J Korean Med Assoc.
2004 May;47(5):394-402. 10.5124/jkma.2004.47.5.394.
A Continuous Increase in Prevalence of state Cancer in Korea and Its Causes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of rology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Yongsan Hospital, Korea. saeckim@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 2137873
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2004.47.5.394
Abstract
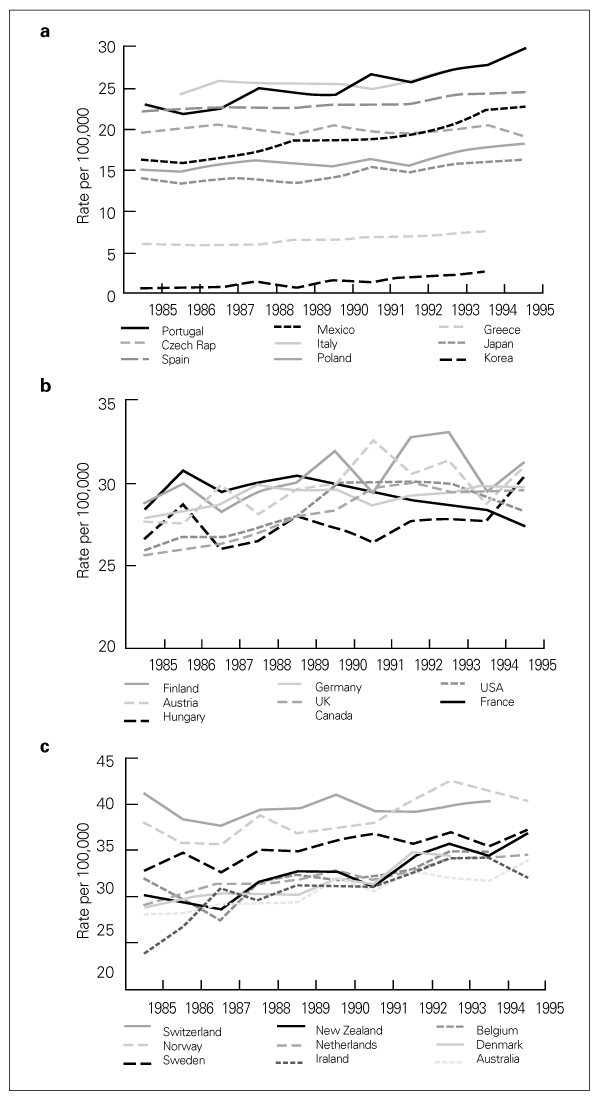
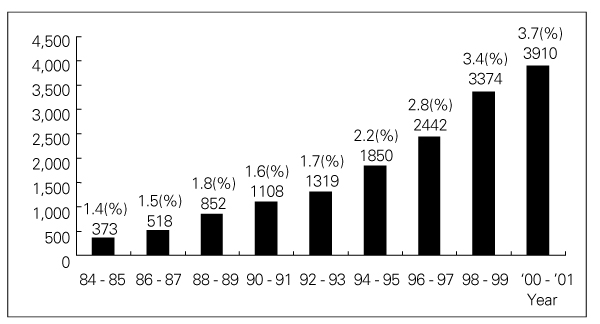
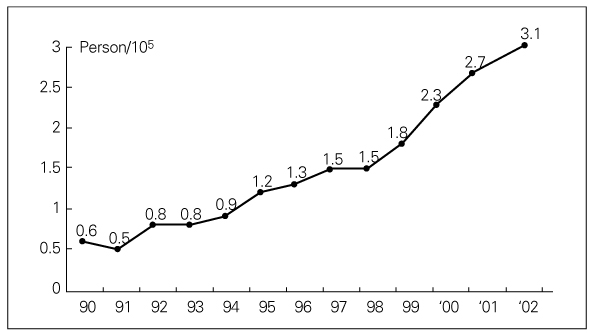
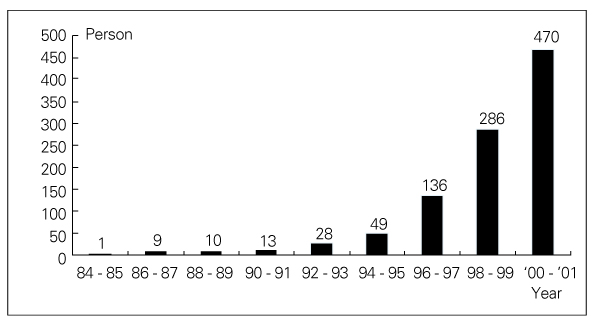
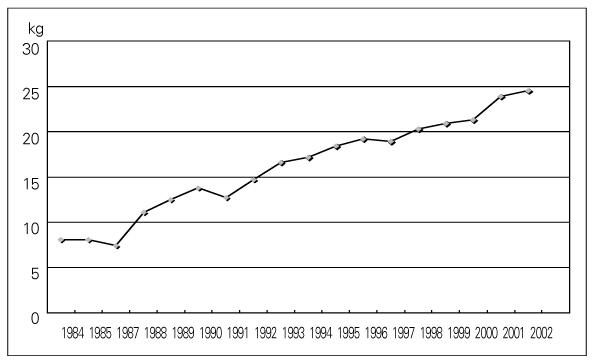
- A Continuous Increase in Prevalence of Prostate Cancer in Korea and Its Causes Prostate cancer has become the most common neoplasm in men and the second leading cause of cancer death in Western countries, while the Asian populations have the lowest incidence and mortality rates. However, the incidence of prostate cancer has been rapidly increasing in the past 10 years in Asian populations including Korean, although it is still much lower than in Western populations. The prostate cancer is now the 6th leading cancer in Korean men and resulted in 744 deaths (3.1 per 105) in 2002. Comparative geographic pathologic autopsy studies shows no difference in the incidence of latent prostate cancer between countries with high and low risk of clinical prostate cancer. However, the foci of the latent prostate cancer are frequently larger and more aggressive in countries with high incidence and mortality rate. Consequently, the different incidence of the clinical prostate cancer is not based on different initiation of malignant transformation, but on different promoting factors. Three risk factors may be responsible for the increase of prostate cancer in Korea: increase in population of aging men, increase in detection rate using prostate specific antigen, and high fat diet.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Incidence, Epidemiology and Patterns of Progression of Prostate Cancer
Se Joong Kim, Sun Il Kim
J Korean Med Assoc. 2010;53(2):92-97. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2010.53.2.92.
Reference
-
1. Presti JC Jr. Tanagho EA, McAninch JW, editors. Neoplasm of the prostate gland. Smith's General Urology. 2000. 15th ed. New York: Lange Medical Books;399–421.2. Varenhorst E, Carlsson P, Pederson K. Clinical and economic considerations in the treatment of prostate cancer. Pharmaco Econ. 1994. 6:127–141.
Article3. Brawley OW, Kramer BS. Dawson NA, Vogelzang NJ, editors. The epidemiology and prevention of prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer. 1994. New York: Wiley-Liss;47–64.4. Hsing AW, Tsao L, Devesa SS. International trends and patterns of prostate cancer incidence and mortality. Int J Cancer. 2000. 85:60–67.
Article5. Pu YS. Prostate cancer in Taiwan:epidemiology and risk factors. Int J Androl. 2000. 23:Suppl 2. 34–36.
Article6. Gu F. Epidemiological survey of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatic cancer in China. Chin Med J. 2000. 113:299–302.7. Chang CK, Yu HJ, Chan KW, Lai MK. Secular trend and age-period-cohort analysis of prostate cancer mortality in Taiwan. J Urol. 1997. 158:1845–1848.
Article8. Quinn M, Babb P. Patterns and trends in prostate cancer incidence, survival, prevalence and mortality. Part II: individual countries. BJU Int. 2002. 90:174–178.
Article9. Sasagawa I, Nakada T. Epidemiology of prostatic cancer in east Asia. Ach Androl. 2001. 47:195–201.
Article11. Dohm G. Epidemiologic aspects of latent and clinically manifest carcinoma of the prostate. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1983. 106:210–218.
Article12. Steinberg GN, Carter BS, Beaty TH, Childs B, Walsh PC. Family history and the risk of prostate cancer. Prostate. 1990. 17:337–347.
Article13. Smith JR, Freije D, Carpten JD, Gronberg H, Xu J, Isaacs SD, et al. Major susceptibility locus for prostate cancer on chromosome 1 suggested by genome wide scan. Science. 1996. 274:1371–1374.
Article14. Xu J, Meyers D, Freije D, Isaacs S, Wiley K, Nusshern D, et al. Evidence for a prostate cancer susceptibility locus on the X chromosome. Nat Genet. 1998. 20:175–179.
Article15. Wilson JMG. Bruce AW, Trachtenberg J, editors. Epidemiology of prostate cancer. Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate. 1991. London: Springer-Verlag;3–17.16. Carter BS, Steinberg GD, Beaty TH, Childs B, Walsh PC. Familial risk factors for prostate cancer. Cancer Surv. 1991. 11:5–13.17. Shibata A, Whittemore AS. Genetic predisposition to prostate cancer: Possible explanations for ethnic differences in risk. Prostate. 1997. 32:65–72.
Article18. Griffiths K, Morton MS, Denis LJ. Diet and Prostate Disease; An IPHC Teaching Programme. 1996. Cardiff: Comp Graphics Services.19. Cook LS, Goldoft M, Schwartz SM, Weiss NS. Incidence of adenocarcinoma of the prostate in Asian immigrants to the United States and their descendants. J Urol. 1999. 161:152–155.
Article20. Akaza K, Stemmermann GN. Comparative study of latent carcinoma of the prostate among Japanese in Japan and Hawaii. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973. 50:1137–1144.21. Whittemore AS, Kolonel LN, Wu AH, John EM, Gallagher RP, Howe GR, et al. Prostate cancer in relation to diet, physical activity, and body size in blacks, whites, and Asians in the United States and Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995. 87:652–661.
Article22. Ross RK, Bernstein L, Lobow RA, Shimizu H, Stanczyk FC, Pike MC. 5-alpha-reductase activity and the risk of prostate cancer among Japanese and US white and black males. Lancet. 1992. 339:887–889.
Article23. Gupta S, Srivastava M, Ahmad N, Bostwick DG, Mukhtar H. Over-expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human prostate adenocarcinoma. Prostate. 2000. 42:73–78.
Article24. Zha S, Gage WR, Sauvageot J, Saria EA, Putzi MJ, Ewing CM, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 is up-regulated in proliferative inflammatory atrophy of the prostate, but not in prostate carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2001. 61:8617–8623.25. Rosenberg L, Palmer JR, Zeba AG, Warshauer ME, Stolley PD, Shapiro S. Vasectomy and the risk of prostate cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 1990. 132:1051–1055.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Resting Energy Expenditure in Patients with Lung Cancer
- The Pain Alterations in Terminal Cancer Patients Who Received Pain Control
- Osteoporosis and Osteoporotic Fractures in Gastrointestinal Disease
- Cancer Statistics in Korea: Incidence, Mortality, Survival, and Prevalence in 2008
- The Epidemiology of Diabetes in Korea