Korean J Gastroenterol.
2009 Aug;54(2):99-107. 10.4166/kjg.2009.54.2.99.
Predictive Significance of Serum IL-6, VEGF, and CRP in Gastric Adenoma and Mucosal Carcinoma before Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. sychoi@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1775964
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2009.54.2.99
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
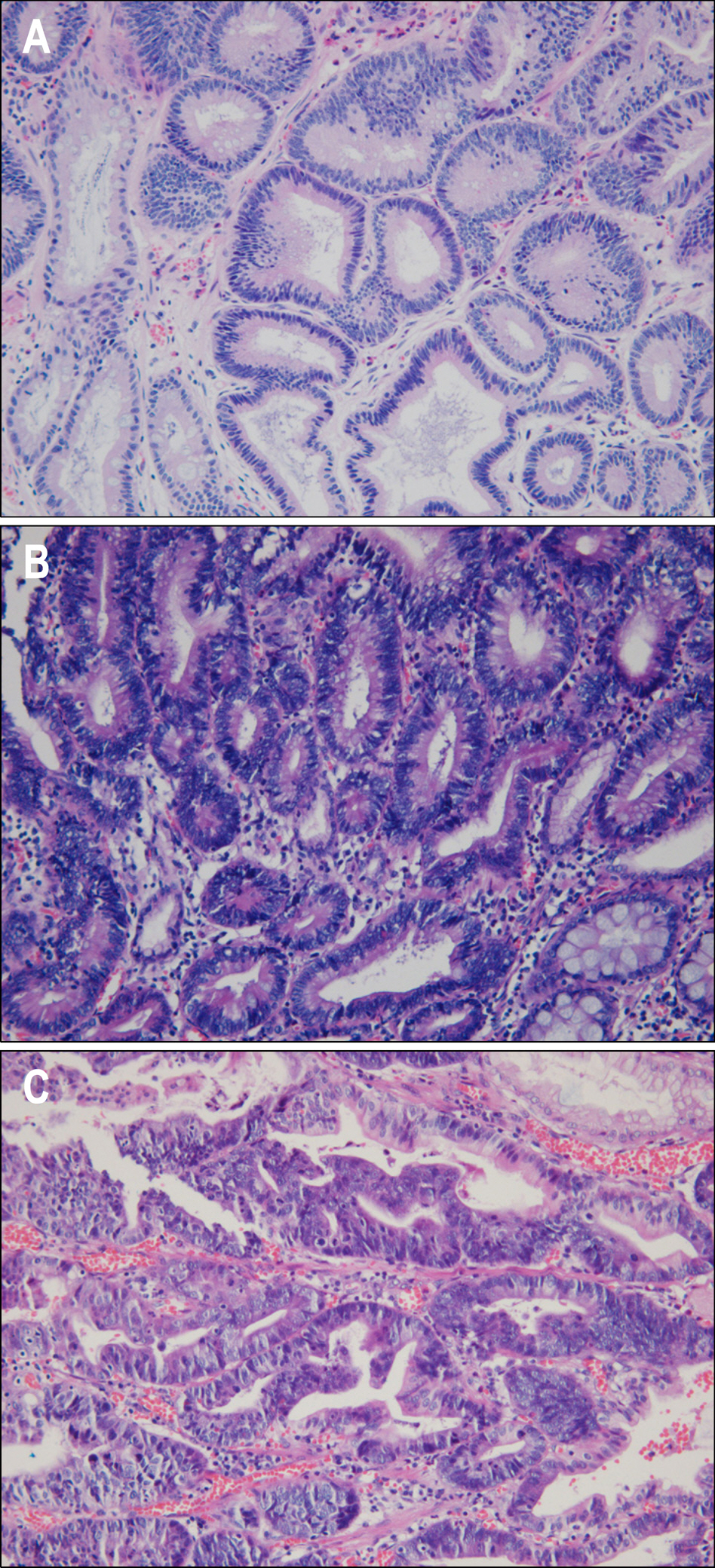
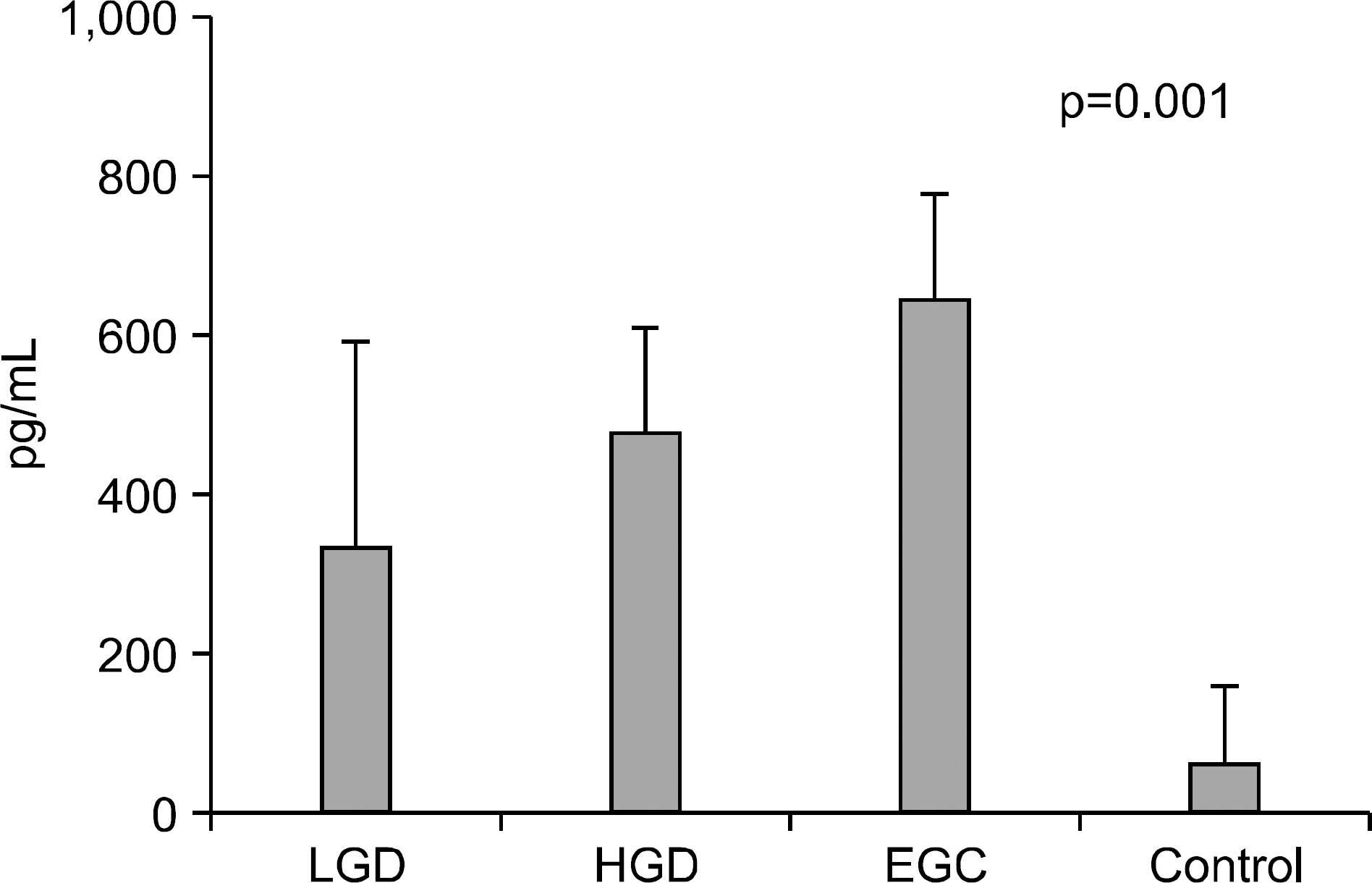
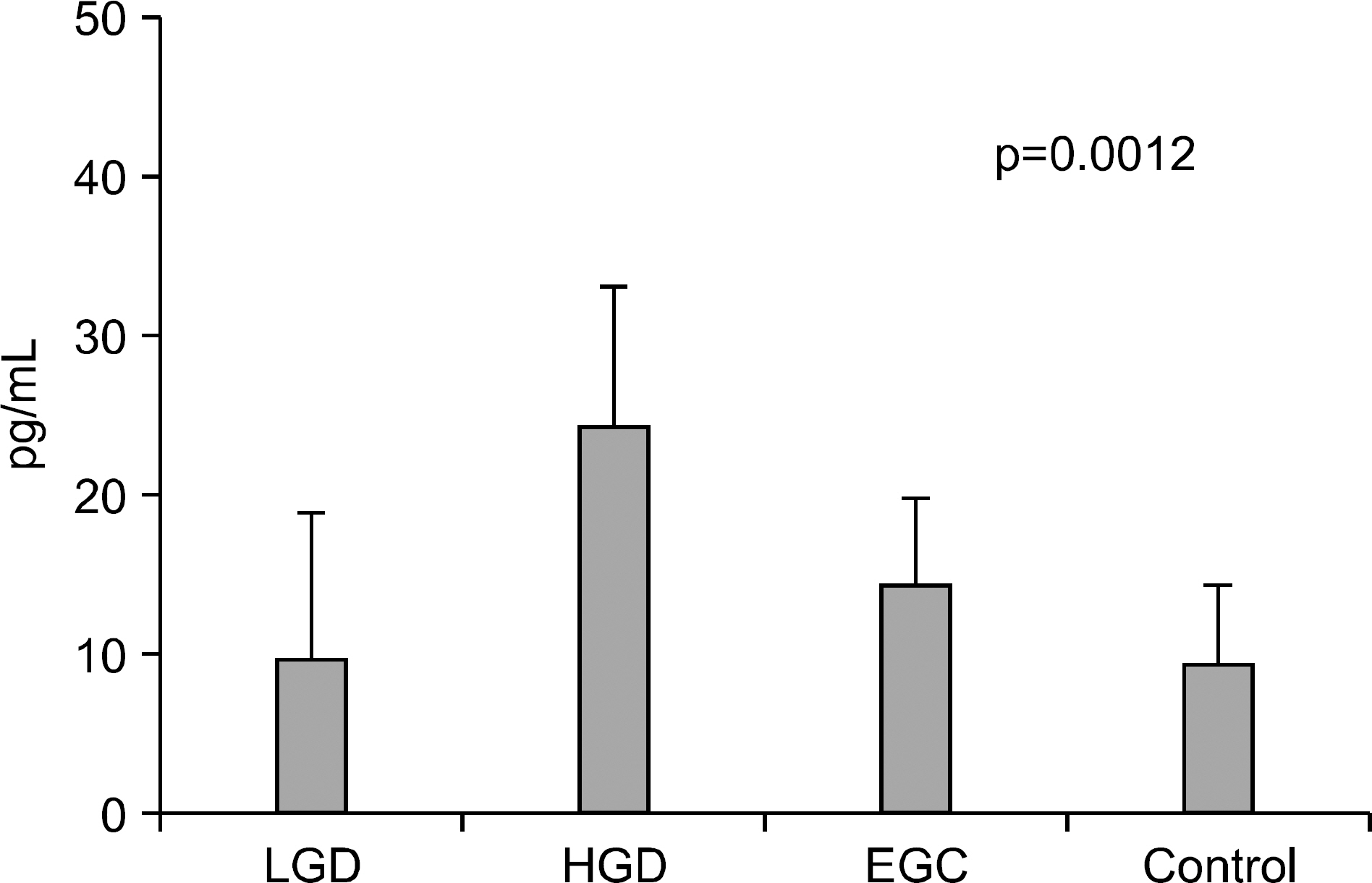
Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is commonly used for radical resection of gastric adenoma and mucosal cancer, but there is about 30% of discrepancy rate between the histology of the endoscopic biopsy and that of the resecwas to clarify the clinical significance of IL-6, VEGF, CRP before ESD. METHODS: We investigated the correlation between serum IL-6, VEGF, CRP level and discrepancy rate of gastric neoplastic lesions (10 low-grade dysplasias, 18 high-grade dysplasias, and 25 early gastic cancers). RESULTS: Serum levels of IL-6 in gastric adenoma and mucosal cancer patients were significantly higher than in healthy controls (p<0.05). Especially, serum IL-6 level of high-grade dysplasia patient was significantly higher than low-grade dysplasia and mucosal cancer patients, and the positive rate, sensitivity, and negative predictive value of serum IL-6 levels were higher in high-grade dysplasia patient compared to low-grade dysplasia patient and mucosal cancer patient. Serum levels of VEGF in patients with gastric adenoma and mucosal cancer were significantly higher than healthy controls (p<0.01). Serum levels of CRP in patients with mucosal cancer were significantly higher than in the controls (p<0.05), and the positive rate, sensitivity, and positive predictive value of serum CRP levels were higher in high-grade dysplasia and mucosal cancer patients compared to low-grade dysplasia patient. CONCLUSIONS: Serum levels of IL-6, VEGF, and CRP in patients with gastric neoplastic lesions were significantly higher than healthy controls, especially, serum IL-6 level of high grade dysplasia patient was significantly higher than low-grade dysplasia and mucosal cancer patients.
Keyword
- Serum IL-6; VEGF; CRP; Adenoma; Cancer
MeSH Terms
-
Adenoma/*diagnosis/pathology/surgery
Adult
Aged
C-Reactive Protein/*analysis
Carcinoma/*diagnosis/pathology/surgery
Diagnosis, Differential
Female
Gastric Mucosa/*surgery
Gastroscopy
Humans
Interleukin-6/*blood
Male
Middle Aged
Predictive Value of Tests
Stomach Neoplasms/*diagnosis/pathology/surgery
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors/*blood
Figure
Reference
-
1. Howson CP, Hiyama T, Wynder EL. The decline in gastric cancer: epidemiology of an unplanned triumph. Epidemiol Rev. 1986; 8:1–27.
Article2. Zinvy J, Wang TC, Yantiss R, et al. Role of therapy or monitoring in preventing progression to gastric cancer. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003; 36:50–60.3. Ohno S, Fujii T, Ueda S, et al. Predictive factors and timing for liver recurrence after curative resection of gastric carcinoma. Am J Surg. 2003; 185:258–263.
Article4. Cahill RJ, Kilgallen C, Beattie S, et al. Gastric epithelial cell kinetics in the progression from normal mucosa to gastric carcinoma. Gut. 1996; 38:177–181.
Article5. Bodger K, Crabtree JE. Helicobacter pylori and gastric inflammation. Br Med Bull. 1998; 54:139–150.6. Blaser MJ, Parsonnet J. Parasitism by the ‘slow’ bacterium Helicobacter pylori leads to altered gastric homeostasis and neoplasia. J Clin Invest. 1994; 94:4–8.7. Forman D. Helicobacter pylori infection and cancer. Br Med Bull. 1998; 54:71–78.8. O'Connor F, Buckley M, O'Morain C. Helicobacter pylori: the cancer link. J R Soc Med. 1996; 88:674–678.9. Chatelain D, de Lajarte Thirouard AS, Tiret E, Flejou JF. Adenocarcinoma of the upper esophagus arising in heterotopic gastric mucosa: common pathogenesis with Barrett's adenocarcinoma? Virchows Arch. 2002; 441:406–411.
Article10. Tanahashi T, Kita M, Kodama T, et al. Cytokine expression and production by purified Helicobacter pylori urease in human gastric epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 2000; 68:664–671.11. Yamaoka Y, Kodama T, Kita M, et al. Relation between cy-tokines and Helicobacter pylori in gastric cancer. Helicobacter. 2001; 6:116–124.12. Arii K, Tanimura H, Iwahashi M, et al. Neutrophil functions and cytokine production in patients with gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000; 47:291–297.13. Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Vandersteen DP, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991; 325:1127–1131.14. Senger DR, Brown LF, Claffey KP, et al. Vascular permeability factor, tumor angiogenesis and stroma generation. Invasion Metastasis. 1994; 14:385–394.15. Ikeguchi M, Oka S, Saito H, et al. The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and proliferative activity of cancer cells in gastric cancer. Langenbeck's Arch Surg. 1999; 384:264–270.
Article16. Maehara Y, Kabashima A, Koga T, et al. Vascular invasion and potential for tumor angiogenesis and metastasis in gastric carcinoma. Surgery. 2000; 128:408–416.
Article17. Cohen T, Nahari D, Cerem LW, Neufeld G, Levi BZ. Interleukin 6 induces the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:736–741.
Article18. Kallio R, Surcel HM, Bloigu A, et al. C-reactive protein, pro-calcitonin and interleukin-8 in the primary diagnosis of infections in cancer patients. Eur J Cancer. 2000; 36:889–894.
Article19. Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma. Gastric Cancer. 1998; 1:10–24.20. Kim HK, Song KS, Park YS, et al. Elevated levels of circulating platelet microparticles, VEGF, IL6 and RANTES in patients with gastric cancer: possible role of a metastasis predictor. Eur J Cancer. 2003; 39:184–191.
Article21. Jang JS, Lee EJ, Lee SW, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer and gastric adenoma. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2007; 49:256–263.22. Min BH, Lee JH, Kim JJ, et al. Clinical outcome of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for treating early gastric cancer: comparison with endoscopicy mucosal resection after circumferential precutting (EMR-P). Dig Liver Dis. 2009; 41:201–209.23. Park EH, Choi SR, Jeong JS, et al. The histologic discrepancy before and after endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric adenoma and early gastric cancer. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 34:125–131.24. Yamada H, Ikegami M, Shimoda T, et al. Longterm follow-up study of gastric adenoma/dysplasia. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:390–396.
Article25. Hay LJ. Surgical management of gastric polyp and adenomas. Surgery. 1956; 39:114–119.26. Jo YJ, Lee SJ, Jo JY, et al. The effectiveness of biomarkers to detect micrometastasis of gastric adenocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 20:45.27. Oh SY, Kwon HC, Kim SY, et al. Clinicopathologic significance of HIF-1α, p53, and VEGF expression and preoperative serum VEGF level in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2008; 8:123.
Article28. Rugge M, Cassaro M, Di Mario F, et al. The long term outcome of gastric non-invasive neoplasia. Gut. 2003; 52:111–116.
Article29. Wu CW, Wang SR, Chao MF, et al. Serum interleukin-6 levels reflect disease status of gastric cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91:1417–1422.30. Yonemura Y, Endo Y, Fujita H, et al. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor C expression in the development of lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1999; 5:1823–1829.31. Huang SP, Wu MS, Wang HP, et al. Correlation between serum levels of interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor in gastric carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002; 17:1165–1169.
Article32. McMillan DC, Wotherspoon HA, Fearon KC, et al. A prospective study of tumor recurrence and the acute-phase response after apparently curative colorectal cancer surgery. Am J Surg. 1995; 170:319–322.
Article33. De Mello J, Struthers L, Turner R, Cooper EH, Giles GR. Multivariate analyses as aids to diagnosis and assessment of prognosis in gastrointestinal cancer. Br J Cancer. 1983; 48:341–348.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- History and Development of Accessories for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Endoscopic Treatment of Gastric Adenoma
- A Case of Acute Myocardial Infarction Occurred Immediately after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- The Histologic Discrepancy before and after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of Gastric Adenoma and Early Gastric Cancer
- Serrated Adenoma with Adenocarcinoma of Stomach Treated by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection