Korean J Gastroenterol.
2012 Oct;60(4):258-261. 10.4166/kjg.2012.60.4.258.
A Case of Intraperitoneal Immunoglobulin G4-related Inflammatory Pseudotumor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jbkim87@hallym.or.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1775811
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2012.60.4.258
Abstract
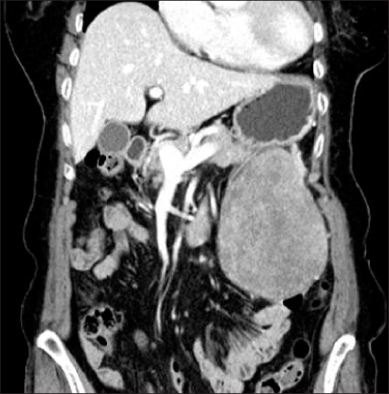
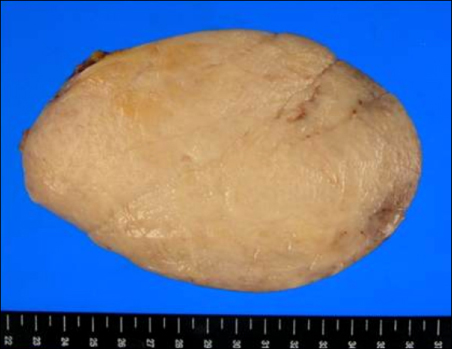
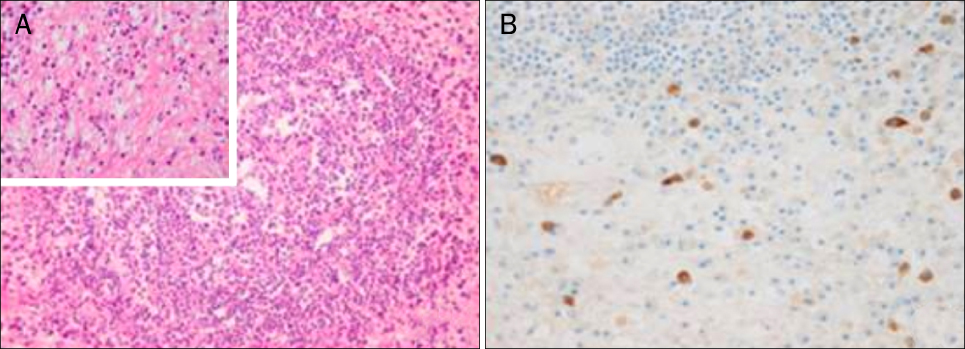
- The term inflammatory pseudotumor (IPT) has been used to describe inflammatory and fibrosing tumoral processes of an undetermined cause that may involve a variety of organ system. IgG4-related disease is a newly recognized fibroinflammatory condition characterized by IgG4-producing plasma cell expansion in affected organs and, often but not always, elevated serum IgG4 concentrations. IgG4-related IPTs, a subtype of IPT, are characterized by dense infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells and stromal fibrosis. The association between inflammatory pseudotumor and IgG4 was first reported with a regard to sclerosing pancreatitis. Despite there are many reports on intraperitoneal IPTs including both cellular and lymphoplasmacytic type, only a few cases have been confirmed to be IgG4-related. We experienced a case of intraperitoneal IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumor in an 83-year-old woman presenting with epigastric pain and malaise. Surgical specimens revealed an IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumor.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sakemi R, So S, Morimitsu Y, et al. A case of IgG4-related sclerosing disorders involving the mesentery and the pancreas. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2011. 108:969–977.2. Nomura Y, Naito Y, Eriguchi N, et al. A case of IgG4-related sclerosing mesenteritis. Pathol Res Pract. 2011. 207:518–521.3. Chen TS, Montgomery EA. Are tumefactive lesions classified as sclerosing mesenteritis a subset of IgG4-related sclerosing disorders? J Clin Pathol. 2008. 61:1093–1097.4. Masterson L, Del Pero MM, Donnelly N, Moffat DA, Rytina E. Immunoglobulin G4 related systemic sclerosing disease involving the temporal bone. J Laryngol Otol. 2010. 124:1106–1110.5. Bahadori M, Liebow AA. Plasma cell granulomas of the lung. Cancer. 1973. 31:191–208.6. Zen Y, Kasahara Y, Horita K, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the breast in a patient with a high serum IgG4 level: histologic similarity to sclerosing pancreatitis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005. 29:275–278.7. Zen Y, Fujii T, Sato Y, Masuda S, Nakanuma Y. Pathological classification of hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor with respect to IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2007. 20:884–894.8. Zen Y, Kitagawa S, Minato H, et al. IgG4-positive plasma cells in inflammatory pseudotumor (plasma cell granuloma) of the lung. Hum Pathol. 2005. 36:710–717.9. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:732–738.10. Adsay NV, Basturk O, Klimstra DS, Klöppel G. Pancreatic pseudotumors: non-neoplastic solid lesions of the pancreas that clinically mimic pancreas cancer. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2004. 21:260–267.11. Zen Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, et al. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis with and without hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor, and sclerosing pancreatitis-associated sclerosing cholangitis: do they belong to a spectrum of sclerosing pancreatitis? Am J Surg Pathol. 2004. 28:1193–1203.12. Rollins KE, Mehta SP, O'Donovan M, Safranek PM. Gastric IgG4-related autoimmune fibrosclerosing pseudotumour: a novel location. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2011. 2011:873087.13. Kim SA, Lee SR, Huh J, Shen SS, Ro JY. IgG4-associated inflammatory pseudotumor of ureter: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 3 cases. Hum Pathol. 2011. 42:1178–1184.14. Shoji S, Nakano M, Usui Y. IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumor of the kidney. Int J Urol. 2010. 17:389–390.15. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012. 366:539–551.16. Masaki Y, Kurose N, Umehara H. IgG4-related disease: a novel lymphoproliferative disorder discovered and established in Japan in the 21st century. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2011. 51:13–20.17. Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Levy MJ, et al. Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis: the Mayo Clinic experience. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. 4:1010–1016.18. Yamamoto H, Yamaguchi H, Aishima S, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor versus IgG4-related sclerosing disease and inflammatory pseudotumor: a comparative clinicopathologic study. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009. 33:1330–1340.19. Choi EK, Kim MH, Lee TY, et al. The sensitivity and specificity of serum immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin G4 levels in the diagnosis of autoimmune chronic pancreatitis: Korean experience. Pancreas. 2007. 35:156–161.20. Neild GH, Rodriguez-Justo M, Wall C, Connolly JO. Hyper-IgG4 disease: report and characterisation of a new disease. BMC Med. 2006. 4:23.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Unique Imaging Features in Hepatic Actinomycosis Accompanied by an IgG4-Related Inflammatory Pseudotumor: A Case Report
- Hepatic Immunoglobulin G4-related Inflammatory Pseudotumor Mimicking Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Immunoglobulin G4-Related Inflammatory Pseudotumor Presenting as a Solitary Mass in the Stomach
- Multi-Organ Involvement of an Immunoglobulin G4-Related Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Urogenital Tract: A Case Report
- Solitary immunoglobulin G4-related inflammatory pseudotumor in the abdomen wall