Semi-Automatic Measurement of the Airway Dimension by Computed Tomography Using the Full-With-Half-Maximum Method: a Study of the Measurement Accuracy according to the Orientation of an Artificial Airway
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. seojb@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Industrial Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1758457
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2008.9.3.236
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
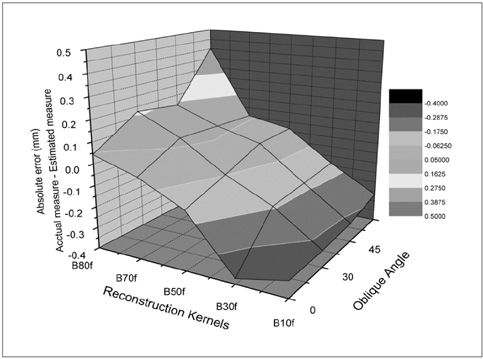
To develop an algorithm to measure the dimensions of an airway oriented obliquely on a volumetric CT, as well as assess the effect of the imaging parameters on the correct measurement of the airway dimension. MATERIALS AND METHODS: An airway phantom with 11 poly-acryl tubes of various lumen diameters and wall thicknesses was scanned using a 16-MDCT (multidetector CT) at various tilt angles (0, 30, 45, and 60degree). The CT images were reconstructed at various reconstruction kernels and thicknesses. The axis of each airway was determined using the 3D thinning algorithm, with images perpendicular to the axis being reconstructed. The luminal radius and wall thickness was measured by the full-width-half-maximum method. The influence of the CT parameters (the size of the airways, obliquity on the radius and wall thickness) was assessed by comparing the actual dimension of each tube with the estimated values. RESULTS: The 3D thinning algorithm correctly determined the axis of the oblique airway in all tubes (mean error: 0.91 +/- 0.82degree). A sharper reconstruction kernel, thicker image thickness and larger tilt angle of the airway axis resulted in a significant decrease of the measured wall thickness and an increase of the measured luminal radius. Use of a standard kernel and a 0.75-mm slice thickness resulted in the most accurate measurement of airway dimension, which was independent of obliquity. CONCLUSION: The airway obliquity and imaging parameters have a strong influence on the accuracy of the airway wall measurement. For the accurate measurement of airway thickness, the CT images should be reconstructed with a standard kernel and a 0.75 mm slice thickness.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Quantitative CT Imaging in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Review of Current Status and Future Challenges
Young Hoon Cho, Joon Beom Seo, Sang Min Lee, Sang Min Lee, Jooae Choe, Dabee Lee, Namkug Kim
J Korean Soc Radiol. 2018;78(1):1-12. doi: 10.3348/jksr.2018.78.1.1.An Engineering View on Megatrends in Radiology: Digitization to Quantitative Tools of Medicine
Namkug Kim, Jaesoon Choi, Jaeyoun Yi, Seungwook Choi, Seyoun Park, Yongjun Chang, Joon Beom Seo
Korean J Radiol. 2013;14(2):139-153. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.139.Prediction of Treatment Response in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease by Determination of Airway Dimensions with Baseline Computed Tomography
Hyo Jung Park, Sang Min Lee, Jooae Choe, Sang Min Lee, Namkug Kim, Jae Seung Lee, Yeon-Mok Oh, Joon Beom Seo
Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(2):304-312. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0204.
Reference
-
1. Weibel ER, Taylor CR. Design and structure of human lung. Pulmonary disease and disorders. 1988. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill;11–60.2. Peter JB, Trevor TH. Prospects for new drugs for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 2004. 364:985–996.3. D'Souza ND, Reinhardt JM, Hoffman EA. ASAP: interactive quantification of 2D airway geometry. SPIE Medical Imaging. 1996. 2709:180–196.4. Awadh N, Müller NL, Park CS, Abboud RT, FitzGerald JM. Airway wall thickness in patients with near fatal asthma and control groups: assessment with high resolution computed tomographic scanning. Thorax. 1998. 53:248–253.5. Brown RH, Herold CJ, Hirshman CA, Zerhouni EA, Mitzner W. In vivo measurements of airway reactivity using high-resolution computed tomography. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991. 144:208–212.6. Brown RH, Zerhouni EA, Mitzner W. Variability in the size of individual airways over the course of one year. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. 151:1159–1164.7. McNamara AE, Müller NL, Okazawa M, Arntorp J, Wiggs BR, Paré PD. Airway narrowing in excised canine lungs measured by high-resolution computed tomography. J Appl Physiol. 1992. 73:307–316.8. Saba OI, Hoffman EA, Reinhardt JM. Maximizing quantitative accuracy of lung airway lumen and wall measures obtained from X-ray CT imaging. J Appl Physiol. 2003. 95:1063–1075.9. Kim DY, Chung SM, Park JW. Automatic navigation path generation based on two-phase adaptive region-growing algorithm for virtual angioscopy. Med Eng Phys. 2006. 28:339–347.10. Ferguson JS, McLennan G. Virtual bronchoscopy. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005. 2:488–491. 504–505.11. Kim N, Seo JB, Song KS, Chae EJ, Kang SH. Semi-automatic measurement of the airway dimension at computed tomography using the full-width-half-maximum method: study on the measurement accuracy according to CT parameters and size of the airway. Korean J Radiol. 2008. 9:226–235.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Semi-Automatic Measurement of the Airway Dimension by Computed Tomography Using the Full-Width-Half-Maximum Method: a Study on the Measurement Accuracy according to the CT Parameters and Size of the Airway
- Quantitative Analysis of Airway Walls Using CT Software
- Three-dimensional evaluation of the relationship between nasopharyngeal airway shape and adenoid size in children
- Anatomical Measurement of The Upper Airway Dimensions with Computed Tomography
- Airway Measurement for Airway Remodeling Defined by Post-Bronchodilator FEV1/FVC in Asthma: Investigation Using Inspiration-Expiration Computed Tomography