Korean J Radiol.
2008 Jun;9(3):226-235. 10.3348/kjr.2008.9.3.226.
Semi-Automatic Measurement of the Airway Dimension by Computed Tomography Using the Full-Width-Half-Maximum Method: a Study on the Measurement Accuracy according to the CT Parameters and Size of the Airway
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. seojb@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Industrial Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1758456
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2008.9.3.226
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
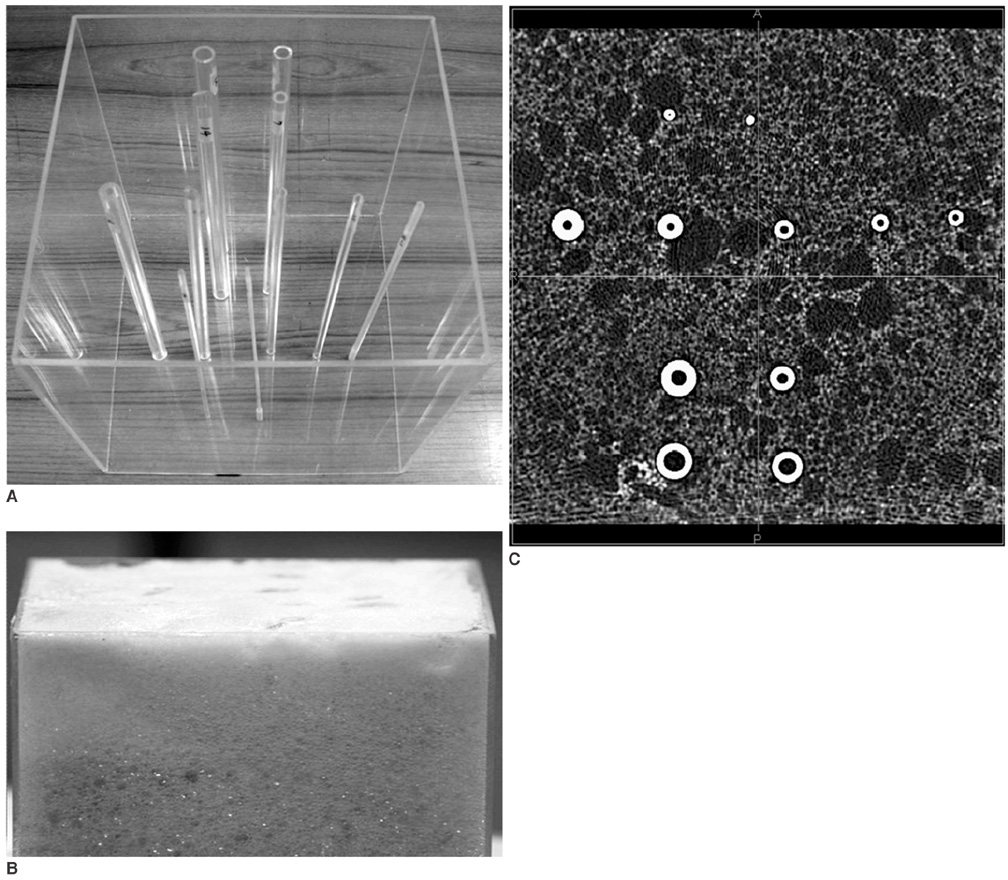
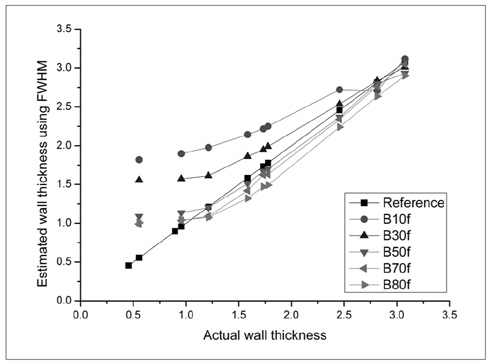
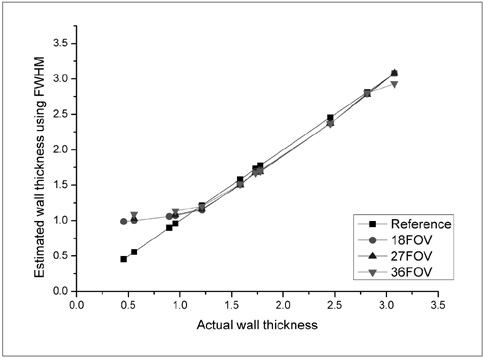
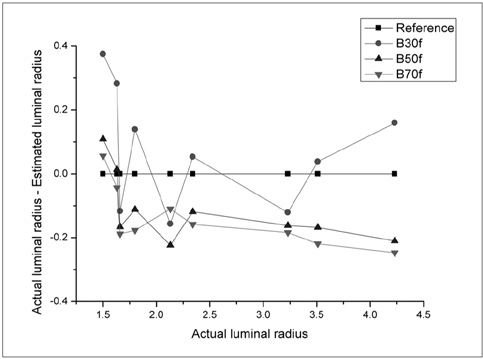
To assess the influence of variable factors such as the size of the airway and the CT imaging parameters such as the reconstruction kernel, field-of-view (FOV), and slice thickness on the automatic measurement of airway dimension. MATERIALS AND METHODS: An airway phantom was fabricated that contained eleven poly-acryl tubes of various lumen diameters and wall thicknesses. The measured density of the poly-acryl wall was 150 HU, and the measured density of the airspace filled with polyurethane foam was -900 HU. CT images were obtained using a 16-MDCT (multidetector CT) scanner and were reconstructed with various reconstruction kernels, thicknesses and FOV. The luminal radius and wall thickness were measured using in-house software based on the full-width-half-maximum method. The measured values as determined by CT and the actual dimensions of the tubes were compared. RESULTS: Measurements were most accurate on images reconstructed with use of a standard kernel (mean error: -0.03 +/- 0.21 mm for wall thickness and -0.12 +/- 0.11 mm for the luminal radius). There was no significant difference in accuracy among images with the use of variable slice thicknesses or a variable FOV. Below a 1-mm threshold, the measurement failed to represent the change of the real dimensions. CONCLUSION: Measurement accuracy was strongly influenced by the specific reconstruction kernel utilized. For accurate measurement, standardization of the imaging protocol and selection of the appropriate anatomic level are essential.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
An Engineering View on Megatrends in Radiology: Digitization to Quantitative Tools of Medicine
Namkug Kim, Jaesoon Choi, Jaeyoun Yi, Seungwook Choi, Seyoun Park, Yongjun Chang, Joon Beom Seo
Korean J Radiol. 2013;14(2):139-153. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.139.
Reference
-
1. Weibel ER, Taylor CR. Design and structure of human lung. Pulmonary disease and disorders. 1988. New York: McGraw-Hill;11–60.2. Barnes PJ, Hansel TT. Prospects for new drugs for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 2004. 364:985–996.3. Schwab RJ, Gefter WB, Pack AI, Hoffman EA. Dynamic imaging of the upper airway during respiration in normal subjects. J Appl Physiol. 1993. 74:1504–1514.4. Amirav I, Kramer SS, Grunstein MM, Hoffman EA. Assessment of methacholine-induced airway constriction by ultrafast high-resolution computed tomography. J Appl Physiol. 1993. 75:2239–2250.5. Brown RH, Herold CJ, Hirshman CA, Zerhouni EA, Mitzner W. Individual airway constrictor response heterogeneity to histamine assessed by high-resolution computed tomography. J Appl Physiol. 1993. 74:2615–2620.6. Block M, Liu YH, Harris LD, Robb RA, Ritman EL. Quantitative analysis of a vascular tree model with the dynamic spatial reconstructor. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1984. 8:390–400.7. Wood SA, Zerhouni EA, Hoford JD, Hoffman EA, Mitzner W. Measurement of three-dimensional lung tree structures by using computed tomography. J Appl Physiol. 1995. 79:1687–1697.8. King MA, Long DT, Brill AB. SPECT volume quantitation: influence of spatial resolution, source size and shape, and voxel size. Med Phys. 1991. 18:1016–1024.9. Van Brabandt H, Cauberghs M, Verbeken E, Moerman P, Lauweryns JM, Van de Woestijne KP. Partitioning of pulmonary impedance in excised human and canine lungs. J Appl Physiol. 1983. 55:1733–1742.10. Yanai M, Sekizawa K, Ohrui T, Sasaki H, Takishima T. Site of airway obstruction in pulmonary disease: direct measurement of intrabronchial pressure. J Appl Physiol. 1992. 72:1016–1023.11. Nakano Y, Wong JC, de Jong PA, Buzatu L, Nagao T, Coxson HO, et al. The prediction of small airway dimensions using computed tomography. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005. 171:142–146.12. Hasegawa M, Nasuhara Y, Onodera Y, Makita H, Nagai K, Fuke S, et al. Airflow limitation and airway dimensions in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. 173:1309–1315.13. McNamara AE, Muller NL, Okazawa M, Arntorp J, Wiggs BR, Pare PD. Airway narrowing in excised canine lungs measured by high-resolution computed tomography. J Appl Physiol. 1992. 73:307–316.14. Awadh N, Muller NL, Park CS, Abboud RT, FitzGerald JM. Airway wall thickness in patients with near fatal asthma and control groups: assessment with high resolution computed tomographic scanning. Thorax. 1998. 53:248–253.15. Niimi A, Matsumoto H, Amitani R, Nakano Y, Mishima M, Minakuchi M, et al. Airway wall thickness in asthma assessed by computed tomography. Relation to clinical indices. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 162:1518–1523.16. Nakano Y, Muro S, Sakai H, Hirai T, Chin K, Tsukino M, et al. Computed tomographic measurements of airway dimensions and emphysema in smokers. Correlation with lung function. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 162:1102–1108.18. Little SA, Sproule MW, Cowan MD, Macleod KJ, Robertson M, Love JG, et al. High resolution computed tomographic assessment of airway wall thickness in chronic asthma: reproducibility and relationship with lung function and severity. Thorax. 2002. 57:247–253.19. Gono H, Fujimoto K, Kawakami S, Kubo K. Evaluation of airway wall thickness and air trapping by HRCT in asymptomatic asthma. Eur Respir J. 2003. 22:965–971.20. Aziz ZA, Wells AU, Desai SR, Ellis SM, Walker AE, MacDonald S, et al. Functional impairment in emphysema: contribution of airway abnormalities and distribution of parenchymal disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005. 185:1509–1515.21. Orlandi I, Moroni C, Camiciottoli G, Bartolucci M, Pistolesi M, Villari N, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: thin-section CT measurement of airway wall thickness and lung attenuation. Radiology. 2005. 234:604–610.22. Lee YK, Oh YM, Lee JH, Kim EK, Lee JH, Kim N, et al. Quantitative assessment of emphysema, airtrapping, and airway thickening on computed tomography. Lung. in press, DOI: 10.1007/S00408-008-9071-0.23. Kalender WA. Computed tomography, fundamentals, system technology, image quality, applications. 2005. 2nd revised edition. Publicis Corporate Publishing;26–30.24. Rollano-Hijarrubia E, Stokking R, van der Meer F, Niessen WJ. Imaging of small high-density structures in CT: a phantom study. Acad Radiol. 2006. 13:893–908.25. Kim N, Seo JB, Song KS, Chae EJ, Kang SH. Semi-automatic measurement of the airway dimension at computed tomography using the full-with-half-maximum method: study on the measurement accuracy according to orientation of an artificial airway. Korean J Radiol. 2008. 9:236–242.26. McNamara AE, Muller NL, Okazawa M, Arntorp J, Wiggs BR, Pare PD. Airway narrowing in excised canine lungs measured by high-resolution computed tomography. J Appl Physiol. 1992. 73:307–316.27. Gelb AF, Hogg JC, Muller NL, Schein MJ, Kuei J, Tashkin DP, et al. Contribution of emphysema and small airways in COPD. Chest. 1996. 109:353–359.28. Gelb AF, Zamel N, Hogg JC, Muller NL, Schein MJ. Pseudophysiologic emphysema resulting from severe small-airways disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 158:815–819.29. Fujimoto K, Kitaguchi Y, Kubo K, Honda T. Clinical analysis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease phenotypes classified using high-resolution computed tomography. Respirology. 2006. 11:731–740.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Semi-Automatic Measurement of the Airway Dimension by Computed Tomography Using the Full-With-Half-Maximum Method: a Study of the Measurement Accuracy according to the Orientation of an Artificial Airway
- An experimental study on accuracy and error range of CT measurement
- Quantitative Analysis of Airway Walls Using CT Software
- Airway Measurement for Airway Remodeling Defined by Post-Bronchodilator FEV1/FVC in Asthma: Investigation Using Inspiration-Expiration Computed Tomography
- The Effect of Mandibular Repositioning Device on Airway Size and Airway Collapsibility in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Cine CT during Sleep