Korean J Gastroenterol.
2010 Oct;56(4):249-254. 10.4166/kjg.2010.56.4.249.
A Case of Acute Myocardial Infarction Occurred Immediately after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. seenae99@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 1718361
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2010.56.4.249
Abstract
- Endoscopic methods such as endoscopic mucosal resection or endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) have been increasingly used for the treatment of gastric adenoma and early gastric cancer. Especially, ESD is very useful since it allows en bloc resection of large lesions. Bleeding and perforation are well known as common complications after ESD. However, there is no report of acute myocardial infarction associated with ESD. We report a case of acute myocardial infarction which was detected immediately after ESD.
MeSH Terms
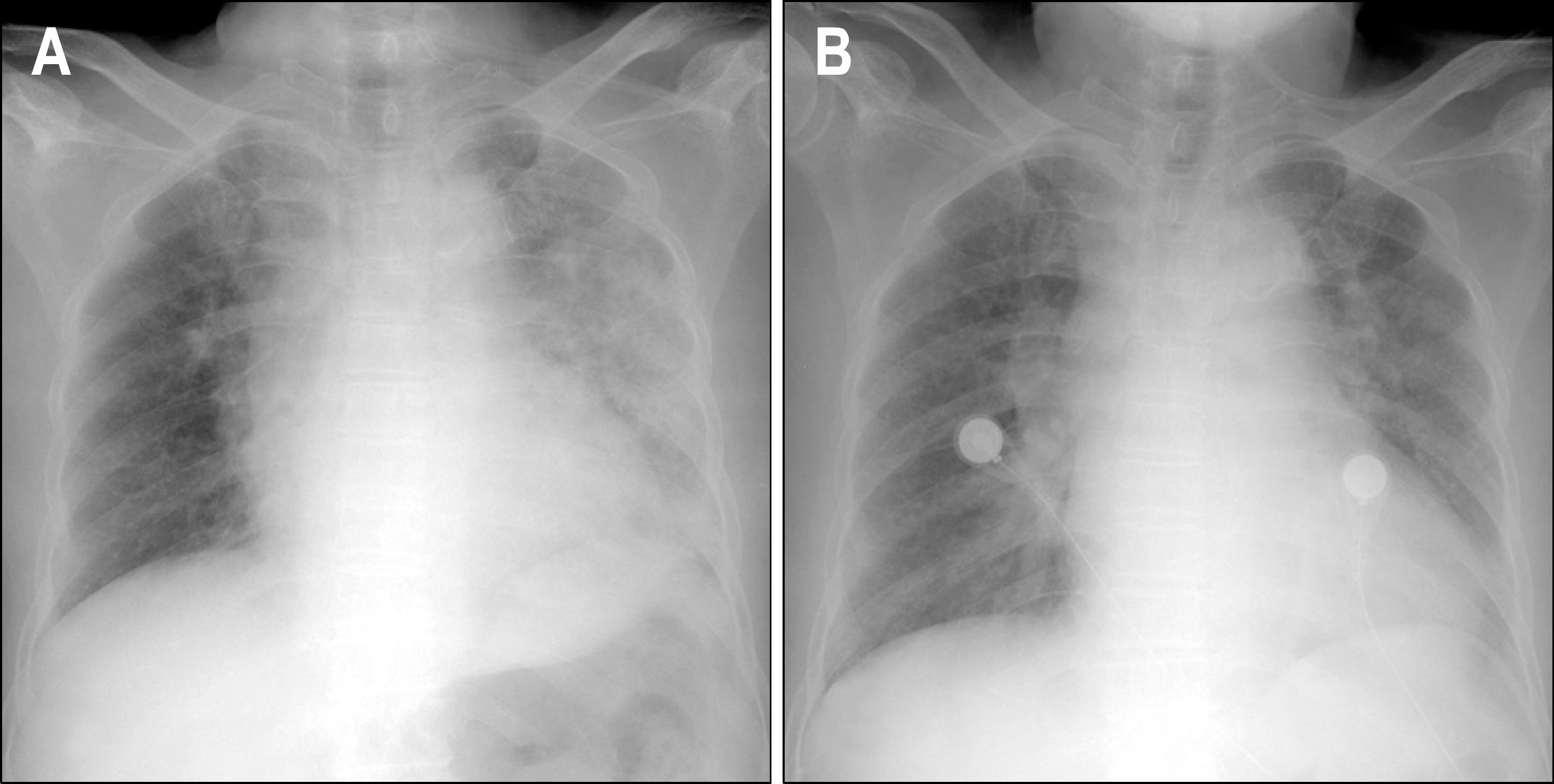
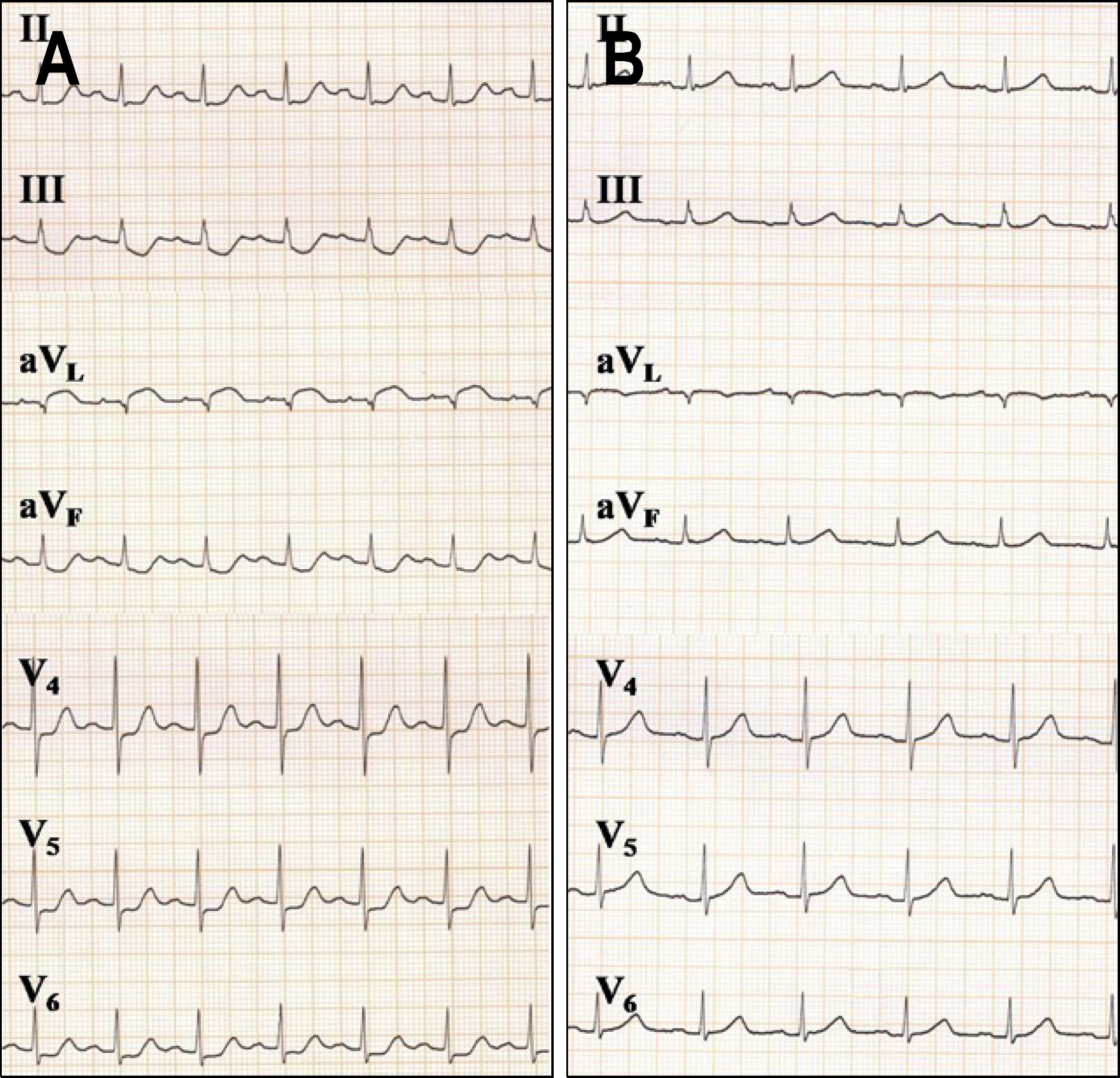
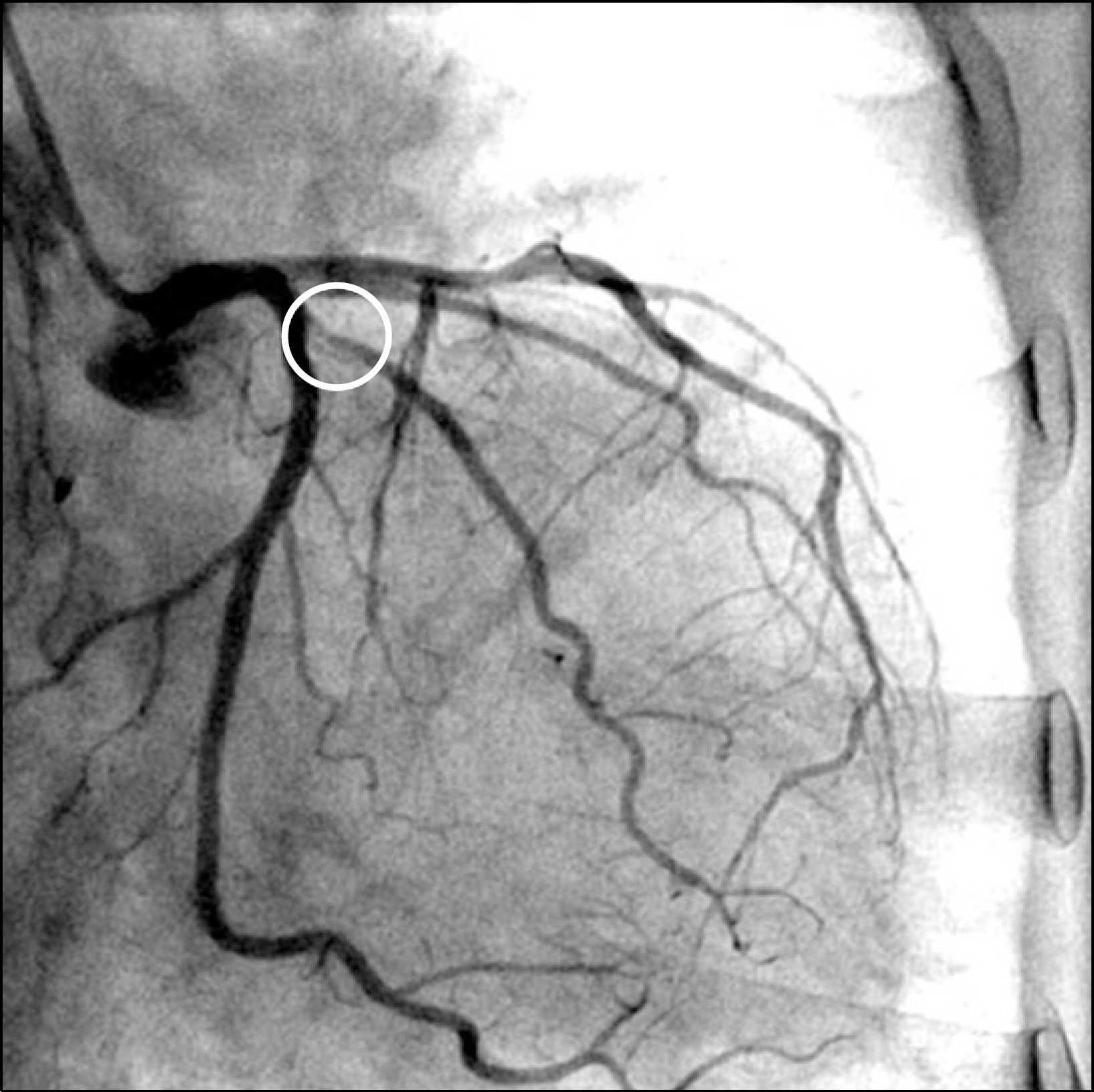
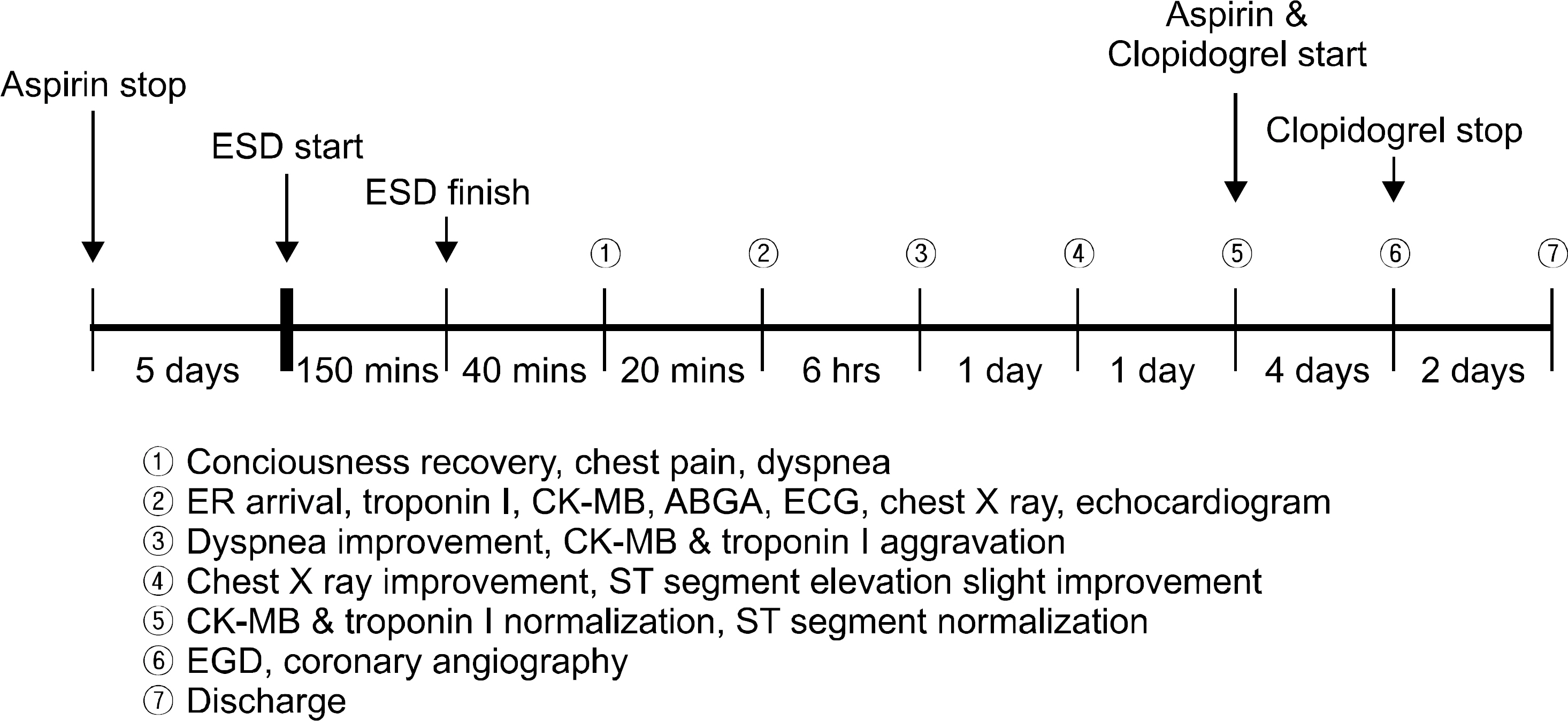
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gotoda T, Yamamoto H, Soetikno RM. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2006; 41:929–942.
Article2. Chung IK, Lee JH, Lee SH, et al. Therapeutic outcomes in 1000 cases of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric neoplasms: Korean ESD Study Group multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:1228–1235.
Article3. Kim JJ, Lee JH, Jung HY, et al. EMR for early gastric cancer in Korea: a multicenter retrospective study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:693–700.4. Yachimski P, Hur C. Upper endoscopy in patients with acute myocardial infarction and upper gastrointestinal bleeding: results of a decision analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2009; 54:701–711.
Article5. Lee EK, Jeon SW, Oh JT, et al. The feasibility and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric neoplasm in elderly Korean patients. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 38:323–331.6. Min BH, Lee JH, Kim JJ, et al. Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for treating early gastric cancer: comparison with endoscopic mucosal resection after circumferential precutting (EMR-P). Dig Liver Dis. 2009; 41:201–209.
Article7. Kakushima N, Fujishiro M. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastrointestinal neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:2962–2967.
Article8. Cao Y, Liao C, Tan A, Gao Y, Mo Z, Gao F. Meta-analysis of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection for tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:751–757.
Article9. Habr-Gama A, Waye JD. Complications and hazards of gastrointestinal endoscopy. World J Surg. 1989; 13:193–201.
Article10. Shahmir M, Schuman BM. Complications of fiberoptic endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1980; 26:86–91.
Article11. Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, et al. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): case-control study. Lancet. 2004; 364:937–952.
Article12. Jung HY, Choi KD, Song HJ, Lee GH, Kim JH. Risk management in endoscopic submucosal dissection using needle knife in Korea. Dig Endosc. 2007; 19(suppl 1):S5–S8.
Article13. Becker RC, Scheiman J, Dauerman HL, et al. Management of platelet-directed pharmacotherapy in patients with athero-sclerotic coronary artery disease undergoing elective endoscopic gastrointestinal procedures. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104:2903–2917.
Article14. Eisen GM, Baron TH, Dominitz JA, et al. Guideline on the management of anticoagulation and antiplatelet therapy for endoscopic procedures. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:775–779.
Article15. Lee CT, Huang SP, Cheng TY, et al. Factors associated with myocardial infarction after emergency endoscopy for upper gastrointestinal bleeding in high-risk patients: a prospective observational study. Am J Emerg Med. 2007; 25:49–52.
Article16. Haffner SM, Lehto S, Rö nnemaa T, Pyö rä lä K, Laakso M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:229–234.
Article17. Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy RP, Hennekens CH. Inflammation, aspirin, and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy men. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336:973–979.
Article18. Assmann G, Cullen P, Schulte H. Simple scoring scheme for calculating the risk of acute coronary events based on the 10-year follow-up of the prospective cardiovascular Munster (PROCAM) study. Circulation. 2002; 105:310–315.
Article19. Anderson KM, Odell PM, Wilson PW, Kannel WB. Cardiovascular disease risk profiles. Am Heart J. 1991; 121:293–298.
Article20. Mehta SK, Frutkin AD, Lindsey JB, et al. Bleeding in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: the development of a clinical risk algorithm from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2009; 2:222–229.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Myocardial Infarction Occurred after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection under Bridging Therapy with Low Molecular Weight Heparin
- History and Development of Accessories for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Acute Myocardial Infarction in Patient with Spontaneous Coronary
- A Case of Acute Aortic Dissection Involved Left and Right Coronary Arterial Ostia diagnosed with Transesophageal Echocardiography
- A Case of Pneumorrhachis and Pneumoscrotum Following Colon Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection