Recent Changes in the Clinicopathologic Features of Korean Men with Prostate Cancer: A Comparison with Western Populations
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hanyong.choi@samsung.com
- 4Department of Urology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Urology, Hallym University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1776989
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.3.543
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to evaluate the recent changes in the clinicopathologic features of prostate cancer in Korea and to compare these features with those of Western populations.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the data of 1582 men undergoing radical prostatectomy for clinically localized prostate cancer between 1995 and 2007 at 10 institutions in Korea for comparison with Western studies. The patients were divided into two groups in order to evaluate the recent clinicopathological changes in prostate cancer: Group 1 had surgery between 1995 and 2003 (n=280) and Group 2 had surgery between 2004 and 2007 (n=1302). The mean follow-up period was 24 months.
RESULTS
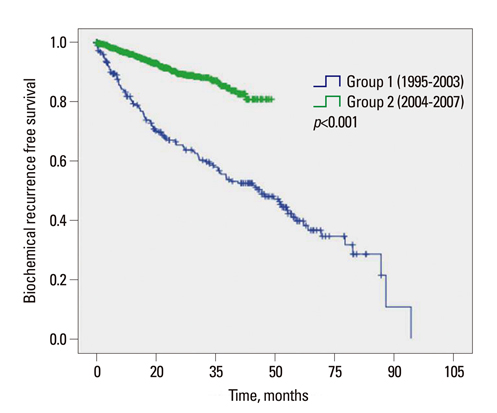
Group 1 had a higher prostate-specific antigen level than Group 2 (10.0 ng/mL vs. 7.5 ng/mL, respectively; p<0.001) and a lower proportion of biopsy Gleason scores < or =6 (35.0% vs. 48.1%, respectively; p<0.001). The proportion of patients with clinical T1 stage was higher in Group 2 than in Group 1. Group 1 had a lower proportion of organ-confined disease (59.6% vs. 68.6%; p<0.001) and a lower proportion of Gleason scores < or =6 (21.3% vs. 33.0%; p<0.001), compared to Group 2. However, the relatively higher proportion of pathologic Gleason scores < or =6 in Group 2 was still lower than those of Western men, even though the proportion of organ-confined disease reached to that of Western series.
CONCLUSION
Korean men with prostate cancer currently present better clinicopathologic parameters. However, in comparison, Korean men still show relatively worse pathologic Gleason scores than Western men.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Changes in Clinical Characteristics of Patients with an Initial Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer in Korea: 10-Year Trends Reported by a Tertiary Center
Ji Eun Heo, Hyun Kyu Ahn, Jinu Kim, Byung Ha Chung, Kwang Suk Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(6):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e42.Charlson Comorbidity Index Is an Important Prognostic Factor for Long-Term Survival Outcomes in Korean Men with Prostate Cancer after Radical Prostatectomy
Joo Yong Lee, Dae Hun Lee, Nam Hoon Cho, Koon Ho Rha, Young Deuk Choi, Sung Joon Hong, Seung Choul Yang, Kang Su Cho
Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(2):316-323. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.2.316.Selection Criteria for Active Surveillance of Patients with Prostate Cancer in Korea: A Multicenter Analysis of Pathology after Radical Prostatectomy
Chang Wook Jeong, Sung Kyu Hong, Seok Soo Byun, Seong Soo Jeon, Seong Il Seo, Hyun Moo Lee, Hanjong Ahn, Dong Deuk Kwon, Hong Koo Ha, Tae Gyun Kwon, Jae Seung Chung, Cheol Kwak, Hyung Jin Kim
Cancer Res Treat. 2018;50(1):265-274. doi: 10.4143/crt.2016.477.
Reference
-
1. Giovannucci E, Platz EA. Vogelzang NJ, Scardino PT, Shipley WU, Debruyne FMJ, Linehan WM, editors. Epidemiology of prostate cancer. Comprehensive Textbook of Genitourinary Oncology. 2006. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;9–22.2. Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010. 60:277–300.
Article3. Korea Statistical Information Service. accessed on 2010 October 30. Available at: http://www.kostat.go.kr.4. Kim KI, Chang HJ, Cho YS, Youn TJ, Chung WY, Chae IH, et al. Current status and characteristics of hypertension control in community resident elderly Korean people: data from a Korean longitudinal study on health and aging (KLoSHa study). Hypertens Res. 2008. 31:97–105.
Article5. http://www.ncc.re.kr. Accessed March 2012.6. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005. 55:74–108.
Article7. Seo HK, Chung MK, Ryu SB, Lee KH. Korean Urological Oncologic Society Prostate Cancer Study Group. Detection rate of prostate cancer according to prostate-specific antigen and digital rectal examination in Korean men: a nationwide multicenter study. Urology. 2007. 70:1109–1112.
Article8. Song C, Ro JY, Lee MS, Hong SJ, Chung BH, Choi HY, et al. Prostate cancer in Korean men exhibits poor differentiation and is adversely related to prognosis after radical prostatectomy. Urology. 2006. 68:820–824.
Article9. Epstein JI, Allsbrook WC Jr, Amin MB, Egevad LL. ISUP Grading Committee. The 2005 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005. 29:1228–1242.
Article10. Freedland SJ, Sutter ME, Dorey F, Aronson WJ. Defining the ideal cutpoint for determining PSA recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Prostate-specific antigen. Urology. 2003. 61:365–369.
Article11. Grossfeld GD, Latini DM, Downs T, Lubeck DP, Mehta SS, Carroll PR. Is ethnicity an independent predictor of prostate cancer recurrence after radical prostatectomy? J Urol. 2002. 168:2510–2515.
Article12. Freedland SJ, Amling CL, Dorey F, Kane CJ, Presti JC Jr, Terris MK, et al. Race as an outcome predictor after radical prostatectomy: results from the Shared Equal Access Regional Cancer Hospital (SEARCH) database. Urology. 2002. 60:670–674.
Article13. Hernandez DJ, Nielsen ME, Han M, Partin AW. Contemporary evaluation of the D'amico risk classification of prostate cancer. Urology. 2007. 70:931–935.
Article14. Godley PA, Schenck AP, Amamoo MA, Schoenbach VJ, Peacock S, Manning M, et al. Racial differences in mortality among Medicare recipients after treatment for localized prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003. 95:1702–1710.
Article15. Haenszel W, Kurihara M. Studies of Japanese migrants. I. Mortality from cancer and other diseases among Japanese in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968. 40:43–68.16. Yu H, Harris RE, Gao YT, Gao R, Wynder EL. Comparative epidemiology of cancers of the colon, rectum, prostate and breast in Shanghai, China versus the United States. Int J Epidemiol. 1991. 20:76–81.
Article17. The Korean Urological Association. Data on statistics of management in resident training hospital in the Korean Urological Association in the year 2007. Korean J Urol. 2008. 49:1171–1172.18. Song C, Ahn H, Lee MS, Park J, Kwon TG, Kim HJ, et al. Mass screening for prostate cancer in Korea: a population based study. J Urol. 2008. 180:1949–1952.
Article19. Cohen JH, Schoenbach VJ, Kaufman JS, Talcott JA, Schenck AP, Peacock S, et al. Racial differences in clinical progression among Medicare recipients after treatment for localized prostate cancer (United States). Cancer Causes Control. 2006. 17:803–811.
Article20. van Houten ME, Gooren LJ. Differences in reproductive endocrinology between Asian men and Caucasian men--a literature review. Asian J Androl. 2000. 2:13–20.21. Wu AH, Whittemore AS, Kolonel LN, Stanczyk FZ, John EM, Gallagher RP, et al. Lifestyle determinants of 5alpha-reductase metabolites in older African-American, white, and Asian-American men. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2001. 10:533–538.22. Hoffman MA, DeWolf WC, Morgentaler A. Is low serum free testosterone a marker for high grade prostate cancer? J Urol. 2000. 163:824–827.
Article23. Hsing AW, Chu LW, Stanczyk FZ. Androgen and prostate cancer: is the hypothesis dead? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008. 17:2525–2530.
Article24. Roehl KA, Han M, Ramos CG, Antenor JA, Catalona WJ. Cancer progression and survival rates following anatomical radical retropubic prostatectomy in 3,478 consecutive patients: long-term results. J Urol. 2004. 172:910–914.
Article25. Schroeck FR, Aronson WJ, Presti JC Jr, Terris MK, Kane CJ, Amling CL, et al. Do nomograms predict aggressive recurrence after radical prostatectomy more accurately than biochemical recurrence alone? BJU Int. 2009. 103:603–608.
Article26. Capitanio U, Karakiewicz PI, Jeldres C, Briganti A, Gallina A, Suardi N, et al. The probability of Gleason score upgrading between biopsy and radical prostatectomy can be accurately predicted. Int J Urol. 2009. 16:526–529.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Continuous Increase in Prevalence of state Cancer in Korea and Its Causes
- Racial Differences in Prostate Cancer Characteristics and Cancer-Specific Mortality: An Overview
- Germline pathogenic variants in unselected Korean men with prostate cancer
- Prostate-Specific Antigen-Based Prostate Cancer Screening: One for All or Individualized for Each Race? – A Narrative Review
- Pathogenesis of Prostate Cancer