Yonsei Med J.
2013 Jan;54(1):253-257. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.1.253.
Patients with Arthritis Undergoing Surgery: How Should We Manage Tumour Necrosis Factor Blocking Agents Perioperatively?: A Systematic Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Section of Rheumatology, 2nd Department of Medicine, General Hospital Linz, Linz, Austria. herwigpi@yahoo.com
- 2Paracelsus Medical University, Salzburg, Austria.
- 3Department of Pediatric Rheumatology, Klinikum Bad Bramstedt, Bad Bramstedt, Germany.
- 4Department of Orthopedics and Orthopedic Surgery, General Hospital Linz, Linz, Austria.
- 5Internal Medicine III, Medical University Vienna, Vienna, Austria.
- 6Rheumatology Unit, Clinical Department of General Internal Medicine, Innsbruck Medical University, Innsbruck, Austria.
- KMID: 1776947
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.1.253
Abstract
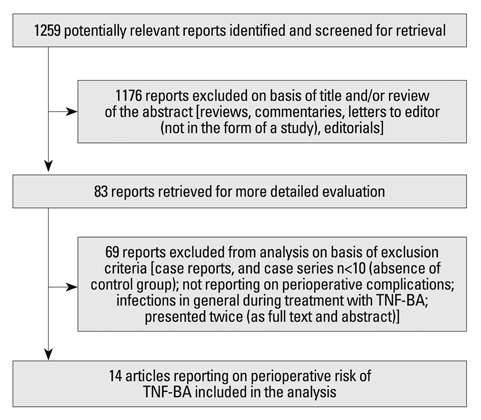
- We systematically reviewed the literature on the infectious risk in patients treated with tumour necrosis factor blocking agents (TNF-BA) undergoing surgery: we searched the Medline (PubMed) and the online archive from the Annual European Congress of Rheumatology and the Annual Scientific Meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Of total 1259 reports, 14 were finally analysed. With one exception all were retrospective. Four of 6 studies compared patients on TNF-BA with those not receiving TNF-BA, and found an increased risk of infection with the use of TNF-BA. None of the other studies which compared continued with discontinued treatment at surgery found an increased risk of infection, when the medication was continued perioperatively. In conclusion, while in theory there is an increased risk of infections when TNF-BA are administered perioperatively, the available literature does not necessarily support this. It rather appears that patients receiving TNF-BA are a priori at a higher risk of postoperative infections. Scheduling surgery at the end of the drug interval and adding one "safety" week prior to surgery should be an acceptable plan in daily clinical practice.
MeSH Terms
-
Antibodies, Monoclonal/therapeutic use
Antibodies, Monoclonal, Humanized/therapeutic use
Antirheumatic Agents/therapeutic use
Arthritis/*surgery
Humans
Immunoglobulin Fab Fragments/therapeutic use
Immunoglobulin G/therapeutic use
*Infection
Perioperative Period
Polyethylene Glycols/therapeutic use
Postoperative Complications/prevention & control
Postoperative Period
Receptors, Tumor Necrosis Factor/therapeutic use
Retrospective Studies
Risk
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/*antagonists & inhibitors
Antibodies, Monoclonal
Antibodies, Monoclonal, Humanized
Antirheumatic Agents
Immunoglobulin Fab Fragments
Immunoglobulin G
Polyethylene Glycols
Receptors, Tumor Necrosis Factor
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. Listing J, Strangfeld A, Kary S, Rau R, von Hinueber U, Stoyanova-Scholz M, et al. Infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologic agents. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. 52:3403–3412.
Article2. den Broeder AA, Creemers MC, Fransen J, de Jong E, de Rooij DJ, Wymenga A, et al. Risk factors for surgical site infections and other complications in elective surgery in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with special attention for anti-tumor necrosis factor: a large retrospective study. J Rheumatol. 2007. 34:689–695.3. Pieringer H, Stuby U, Biesenbach G. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis undergoing surgery: how should we deal with antirheumatic treatment? Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2007. 36:278–286.
Article4. Bibbo C, Goldberg JW. Infectious and healing complications after elective orthopaedic foot and ankle surgery during tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibition therapy. Foot Ankle Int. 2004. 25:331–335.
Article5. Giles JT, Bartlett SJ, Gelber AC, Nanda S, Fontaine K, Ruffing V, et al. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapy and risk of serious postoperative orthopedic infection in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. 55:333–337.
Article6. Talwalkar SC, Grennan DM, Gray J, Johnson P, Hayton MJ. Tumour necrosis factor alpha antagonists and early postoperative complications in patients with inflammatory joint disease undergoing elective orthopaedic surgery. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:650–651.
Article7. Wendling D, Balblanc JC, Brousse A, Lohse A, Lehuede G, Garbuio P, et al. Surgery in patients receiving anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: an observational study on 50 surgical procedures. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:1378–1379.
Article8. Ruyssen-Witrand A, Gossec L, Salliot C, Luc M, Duclos M, Guignard S, et al. Complication rates of 127 surgical procedures performed in rheumatic patients receiving tumor necrosis factor alpha blockers. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007. 25:430–436.9. Corrao S, Pistone G, Arnone S, Calvo L, Scaglione R, Licata G. Surgery during etanercept therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: is it time to follow patient preferences? Intern Emerg Med. 2008. 3:73–75.
Article10. Hirano Y, Kojima T, Kanayama Y, Shioura T, Hayashi M, Kida D, et al. Influences of anti-tumour necrosis factor agents on postoperative recovery in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2010. 29:495–500.
Article11. Kawakami K, Ikari K, Kawamura K, Tsukahara S, Iwamoto T, Yano K, et al. Complications and features after joint surgery in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with tumour necrosis factor-alpha blockers: perioperative interruption of tumour necrosis factor-alpha blockers decreases complications? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010. 49:341–347.
Article12. Shergy WJ, Phillips RM, Hunt RE, Hernandez J. Infliximab and its impact on surgical outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:Suppl 3. 1511.13. Matthews JLK, Martin L, Hu R. Postoperative complications in rheumatoid arthritis patients on anti-TNF therapies undergoing orthopaedic procedures. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. 65:Suppl 2. 331.14. Arkfeld DG, Kasraeian S, Metyas S, Itomura J. Use of anti-TNF agents in 15 rheumatoid arthritis patients undergoing total elbow arthroplasty. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007. 66:Suppl 2. 534.15. Dixon WG, Lunt M, Watson KD, Hyrich KL. Anti-TNF therapy and the risk of serious post-operative infection: results from the BSR biologics register (BSRBR). Ann Rheum Dis. 2007. 66:Suppl 2. 118.16. Kanbe K, Inoue K, Chiba J. Risk factors of infection after orthopaedic surgery with infliximab for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007. 66:Suppl 2. 174.17. Ding T, Ledingham J, Luqmani R, Westlake S, Hyrich K, Lunt M, et al. BSR and BHPR rheumatoid arthritis guidelines on safety of anti-TNF therapies. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010. 49:2217–2219.
Article18. Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM, Anuntiyo J, Finney C, Curtis JR, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2008 recommendations for the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. 59:762–784.
Article19. Neufassung der Empfehlungen der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Rheumatologie zur Therapie mit Tumornekrosefaktor-hemmenden Wirkstoffen bei entzündlichrheumatischen Erkrankungen (Stand März 2006). http://dgrh.de/fileadmin/media/Praxis___Klinik/Therapie-Empfehlungen/TNF-Blocker_06.pdf.20. Grennan DM, Gray J, Loudon J, Fear S. Methotrexate and early postoperative complications in patients with rheumatoid arthritis undergoing elective orthopaedic surgery. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001. 60:214–217.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Review of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors on Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Pharmacologic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- Management of the arthritis related osteoporosis
- Effect of anti-rheumatic agents on periodontal parameters and biomarkers of inflammation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Biologic Agent for Rheumatoid Arthritis