57.1% resistance to amikacin. All of the 49 isolates (100%) showed positive results in the modified Hodge test and negative results in the EDTA-disk synergy test. They all (100%) possessed the encoding gene for an intrinsic OXA-51-like carbapenemase and an acquired OXA-23-like carbapenemase in the multiplex PCR assay. PFGE patterns revealed that all isolates were clonally related from A1 to A14.
CONCLUSION
It is concluded that all of the 49 IRAB isolates acquired resistance to imipenem by producing OXA-23 carbapenemase and they might have originated from a common source.
MeSH Terms
-
Acinetobacter Infections/epidemiology/*microbiology
Acinetobacter baumannii/*drug effects/genetics
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*pharmacology
Cephalosporins/pharmacology
Ciprofloxacin/pharmacology
Disease Outbreaks
Drug Resistance, Multiple, Bacterial/genetics/physiology
Electrophoresis, Gel, Pulsed-Field
Gentamicins/pharmacology
Humans
Imipenem/*pharmacology
Korea/epidemiology
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
beta-Lactamases/genetics/*metabolism
beta-Lactams/*pharmacology
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Increase of Ceftazidime- and Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and Imipenem-Resistant Acinetobacter spp. in Korea: Analysis of KONSAR Study Data from 2005 and 2007
Kyungwon Lee, Mi Ae Lee, Chae Hoon Lee, Jongwook Lee, Kyoung Ho Roh, Sunjoo Kim, Jin Ju Kim, Eunmi Koh, Dongeun Yong, Yunsop Chong,
Yonsei Med J. 2010;51(6):901-911. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.6.901.Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter spp.: Increasingly Problematic Nosocomial Pathogens
Kyungwon Lee, Dongeun Yong, Seok Hoon Jeong, Yunsop Chong
Yonsei Med J. 2011;52(6):879-891. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.6.879.Colonization Prevalence and Risk Factor Analysis of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in an Intensive Care Unit without Outbreaks
Young Ah Kim, Yoon Soo Park, Sang Sun Lee, Young Jun Son, Jeong Hwa Yeon, Young Hee Seo, Kyungwon Lee
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2019;24(2):81-87. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2019.24.2.81.Four Children with Multidrug-resistant Acinetobactor baumanii Infections in the Intensive Care Units of a University Hospital
Kyung Suk Lee, Gyu Min Lee, Hoi Soo Yoon, Sa Jun Chung, Sung-Ho Cha, Hee-Kyung Chun
Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2011;18(1):97-102. doi: 10.14776/kjpid.2011.18.1.97.
Reference
-
1. Bergogne-Bérézin E, Towner KJ. Acinetobacter spp. as nosocomial pathogens: microbiological, clinical, and epidemiological features. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1996. 9:148–165.
Article2. Jeong SH, Bae IK, Park KO, An YJ, Sohn SG, Jang SJ, et al. Outbreaks of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii producing carbapenemases in Korea. J Microbiol. 2006. 44:423–431.3. Murray CK, Hospenthal DR. Treatment of multidrug resistant Acinetobacter. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2005. 18:502–506.
Article4. Lee K, Lee HS, Jang SJ, Park AJ, Lee MH, Song WK, et al. Antimicrobial resistance surveillance of bacteria in 1999 in Korea with a special reference to resistance of enterococci to vancomycin and gram-negative bacilli to third generation cephalosporin, imipenem, and fluoroquinolone. J Korean Med Sci. 2001. 16:262–270.
Article5. Hong SG, Yong DE, Lee KW, Kim EC, Lee WK, Jeung SH, et al. Antimicrobial resistance of clinically important bacteria isolated from hospitals located in representative provinces of Korea. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 6:29–36.6. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Document M100-S13. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 13th informational supplement. 2003. Wayne, Pa: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards.7. Lee K, Chong Y, Shin HB, Kim YA, Yong D, Yum JH. Modified-Hodge and EDTA-disk synergy tests to screen metallo-beta-lactamase-producing strains of Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter species. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2001. 7:88–91.
Article8. Woodford N, Ellington MJ, Coelho JM, Turton JF, Ward ME, Brown S, et al. Multiplex PCR for genes encoding prevalent OXA carbapenemases in Acinetobacter spp. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006. 27:351–353.
Article9. Seifert H, Dolzani L, Bressan R, van der Reijden T, van Strijen B, Stefanik D, et al. Standardization and interlaboratory reproducibility assessment of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis-generated fingerprints of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:4328–4335.
Article10. McBride ME, Duncan WC, Knox JM. The Environment and the Microbial Ecology of Human Skin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977. 33:603–608.
Article11. Wagenvoort JH, Joosten EJ. An outbreak Acinetobacter baumannii that mimics MRSA in its environmental longevity. J Hosp Infect. 2002. 52:226–227.
Article12. Villers D, Espaze E, Coste-Burel M, Giauffret F, Ninin E, Nicolas F, et al. Nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii infections: microbiological and clinical epidemiology. Ann Intern Med. 1998. 129:182–189.
Article13. Abbo A, Navon-Venezia S, Hammer-Muntz O, Krichali T, Siegman-Igra Y, Carmeli Y. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005. 11:22–29.14. Poirel L, Nordmann P. Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii : mechanisms and epidemiology. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006. 12:826–836.
Article15. Queenan AM, Bush K. Carbapenemases: the versatile beta-lactamases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007. 20:440–458.16. Yum JH, Yi K, Lee H, Yong D, Lee K, Kim JM, et al. Molecular characterization of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter genomospecies 3 from Korea: identification of two new integrons carrying the bla (VIM-2) gene cassettes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002. 49:837–840.
Article17. Lee K, Yum JH, Yong D, Lee HM, Kim HD, Docquier JD, et al. Novel acquired metallo-beta-lactamase gene, bla (SIM-1), in a class 1 integron from Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from Korea. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. 49:4485–4491.
Article18. Brown S, Amyes S. OXA (beta)-lactamases in Acinetobacter: the story so far. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006. 57:1–3.19. Paton R, Miles RS, Hood J, Amyes SG, Miles RS, Amyes SG. ARI 1: beta-lactamase-mediated imipenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 1993. 2:81–87.20. Scaife W, Young HK, Paton RH, Amyes SG. Transferable imipenem-resistance in Acinetobacter species from a clinical source. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1995. 36:585–586.
Article21. Donald HM, Scaife W, Amyes SG, Young HK. Sequence analysis of ARI-1, a novel OXA beta-lactamase, responsible for imipenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii 6B92. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000. 44:196–199.
Article22. Bou G, Cerveró G, Domínguez MA, Quereda C, Martínez-Beltrán J. Characterization of a nosocomial outbreak caused by a multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii strain with a carbapenem-hydrolyzing enzyme: high-level carbapenem resistance in A. baumannii is not due solely to the presence of beta-lactamases. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:3299–3305.
Article23. Héritier C, Poirel L, Aubert D, Nordmann P. Genetic and functional analysis of the chromosome-encoded carbapenem-hydrolyzing oxacillinase OXA-40 of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. 47:268–273.
Article24. Da Silva GJ, Quinteira S, Bértolo E, Sousa JC, Gallego L, Duarte A, et al. Long-term dissemination of an OXA-40 carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter baumannii clone in the Iberian Peninsula. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004. 54:255–258.
Article25. Dalla-Costa LM, Coelho JM, Souza HA, Castro ME, Stier CJ, Bragagnolo KL, et al. Outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii producing the OXA-23 enzyme in Curitiba, Brazil. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:3403–3406.
Article26. Naas T, Levy M, Hirschauer C, Marchandin H, Nordmann P. Outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii producing the carbapenemase OXA-23 in a tertiary care hospital of Papeete, French Polynesia. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:4826–4829.
Article27. Marqué S, Poirel L, Héritier C, Brisse S, Blasco MD, Filip R, et al. Regional occurrence of plasmid-mediated carbapenem-hydrolyzing oxacillinase OXA-58 in Acinetobacter spp. in Europe. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:4885–4888.
Article28. Poirel L, Marqué S, Héritier C, Segonds C, Chabanon G, Nordmann P. OXA-58, a novel class D {beta}-lactamase involved in resistance to carbapenems in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. 49:202–208.
Article29. Jeon BC, Jeong SH, Bae IK, Kwon SB, Lee K, et al. Investigation of a nosocomial outbreak of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii producing the OXA-23 beta-lactamase in Korea. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:2241–2245.
Article30. Merkier AK, Centrón D. bla(OXA-51)-type beta-lactamase genes are ubiquitous and vary within a strain in Acinetobacter baumannii. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006. 28:110–113.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Molecular Epidemiology of Infection Caused by OXA-23 or IMP-1 beta-Lactamase-Producing Acinetobacter baumannii
- Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- Prevalence of OXA-23 Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase-Producing Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii in a University Hospital, Busan, Korea
- Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter spp.: Increasingly Problematic Nosocomial Pathogens
- Dissemination of IMP-1 and OXA Type beta-Lactamase in Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii