Yonsei Med J.
2013 May;54(3):720-725. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.720.
Locking Plate in Proximal Tibial Fracture: A Correlation between the Coronal Alignment of Tibia and Joint Screw Angle
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Korea University School of Medicine, Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. osjinho@naver.com
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Technical Support Team, Techno-Park, Senior Products Industrial Center, Busan, Korea.
- 5Department of Biostatistics, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1727889
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.720
Abstract
- PURPOSE
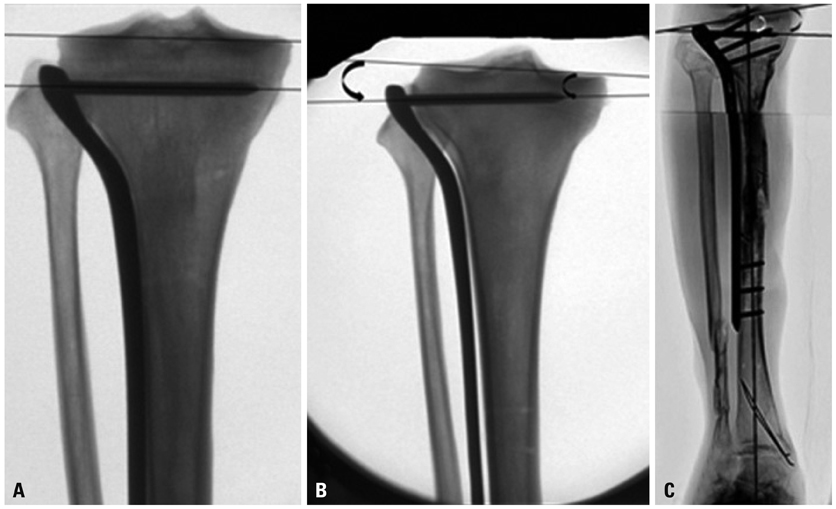
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the relationship between the angle formed between the proximal most screw through the locking compression plate-proximal lateral tibia (LCP PLT) and the joint line, and to evaluate if this angle can be used intraoperatively as an assessment tool to determine normal alignment of the tibia in the coronal plane.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
There are two parts to this study: in the first part, LCP PLT was applied to 30 cadaveric adult tibia. The angle between the joint line and the proximal most screw was measured and termed as the 'joint screw angle' (JSA). In the second part, 56 proximal tibial fractures treated with LCP PLT were retrospectively studied. Two angles were measured on the radiographs, the medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA) and the JSA. Their relationship was analyzed statistically.
RESULTS
The average JSA was 1.16 degrees in the anatomical study. Statistical analysis of the clinical study showed that the normal MPTA had a direct correlation with an acceptable JSA.
CONCLUSION
We therefore conclude that the JSA can be used intraoperatively to assess the achievement of a normal coronal axis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Krieg JC. Proximal tibial fractures: current treatment, results, and problems. Injury. 2003. 34:Suppl 1. A2–A10.
Article2. Waddell JP, Johnston DW, Neidre A. Fractures of the tibial plateau: a review of ninety-five patients and comparison of treatment methods. J Trauma. 1981. 21:376–381.
Article3. Wu CC. Salvage of proximal tibial malunion or nonunion with the use of angled blade plate. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006. 126:82–87.
Article4. Moore TM, Patzakis MJ, Harvey JP. Tibial plateau fractures: definition, demographics, treatment rationale, and long-term results of closed traction management or operative reduction. J Orthop Trauma. 1987. 1:97–119.5. Young MJ, Barrack RL. Complications of internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Rev. 1994. 23:149–154.6. Blokker CP, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB. Tibial plateau fractures. An analysis of the results of treatment in 60 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984. 193–199.
Article7. Cole PA, Zlowodzki M, Kregor PJ. Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) for fractures of the proximal tibia: indications, surgical technique and preliminary results of the UMC Clinical Trial. Injury. 2003. 34:Suppl 1. A16–A29.
Article8. Cole PA, Zlowodzki M, Kregor PJ. Treatment of proximal tibia fractures using the less invasive stabilization system: surgical experience and early clinical results in 77 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:528–535.
Article9. Egol KA, Su E, Tejwani NC, Sims SH, Kummer FJ, Koval KJ. Treatment of complex tibial plateau fractures using the less invasive stabilization system plate: clinical experience and a laboratory comparison with double plating. J Trauma. 2004. 57:340–346.
Article10. Goesling T, Frenk A, Appenzeller A, Garapati R, Marti A, Krettek C. LISS PLT: design, mechanical and biomechanical characteristics. Injury. 2003. 34:Suppl 1. A11–A15.
Article11. Gösling T, Schandelmaier P, Marti A, Hufner T, Partenheimer A, Krettek C. Less invasive stabilization of complex tibial plateau fractures: a biomechanical evaluation of a unilateral locked screw plate and double plating. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:546–551.12. Gosling T, Schandelmaier P, Muller M, Hankemeier S, Wagner M, Krettek C. Single lateral locked screw plating of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005. 439:207–214.
Article13. Phisitkul P, McKinley TO, Nepola JV, Marsh JL. Complications of locking plate fixation in complex proximal tibia injuries. J Orthop Trauma. 2007. 21:83–91.
Article14. Ricci WM, Rudzki JR, Borrelli J Jr. Treatment of complex proximal tibia fractures with the less invasive skeletal stabilization system. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:521–527.
Article15. Schütz M, Kääb MJ, Haas N. Stabilization of proximal tibial fractures with the LIS-System: early clinical experience in Berlin. Injury. 2003. 34:Suppl 1. A30–A35.
Article16. Schütz M, Müller M, Regazzoni P, Höntzsch D, Krettek C, Van der Werken C, et al. Use of the less invasive stabilization system (LISS) in patients with distal femoral (AO33) fractures: a prospective multicenter study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005. 125:102–108.
Article17. Stannard JP, Wilson TC, Volgas DA, Alonso JE. Fracture stabilization of proximal tibial fractures with the proximal tibial LISS: early experience in Birmingham, Alabama (USA). Injury. 2003. 34:Suppl 1. A36–A42.
Article18. Stannard JP, Wilson TC, Volgas DA, Alonso JE. The less invasive stabilization system in the treatment of complex fractures of the tibial plateau: short-term results. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:552–558.
Article19. Weight M, Collinge C. Early results of the less invasive stabilization system for mechanically unstable fractures of the distal femur (AO/OTA types A2, A3, C2, and C3). J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:503–508.
Article20. Krettek C, Miclau T, Grün O, Schandelmaier P, Tscherne H. Intraoperative control of axes, rotation and length in femoral and tibial fractures. Technical note. Injury. 1998. 29:Suppl 3. C29–C39.
Article21. Beck M, Gradl G, Gierer P, Rotter R, Witt M, Mittlmeier T. [Treatment of complicated proximal segmental tibia fractures with the less invasive stabilization locking plate system]. Unfallchirurg. 2008. 111:493–498.
Article22. Goyal KS, Skalak AS, Marcus RE, Vallier HA, Cooperman DR. Analysis of anatomic periarticular tibial plate fit on normal adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007. 461:245–257.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiological Landmarks for the Assessment of the Alignment in the Use of the LCP-PLT (Locking Compression Plate-Proximal Lateral Tibia): An Anatomical and Radiological Study
- A Prospective Study of Fractures of the Tibial Shaft Treated with Intramedullary Interlocking Nail : Comparing One versus Two Distal Screws
- Treatment of Proximal Tibia Fractures Using LCP by MIPO Technique
- Lateralization of Tibial Plateau Reference Point Improves Accuracy of Tibial Resection in Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients with Proximal Tibia Vara
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures: Technical Note