Yonsei Med J.
2005 Jun;46(3):341-346. 10.3349/ymj.2005.46.3.341.
Limited Effect of CpG ODN in Preventing Type 1 Diabetes in NOD Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. cchung@wonju.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Microbiology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 3Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Yonsei University, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Chung-Ang Medical College, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1734067
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2005.46.3.341
Abstract
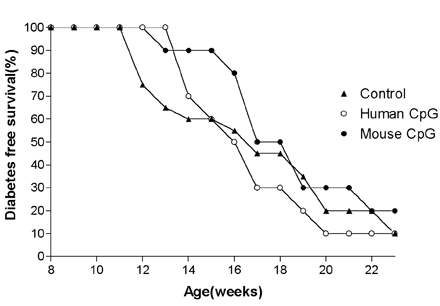
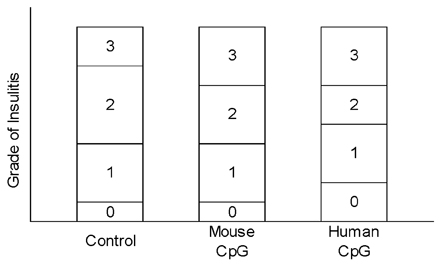
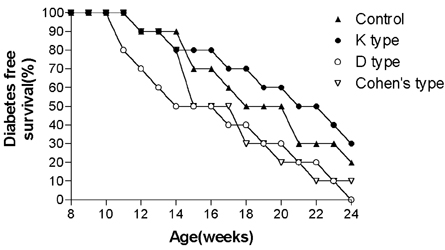
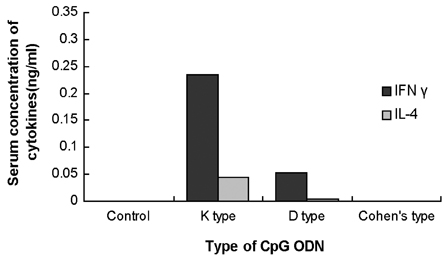
- Type 1 diabetes is considered as Th1 cell mediated autoimmune disease and the suppression of Th1 cells or the activation of Th2 cells has been regarded as a plausible immunologic intervention for the prevention of type 1 diabetogenesis in a rodent model. CpG ODN is an immunostimulatory sequence primarily present in bacterial DNA, viral DNA and BCG. CpG ODN is conventionally classified as a Th1 cell activator, which has been clinically applied to cancer, allergy and infectious disease. Recently, there was a promising report of that CpG ODN administration suppressed the development of type 1 diabetes in NOD mice by inducing Th2 cell mediated cytokine. However, the antidiabetogenic effect of CpG ODN on NOD mice is controversial. Thus, two studies were serially undertaken with various kinds of CpG motif to find a more optimal sequence and administration method. In the first study, CpG ODN was vaccinated four times and pancreatic inflammation and the quantity of serum insulin subsequently evaluated. In the second study, the amounts of IFN gamma and IL-4 in sera were measured as representative cytokines of Th1 and Th2 cells, respectively. As a result, vaccination or continuous injection of CpG ODN failed to show a preventive effect on type 1 diabetogenesis in NOD mice. Structural differences of CpG ODN also had no affect on the result. CpG ODN also consistently showed affect on the pancreatic pathology. The productions of IFN gamma and IL-4 were detected only in the K and D type CpG ODN administration groups. Comparison of the two cytokines leads to the conclusion that CpG ODN generated a Th1-weighted response in both study groups. It was assumed that CpG ODN failed to produce Th2-weighted cytokine milieu, which can overcome the genetically determined phenotype of NOD mice. Given these results, it was concluded that the immunotherapeutic application of CpG ODN on Type 1 diabetes had clear limitations.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schuster DP, Duvuuri V. Diabetes mellitus. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2002. 19:79–107.2. Scott A, Donnelly R. Improving outcomes for young people with diabetes: use of new technology and skills-based training approach is urgently needed. Diabet Med. 2001. 18:861–863.3. Bach JF. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus as an autoimmune disease. Endocr Rev. 1994. 15:516–542.4. Liblau RS, Singer SM, McDevitt HO. Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T cells in the pathogenesis of organ-specific autoimmune disease. Immunol Today. 1995. 16:34–38.5. Tisch R, McDevitt HO. Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Cell. 1996. 85:291–297.6. Wilson SS, White TC, DeLuca D. Therapeutic alteration of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus progression by T cell tolerance to glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 peptides in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 2001. 167:569–577.7. Palmer JP. Immunomodulatory therapy of human type 1 diabetes: lessons from the mouse. J Clin Invest. 2001. 108:31–33.8. Simone EA, Wegmann DR, Eisenbarth GS. Immunologic "vaccination" for the prevention of autoimmune diabetes (type 1A). Diabetes Care. 1999. 22:7–15.9. Serreze DV, Chapman HD, Post CM, Johnson EA, Suarez-Pinzon WL, Rabinovitch A. Th1 to Th2 cytokine shifts in nonobese diabetic mice: Sometimes an outcome, rather than the cause, of diabetes resistance elicited by immunostimulation. J Immunol. 2001. 166:1352–1359.10. Atkinson MA, Leiter EH. The NOD mouse model of type 1 diabetes: As good as it gets? Nature Med. 1999. 5:601–604.11. Delovitch TL, Singh B. The nonobese diabetic mouse as a model of autoimmune diabetes: Immune dysregulation gets the NOD. Immunity. 1997. 7:727–738.12. Krieg AM. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA and their immune effects. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002. 20:709–760.13. Rabinovitch A. Immunoregulatory and cytokine imbalance in the pathogenesis of IDDM. Diabetes. 1994. 43:613–621.14. Tascon RE, Colston MJ, Ragno S, Stavropoulous E, Gregory D, Lowrie DB. Vaccination against tuberculosis by DNA injection. Nature Med. 1996. 2:888–892.15. Krieg AM, Kline JN. Immune effect and therapeutic applications of CpG motif in bacterial DNA. Immunopharmacology. 2000. 48:303–305.16. Krieg AM, Wagner H. Causing a commotion in the blood: immunotherapy progresses from bacteria to bacterial DNA. Immunol Today. 2000. 21:521–526.17. Verthelyi D, Kenney RT, Seder RA, Gam AA, Friedag B, Lkinman DM. CpG oligodeoxynucleotides as vaccine adjuvant in primates. J Immunol. 2002. 168:1659–1663.18. Verthelyi D, Ishii KJ, Gursel M, Takeshita F, Klinman DM. Human peripheral blood cells differentially recognize and respond to two distinct CpG motifs. J Immunol. 2001. 166:2372–2377.19. Kadowaki N, Antonenko S, Liu YJ. Distinct CpG DNA and polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid double-stranded RNA, respectively, stimulate CD 11c-type II dendritic precursor and CD 11c+ dendritic cells to produce type I IFN. J Immunol. 2001. 166:2291–2295.20. Zhang Y, Shoda LK, Brayton KA, Estes DM, Palmer GH, Brown WC. Induction of interleukin-6 and interleukin-12 in bovine B lymphocytes, monocytes, and macrophages by a CpG oligonucleotide (ODN 2059) containing the GTC GTT motif. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2001. 21:871–881.21. Kim SK, Ragupatihi G, Musselli C, Choi S, Park YS, Livingston PO. Comparison of the effect of different immunological adjuvants on the antibody and T-cell response to immunization with MVC1-KLH and GD3-KLH conjugate cancer vaccines. Vaccine. 1999. 18:597–603.22. Juffermans NP, Leemans JC, Florquin S, Verbon A, Kolk AH, Speelman P. CpG oligonucleotides enhances host defense during murine tuberculosis. Infect Immune. 2002. 70:147–152.23. Quintana FJ, Rotem A, Carmi P, Cohen IR. Vaccination with empty plasmid DNA or CpG oligonucleotide inhibits diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice: Modulation of spontaneous 60-k Da heat shock protein autoimmunity. J Immunol. 2000. 165:6148–6155.24. Kim YU, Kang HS, Hwang TS, Chung CH. Prevention of insulitis by BCG administration in NOD mice of the neonatal period. J Wonju Coll Med. 1998. 11:97–105.25. Hwang TS, Kim HS, Kim YU, Chung CH. Prevention of overt diabetes and insulitis by BCG administration in the NOD mice in the breast-fed period. Korean J Anat. 2000. 33:49–54.26. Tokunaga T, Yamamoto T, Yamamoto S. How BCG led to the discovery of immunostimulatory DNA. Jpn J Infect Dis. 1999. 52:1–11.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Mouse Type and Human Type of CpG Oligonucleotide Vaccination on Development of Diabetes in NOD Mice
- Modulation of Eosinophilia and Cytokines of Bronchoalveolar Larvage Fluid(BALF) by CpG Oligodeoxynucleotides(ODN) in a Mouse Model of Established Airway Inflammation
- Morphological studies on pancreas and kidney in cyclophosphamide-induced NOD mice
- The Effect of CpG-Oligodeoxynucleotides with Different Backbone Structures and 3' Hexameric Deoxyriboguanosine Run Conjugation on the Treatment of Asthma in Mice
- Inhibition of diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice by nicotinamide treatment for 5 weeks at the early age