Clin Endosc.
2016 Mar;49(2):197-201. 10.5946/ce.2015.074.
Immunoglobulin G4-Related Inflammatory Pseudotumor Presenting as a Solitary Mass in the Stomach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. bongsul@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2165046
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.074
Abstract
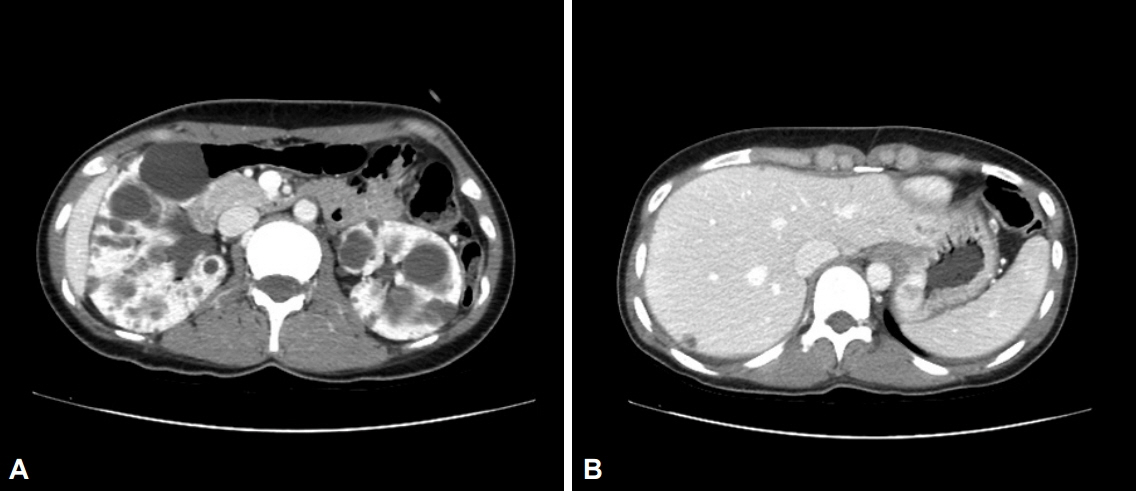
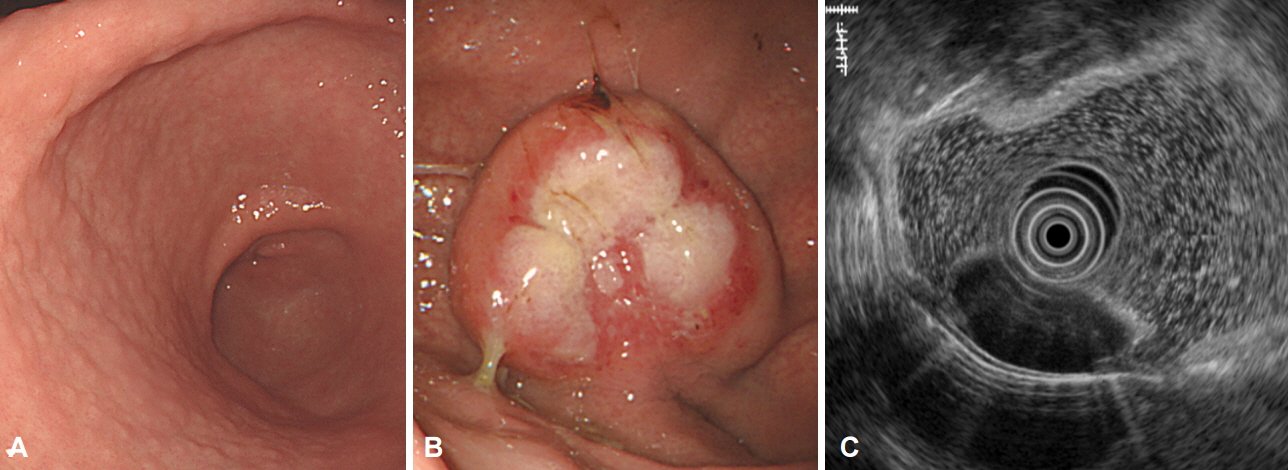
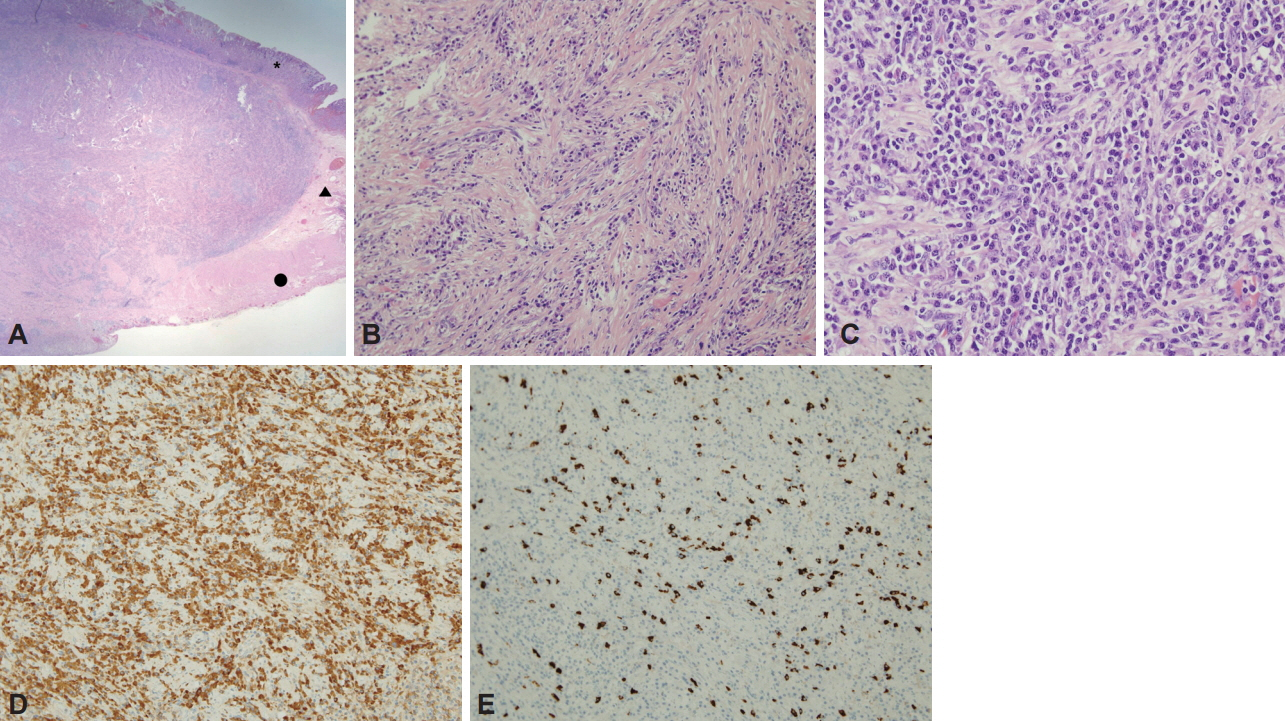
- Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related disease (IgG4RD) is a relatively recently recognized entity that is histopathologically characterized by an extensive infiltration of lymphocytes and IgG4-positive plasma cells with dense fibrosis. IgG4RD is now known to affect any organ system, and a few cases of gastrointestinal lesions have also been reported. However, solitary IgG4RD of the stomach is still very rare. Furthermore, as it can mimic malignant conditions, it is important to recognize this disease to avoid unnecessary surgery. Herein, we present a case of IgG4RD presenting as an isolated subepithelial mass in the stomach.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
IgG4-related Disease in the Stomach which Was Confused with Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): Two Case Reports and Review of the Literature
Ho Seok Seo, Yoon Ju Jung, Cho Hyun Park, Kyo Young Song, Eun Sun Jung
J Gastric Cancer. 2018;18(1):99-107. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2018.18.e8.Gastric IgG4-related disease presenting as a mass lesion and masquerading as a gastrointestinal stromal tumor
Banumathi Ramakrishna, Rohan Yewale, Kavita Vijayakumar, Patta Radhakrishna, Balakrishnan Siddartha Ramakrishna
J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(3):258-262. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2020.02.10.
Reference
-
1. Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22:21–30.2. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:539–551.
Article3. Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38:982–984.
Article4. Kanno A, Satoh K, Kimura K, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis with hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor. Pancreas. 2005; 31:420–423.
Article5. Zen Y, Kitagawa S, Minato H, et al. IgG4-positive plasma cells in inflammatory pseudotumor (plasma cell granuloma) of the lung. Hum Pathol. 2005; 36:710–717.
Article6. Cha DH, Choi CW, Kim S, et al. An IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumor of the greater omentum. Korean J Med. 2013; 84:400–404.
Article7. Rollins KE, Mehta SP, O’Donovan M, Safranek PM. Gastric IgG4-related autoimmune fibrosclerosing pseudotumour: a novel location. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2011; 2011:873087.
Article8. Chetty R, Serra S, Gauchotte G, Märkl B, Agaimy A. Sclerosing nodular lesions of the gastrointestinal tract containing large numbers of IgG4 plasma cells. Pathology. 2011; 43:31–35.
Article9. Na KY, Sung JY, Jang JY, et al. Gastric nodular lesion caused by IgG4-related disease. Pathol Int. 2012; 62:716–718.
Article10. Kim do H, Kim J, Park do H, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related inflammatory pseudotumor of the stomach. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:451–452.11. Fujita T, Ando T, Sakakibara M, Hosoda W, Goto H. Refractory gastric ulcer with abundant IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration: a case report. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:2183–2186.
Article12. Bateman AC, Sommerlad M, Underwood TJ. Chronic gastric ulceration: a novel manifestation of IgG4-related disease? J Clin Pathol. 2012; 65:569–570.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hepatic Immunoglobulin G4-related Inflammatory Pseudotumor Mimicking Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Solitary immunoglobulin G4-related inflammatory pseudotumor in the abdomen wall
- Unique Imaging Features in Hepatic Actinomycosis Accompanied by an IgG4-Related Inflammatory Pseudotumor: A Case Report
- A Case of Intraperitoneal Immunoglobulin G4-related Inflammatory Pseudotumor
- Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease Involving the Urethra: Case Report