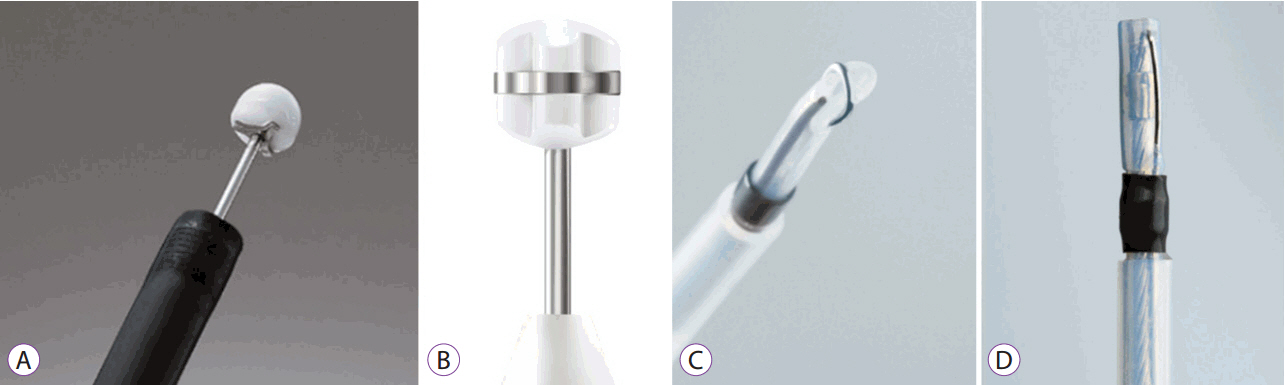
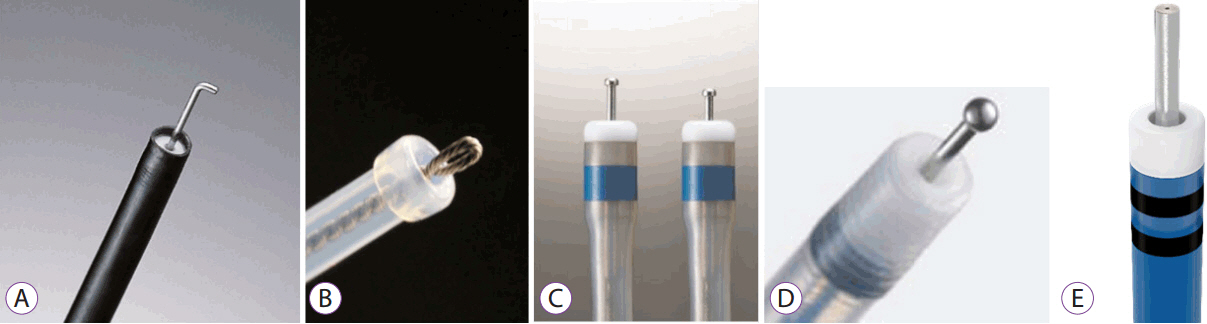
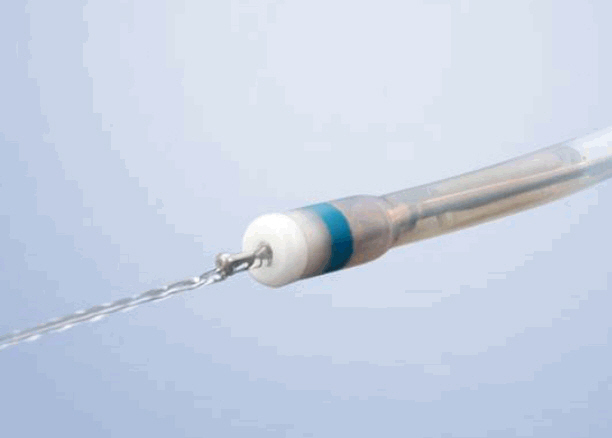
History and Development of Accessories for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Digestive Disease Center and Research Institute, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Hospital , Bucheon, Korea. kopa9445@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2388817
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.078
Abstract
- Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) procedure is composed of circumferential mucosal incision and submucosal dissection. A variety of endoscopic accessories are required to perform mucosal incision and submucosal dissection safely. As a result of the improvements in ESD devices and peripheral equipment and development of the ESD technique, ESD procedures have been performed extensively worldwide. Here I review the history of the development of accessories used in performing ESD procedures.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Diode Laser—Can It Replace the Electrical Current Used in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection?
Yunho Jung, Gwang Ho Baik, Weon Jin Ko, Bong Min Ko, Seong Hwan Kim, Jin Seok Jang, Jae-Young Jang, Wan-Sik Lee, Young Kwan Cho, Sun Gyo Lim, Hee Seok Moon, In Kyung Yoo, Joo Young Cho
Clin Endosc. 2021;54(4):555-562. doi: 10.5946/ce.2020.229.Determining the Safety and Effectiveness of Electrocautery Enhanced Scissors for Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (with Video)
Kelly E. Hathorn, Walter W. Chan, Hiroyuki Aihara, Christopher C. Thompson
Clin Endosc. 2020;53(4):443-451. doi: 10.5946/ce.2019.214.Comparison between a novel core knife and the conventional IT knife 2 for endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric mucosal lesions
Myeongsoon Park, Jin Wook Lee, Dong Woo Shin, Jungseok Kim, Yoo Jin Lee, Ju Yup Lee, Kwang Bum Cho
Clin Endosc. 2022;55(6):767-774. doi: 10.5946/ce.2022.002.Understanding hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection subtleties
João Paulo de Souza Pontual, Alexandre Moraes Bestetti, Diogo Turiani Hourneaux de Moura
Clin Endosc. 2023;56(6):738-740. doi: 10.5946/ce.2023.195.
Reference
-
1. Gotoda T, Ho KY, Soetikno R, Kaltenbach T, Draganov P. Gastric ESD: current status and future directions of devices and training. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014; 24:213–233.2. Sumiyama K, Tajiri H. History of ESD. In : Fukami N, editor. Endoscopic submucosal dissection: principles and practice. New York (NY): Springer-Verlag New York;2015. p. 3–8.3. Hosokawa K, Yoshida S. [Recent advances in endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer]. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1998; 25:476–483.4. Ono H, Hasuike N, Inui T, et al. Usefulness of a novel electrosurgical knife, the insulation-tipped diathermic knife-2, for endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2008; 11:47–52.
Article5. Yahagi N. En-bloc resection of colorectal neoplasma by submucosal dissection method using flex knife. Early Colorectal Cancer. 2003; 7:550–556.6. Yahagi N, Fujishiro M, Kakushima N, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer using the tip of an electrosurgical snare (thin type). Dig Endosc. 2004; 16:34–38.
Article7. Oyama T, Tomori A, Hotta K, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early esophageal cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 3(7 Suppl 1):S67–S70.
Article8. Honma K, Kobayashi M, Watanabe H, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia. Dig Endosc. 2010; 22:307–311.
Article9. Neuhaus H, Wirths K, Schenk M, Enderle MD, Schumacher B. Randomized controlled study of EMR versus endoscopic submucosal dissection with a water-jet hybrid-knife of esophageal lesions in a porcine model. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:112–120.
Article10. Toyonaga T, Nishino E, Man-I M, East JE, Azuma T. Principles of quality controlled endoscopic submucosal dissection with appropriate dissection level and high quality resected specimen. Clin Endosc. 2012; 45:362–374.
Article11. Tanaka S, Terasaki M, Kanao H, Oka S, Chayama K. Current status and future perspectives of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors. Dig Endosc. 2012; 24 Suppl 1:73–79.
Article12. Yamamoto H, Kawata H, Sunada K, et al. Successful en-bloc resection of large superficial tumors in the stomach and colon using sodium hyaluronate and small-caliber-tip transparent hood. Endoscopy. 2003; 35:690–694.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Future Development of Endoscopic Accessories for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Tips and Tricks for Better Endoscopic Treatment of Colorectal Tumors: Usefulness of Cap and Band in Colorectal Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
- Endoscopic Treatment for Early Gastric Cancer
- Endoscopic Treatment of Subepithelial Tumors
- Debates on Colorectal Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection - Traction for Effective Dissection: Gravity Is Enough