Korean Circ J.
2011 Jun;41(6):321-326. 10.4070/kcj.2011.41.6.321.
Interleukin-6 (-636 C/G) Gene Polymorphism in Korean Children With Kawasaki Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. ymhong@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1776189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2011.41.6.321
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
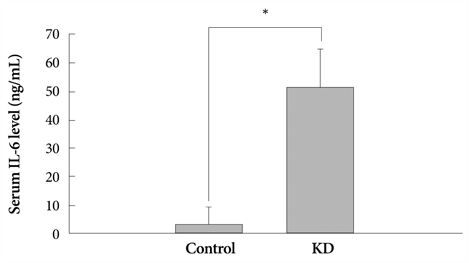
Kawasaki disease (KD) is a multi-systemic vasculitis with coronary artery involvement. Serum interleukin (IL)-6 levels during acute phase showed a significant correlation with the duration of fever in patients with KD who were not treated with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), suggesting that the regulation of IL-6 expression in KD patients may differ from that in normal children. However, there are controversies surrounding the association between IL-6 (-636 C/G) gene polymorphism and development of KD.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
One hundred and nine children with KD and 191 children with congenital heart disease were included in this study. Echocardiography was performed to examine cardiac involvement in patients with KD. Genotyping of the IL-6 (-636 C/G) gene polymorphism was performed using the single-base extension method, and serum IL-6 concentrations were estimated using the sandwich enzyme immunoassay method.
RESULTS
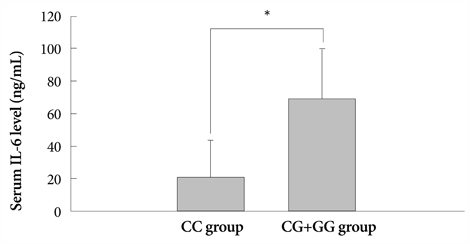
Neutrophil, platelet count, liver function test, total protein and albumin concentrations were significantly different in the KD group and the serum IL-6 concentration was significantly higher in the KD group than the control group. There was no difference between the patients with coronary arterial dilatation (CAD) and those without CAD in the IL-6 (-636 C/G) polymorphism. The serum albumin concentration was significantly lower in patients with KD who had the -636 C/G or GG genotype compared with the control group. The serum IL-6 concentration was significantly higher in patients with KD who had the -636 C/G or GG genotype.
CONCLUSION
There was no association between the IL-6 (-636 C/G) gene polymorphism and development of coronary arterial lesions in KD. Further multicenter studies are required to establish the relationship between the IL-6 (-636 C/G) gene polymorphism and development of KD.
MeSH Terms
-
Child
Coronary Vessels
Dilatation
Echocardiography
Fever
Genotype
Heart Diseases
Humans
Immunoenzyme Techniques
Immunoglobulins
Interleukin-6
Interleukins
Liver Function Tests
Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome
Neutrophils
Platelet Count
Polymorphism, Genetic
Serum Albumin
Vasculitis
Immunoglobulins
Interleukin-6
Interleukins
Serum Albumin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yeo JS, Choi JW. Effectiveness of medium-dose intravenous immunoglobulin (1 g/kg) in the treatment of Kawasaki disease. Korean Circ J. 2010. 40:81–85.2. Lee SJ, Ahn HM, Yoo JH, Hong YM. Carotid intima-media thickness and pulse wave velocity after recovery from Kawasaki disease. Korean Circ J. 2009. 39:264–269.3. Wang CL, Wu YT, Liu CA, Kuo HC, Yang KD. Kawasaki disease infection, immunity and genetics. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005. 24:998–1004.4. Fulton DR, Newberger JW. Long-term cardiac sequelae of Kawasaki disease. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2000. 2:324–329.5. Kato H, Sugimura T, Akagi T, et al. Long-term consequences of Kawasaki disease: a 10- to 21-year follow-up study of 594 patients. Circulation. 1996. 94:1379–1385.6. Lloyd AJ, Walker C, Wilkinso M. Kawasaki disease: is it caused by an infectious agent? Br J Biomed Sci. 2001. 58:122–128.7. Liang SJ, Cheong HI, Noh CI, Yun YS. Role of anti-endothelial cell antibody in the development of coronary arterial lesions in Kawasaki disease. Korean Circ J. 2006. 36:723–731.8. Maury CP, Salo E, Pelkonen D. Circulating interleukin-1 beta in patients with Kawasaki disease. N Engl J Med. 1988. 319:1670–1671.9. Ueno Y, Takano N, Kanegane H, et al. The acute phase nature of interluekin-6: studies in Kawasaki disease and other febrile illness. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989. 76:337–342.10. Hirano T, Akira S, Taga T, Kishimoto T. Biological and clinical aspects of interluekin-6. Immunol Today. 1990. 11:443–449.11. Tanaka C, Mannami T, Kamide K, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 gene associated with blood pressure and atherosclerosis in a Japanese general population. Hypertens Res. 2005. 28:35–41.12. Kim MK, Kim DS. The interleukin-6 level in Kawasaki disease. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1992. 35:515–526.13. Research Committee on Kawasaki Disease. Report of Subcommittee on Standardization of Diagnostic Criteria and Reporting of Coronary Artery Lesions in Kawasaki Disease. 1984. Tokyo, Japan: Ministry of Health and Welfare.14. Hong YM, Jin HS, Park IS, Hong SJ. Association of the matrix metalloproteinase-3 (-439C/G) gene polymorphism with Kawasaki disease in Korean children. Heart Vessels. 2008. 23:341–347.15. Hirao J, Hibi S, Andoh T, Ichimura T. High levels of circulating inter-leukin-4 and interleukin-10 in Kawasaki disease. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997. 112:152–156.16. Cheung YF, Huang GY, Chen CB, et al. Inflammatory gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to Kawasaki disease and its arterial sequelae. Pediatrics. 2008. 122:e608–e614.17. Leung DY, Geha RS, Newberger JW, et al. Two monokines, interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor, render cultured vascular endothelial cells susceptible to lysis by antibodies circulating during Kawasaki syndrome. J Exp Med. 1986. 164:1958–1972.18. Hata A, Onouchi Y. Susceptibility genes for Kawasaki disease: toward implementation of personalized medicine. J Hum Genet. 2009. 54:67–73.19. Blake GJ, Ridker PM. Inflammatory bio-markers and cardiovascular risk prediction. J Intern Med. 2002. 252:283–294.20. Zee RY, Cook NR, Cheng S, et al. Polymorphism in the P seletin and interleukin-4 genes as determinants of stroke: a population-based, prospective genetic analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 2004. 13:389–396.21. Chapman CM, Beilby JP, Humphries SE, Palmer LJ, Thompson PL, Hung J. Association of an allelic variant of interleukin-6 with subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in an Australian community population. Eur Heart J. 2003. 24:1494–1499.22. Jibiki T, Terai M, Shima M, et al. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 gene regulatory region polymorphism and serum levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in Japanese patients with Kawasaki disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. 44:2211–2212.23. Fishman D, Faulds G, Jeffery R, et al. The effect of novel polymorphism in the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene on IL-6 transcription and plasma IL-6 levels, and an association with systemic onset juvenile chronic arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1998. 102:1369–1376.24. Burns JC, Shimizu C, Shike H, et al. Family-based association analysis implications IL-4 in susceptibility to Kawasaki disease. Genes Immun. 2005. 6:438–444.25. Jin HS, Kim HB, Kim BS, et al. The IL-10 (-627 A/C) gene polymorphism may be associated with coronary aneurysms and low albumin in Korean children with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Res. 2007. 61:584–587.26. Linker-Israeli M, Wallace DJ, Prehn JL, Nand R, Li L, Klinenberg JR. A greater variability in the 3'flanking region of the IL-6 gene in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Autoimmunity. 1996. 23:199–209.27. Papassotiropoulos A, Bagli M, Jessen F, et al. A genetic variation of the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 delays the initial onset and reduces the risk for sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1999. 45:666–668.28. Morgan L, Cooper J, Montgomery H, Kitchen N, Humphries SE. The interleukin-6 gene -174G>C and -572G>C promoter polymorphisms are related to cerebral aneurysms. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006. 77:915–917.29. Sohn MH, Hur MW, Kim DS. Interleukin-6 gene gene polymorphism is not associated with Kawasaki disease. Genes Immun. 2001. 2:357–362.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Insertion/Deletion Polymorphism of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Gene in Kawasaki Disease
- The interleukin-6 level in Kawasaki disease
- The soluble interleukin 2 receptor levels in Kawasaki disease
- Association Study of Glutathione-S-Transferase M1/T1 Gene Polymorphism in Korean Children with Kawasaki Disease
- Association of Interleukin-10 A-592C Polymorphism in Taiwanese Children with Kawasaki Disease