Yonsei Med J.
2009 Jun;50(3):414-421. 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.3.414.
Inhibitory Effect of Fentanyl on Phenylephrine-Induced Contraction of the Rat Aorta
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. jtsohn@nongae.gsnu.ac.kr
- 2Institutes of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 1758571
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2009.50.3.414
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: Fentanyl was reported to inhibit the alpha1-adrenoceptor agonist-induced contraction. The goal of this in vitro study was to identify the alpha1-adrenoceptor subtype primarily involved in the fentanyl-induced attenuation of phenylephrine-induced contraction in isolated endothelium-denuded rat aorta.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
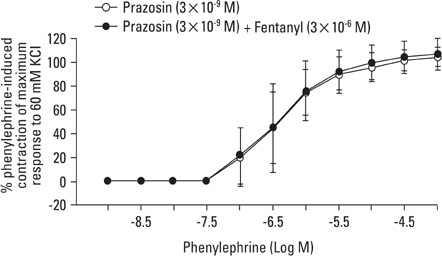
Aortic rings were suspended in order to record isometric tension. Concentration-response curves for phenylephrine (10-9 to 10-5 M) were generated in the presence or absence of one of the following drugs: fentanyl (3x10-7, 10-6, 3x10-6 M), 5-methylurapidil (3x10-8, 10-7, 3x10-7 M), chloroethylclonidine (10-5 M) and BMY 7378 (3x10-9, 10-8, 3x10-8 M). Phenylephrine concentration-response curves were generated in the presence or absence of fentanyl in rings pretreated with either 3x10-9 M prazosin, 10-9 M 5-methylurapidil or 3x10-9 M BMY 7378.
RESULTS
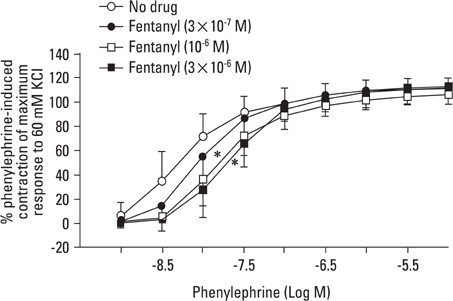
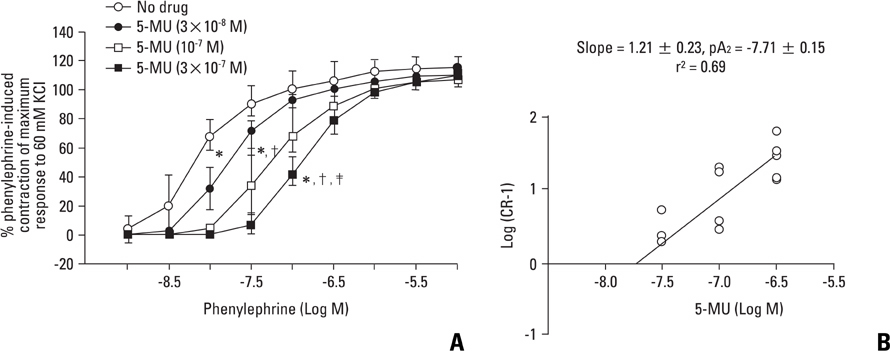
Fentanyl (10-6, 3x10-6 M) attenuated phenylephrine-induced contraction in the rat aorta. 5-Methylurapidil and BMY 7378 produced a parallel rightward shift in the phenylephrine concentration-response curve. The pA2 values for 5-methylurapidil and BMY 7378 were estimated to be 7.71 +/- 0.15 and 8.99 +/- 0.24, respectively. Fentanyl (10-6 M) attenuated phenylephrine-induced contraction in rings pretreated with 10-9 M 5-methylurapidil, but did not alter the rings when pretreated with 3x10-9 M BMY 7378. Pretreatment of the rings with chloroethylclonidine showed a 72.9 +/- 2.3% reduction in phenylephrine-induced maximal contraction.
CONCLUSION
The results suggest that fentanyl attenuates phenylephrine-induced contraction by inhibiting the pathway involved in the alpha1D-adrenoceptor-mediated contraction of the rat aorta.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Graves CL, Downs NH, Browne AB. Cardiovascular effects of minimal analgesic quantities of innovar, fentanyl, and droperidol in man. Anesth Analg. 1975. 54:15–23.2. Freye E. Cardiovascular effects of high dosages of fentanyl, meperidine, and naloxone in dogs. Anesth Analg. 1974. 53:40–47.3. Wynands JE, Townsend GE, Wong P, Whalley DG, Srikant CB, Patel YC. Blood pressure response and plasma fentanyl concentrations during high- and very high-dose fentanyl anesthesia for coronary artery surgery. Anesth Analg. 1983. 62:661–665.4. Toda N, Hatano Y. Alpha-adrenergic blocking action of fentanyl on the isolated aorta of the rabbit. Anesthesiology. 1977. 46:411–416.
Article5. Karasawa F, Iwanou V, Moulds RF. Effects of fentanyl on the rat aorta are mediated by alpha-adrenoceptors rather than by the endothelium. Br J Anaesth. 1993. 71:877–880.6. Sohn JT, Ding X, McCune DF, Perez DM, Murray PA. Fentanyl attenuates alpha1B-adrenoceptor-mediated pulmonary artery contraction. Anesthesiology. 2005. 103:327–334.
Article7. Hieble JP, Bylund DB, Clarke DE, Eikenburg DC, Langer SZ, Lefkowitz RJ, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. X. Recommendation for nomenclature of alpha1-adrenoceptors: consensus update. Pharmacol Rev. 1995. 47:267–270.8. Vargas HM, Gorman AJ. Vascular alpha-1 adrenergic receptor subtypes in the regulation of arterial pressure. Life Sci. 1995. 57:2291–2308.
Article9. Asbún-Bojalil J, Castillo EF, Escalante BA, Castillo C. Does segmental difference in alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype explain contractile difference in rat abdominal and thoracic aorta? Vascul Pharmacol. 2002. 38:169–175.
Article10. Arévalo-León LE, Gallardo-Ortíz IA, Urquiza-Marín H, Villalobos-Molina R. Evidence for the role of alpha1D- and alpha1A-adrenoceptors in contraction of the rat mesenteric artery. Vascul Pharmacol. 2003. 40:91–96.
Article11. Errasti AE, Velo MP, Torres RM, Sardi SP, Rothlin RP. Characterization of alpha1-adrenoceptor subtypes mediating vasoconstriction in human umbilical vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. 126:437–442.
Article12. Low AM, Lu-Chao H, Wang YF, Brown RD, Kwan CY, Daniel EE. Pharmacological and immunocytochemical characterization of subtypes of alpha-1 adrenoceptors in dog aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998. 285:894–901.13. Arunlakshana O, Schild HO. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959. 14:48–58.14. Blaise GA, Witzeling TM, Sill JC, Vinay P, Vanhoutte PM. Fentanyl is devoid of major effects on coronary vasoreactivity and myocardial metabolism in experimental animals. Anesthesiology. 1990. 72:535–541.15. Kenny BA, Chalmers DH, Philpott PC, Naylor AM. Characterization of an alpha1D-adrenoceptor mediating the contractile response of rat aorta to noradrenaline. Br J Pharmacol. 1995. 115:981–986.16. Forray C, Bard JA, Wetzel JM, Chiu G, Shapiro E, Tang R, et al. The alpha 1-adrenergic receptor that mediates smooth muscle contraction in human prostate has the pharmacological properties of the cloned human alpha 1c subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994. 45:703–708.17. Goetz AS, King HK, Ward SDL, True TA, Rimele TJ, Saussy DL Jr. BMY 7378 is a selective antagonist of the D subtype of alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995. 272:R5–R6.18. Saussy DL Jr, Goetz AS, Queen KL, King HK, Lutz MW, Rimele TJ. Structure activity relationships of a series of buspirone analogs at alpha 1 adrenoceptor: further evidence that rat aorta alpha-1 adrenoceptors are of the alpha-1D-subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996. 278:136–144.19. Buckner SA, Oheim KW, Morse PA, Knepper SM, Hancock AA. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor-induced contractility in rat aorta is mediated by the alpha 1 D subtype. Eur J Pharmacol. 1996. 297:241–248.
Article20. Hussain MB, Marshall I. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes mediating contractions to phenylephrine in rat thoracic aorta, mesenteric artery and pulmonary artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. 122:849–858.
Article21. Deng XF, Chemtob S, Varma DR. Characterization of alpha 1D-adrenoceptor subtype in rat myocardium, aorta and other tissues. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. 119:269–276.
Article22. Schwinn DA, Johnston GI, Page SO, Mosley MJ, Wilson KH, Worman NP, et al. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of human alpha-1 adrenergic receptors: sequence corrections and direct comparison with other species homologues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995. 272:134–142.23. Fagura MS, Lydford SJ, Dougall IG. Pharmacological classification of alpha 1-adrenoceptors mediating contractions of rabbit isolated ear artery: comparison with rat isolated thoracic aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. 120:247–258.
Article24. Maruyama K, Suzuki M, Tsuchiya M, Makara Y, Hattori K, Ohnuki T, et al. Discrimination of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat aorta and prostate. Pharmacology. 1998. 57:88–95.
Article25. Michelotti GA, Price DT, Schwinn DA. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor regulation: basic science and clinical implications. Pharmacol Ther. 2000. 88:281–309.
Article26. Sohn JT, Ok SH, Kim HJ, Moon SH, Shin IW, Lee HK, et al. Inhibitory effect of fentanyl on acetylcholine-induced relaxation in rat aorta. Anesthesiology. 2004. 101:89–96.
Article27. Flacke JW, Davis LJ, Flacke WE, Bloor BC, Van Etten AP. Effects of fentanyl and diazepam in dogs deprived of autonomic tone. Anesth Analg. 1985. 64:1053–1059.
Article28. Kawakubo A, Fujigaki T, Uresino H, Zang S, Sumikawa K. Comparative effects of etomidate, ketamine, propofol, and fentanyl on myocardial contractility in dogs. J Anesth. 1999. 13:77–82.
Article29. Suzer O, Suzer A, Aykac Z, Ozuner Z. Direct cardiac effects in isolated perfused rat hearts measured at increasing concentrations of morphine, alfentanil, fentanyl, ketamine, etomidate, thiopentone, midazolam and propofol. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1998. 15:480–485.
Article30. Christensen KL, Mulvany MJ. Location of resistance arteries. J Vasc Res. 2001. 38:1–12.
Article31. Etches RC, Sandler AN, Daley MD. Respiratory depression and spinal opioids. Can J Anaesth. 1989. 36:165–185.
Article32. Artru AA. Cottrell JE, Smith DS, editors. Cerebrospinal fluid. Anesthesia and Neurosurgery. 2001. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby;84–85.
Article33. Hug CC Jr, Murphy MR. Fentanyl disposition in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma and its relationship to ventilatory depression in the dog. Anesthesiology. 1979. 50:342–349.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Ethanol on the Regulation of Smooth Muscle Tone in Rat Aorta
- The Effect of Halothane and Enflurane on the Aorta Contracted with Phenylephrine in Rabbits
- A Study of Vascular Relaxation Mechanism of GS-389, a New Potent Vasodilator
- The Effects of Etomidate in the Strips of a Rat Thoracic Aorta
- Effects of Fentanyl on Relaxation in Smooth Muscle of the Rat Aorta